Recommended Dietary Allowance for healthy immune system – Recommended Dietary Allowance for a healthy immune system is essential for maintaining overall well-being. Our immune system is a complex network of cells and organs that defend us against harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and parasites. A robust immune system relies on a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support its function. This article explores the specific dietary recommendations for bolstering your immune defenses and keeping you healthy.
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) provides guidelines for the daily intake of essential nutrients needed for optimal health. Certain nutrients, such as vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, and selenium, play crucial roles in supporting immune function. Understanding these RDAs and incorporating these nutrients into your diet can significantly enhance your body’s ability to fight off infections and maintain overall well-being.
Understanding the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is a guideline established by the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. It represents the average daily intake level of essential nutrients that are sufficient to meet the needs of nearly all (97-98%) healthy individuals in a specific life stage and gender group. Following the RDA helps ensure that individuals consume adequate amounts of vital nutrients to maintain optimal health, prevent deficiencies, and support various bodily functions, including a robust immune system.
The Importance of RDA for Immune Function
The RDA provides a framework for understanding the crucial role of nutrition in supporting a healthy immune system. By consuming the recommended amounts of key nutrients, individuals can bolster their body’s natural defenses against infections and diseases.
Specific RDAs for Immune-Boosting Nutrients
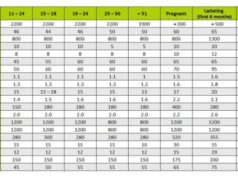
- Vitamin C: This powerful antioxidant plays a vital role in immune function. It supports the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. The RDA for vitamin C is 75 mg for women and 90 mg for men.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is crucial for immune cell function and helps regulate the body’s inflammatory response. The RDA for vitamin D is 600 IU for adults up to 70 years old and 800 IU for those over 70.
- Zinc: Zinc is essential for immune cell development and function. It supports wound healing and helps the body fight off infections. The RDA for zinc is 8 mg for men and 11 mg for women.
- Selenium: Selenium is an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage and supports immune function. The RDA for selenium is 55 mcg for men and 55 mcg for women.
Immune-Boosting Nutrients: Recommended Dietary Allowance For Healthy Immune System
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients plays a crucial role in supporting a robust immune system. These nutrients act as building blocks for immune cells, enhance their function, and regulate inflammatory responses, ultimately contributing to the body’s defense against infections and diseases.
Immune-Boosting Nutrients and Their Roles, Recommended Dietary Allowance for healthy immune system
These nutrients are vital for a healthy immune system, each contributing in unique ways to immune cell function, antibody production, and inflammation regulation.
| Nutrient | RDA (Adults) | Benefits for Immune Function | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | 75-90 mg/day (men/women) |
|
|
| Vitamin D (Cholecalciferol) | 15 mcg/day (adults) |
|
|
| Vitamin E (Tocopherol) | 15 mg/day (adults) |
|
|
| Zinc | 11 mg/day (men) 8 mg/day (women) |
|
|
| Selenium | 55 mcg/day (adults) |
|
|
| Iron | 8 mg/day (men) 18 mg/day (women) |
|
|
Dietary Strategies for Immune Support
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining a strong immune system. By consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods, you provide your body with the building blocks it needs to fight off infections and maintain overall health.
Sample Meal Plan for Immune Support
A well-designed meal plan can help you incorporate immune-boosting nutrients into your daily diet. Here is a sample meal plan that includes a variety of foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants:
Breakfast
- Oatmeal with berries and nuts: Oatmeal is a good source of fiber, which helps support a healthy gut microbiome, essential for immune function. Berries are rich in antioxidants, while nuts provide healthy fats and vitamin E.
- Yogurt with fruit and granola: Yogurt is a good source of probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that support gut health. Fruit provides vitamins and antioxidants, and granola adds fiber and some healthy fats.
- Eggs with whole-wheat toast: Eggs are a good source of protein and vitamins like B12 and D, both important for immune function. Whole-wheat toast provides fiber and complex carbohydrates.
Lunch
- Chicken or fish salad with mixed greens: Chicken and fish are good sources of lean protein, while mixed greens provide vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. You can add other vegetables like carrots, cucumbers, and bell peppers for additional nutrients.
- Whole-wheat sandwich with lean protein and vegetables: Choose a whole-wheat bread for fiber and pair it with lean protein like turkey or chicken breast and a variety of vegetables like lettuce, tomato, and onion.
- Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread: Lentil soup is a good source of protein, fiber, and iron. Pair it with a slice of whole-wheat bread for added fiber.
Dinner
- Salmon with roasted vegetables: Salmon is a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties and can support immune function. Roasted vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and Brussels sprouts provide vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Chicken stir-fry with brown rice: Chicken stir-fry with brown rice is a balanced meal with lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and a variety of vegetables. You can use different vegetables like broccoli, carrots, peppers, and onions.
- Vegetarian chili with whole-wheat cornbread: Vegetarian chili is a hearty and nutritious meal with beans, lentils, and vegetables. Whole-wheat cornbread provides fiber and complex carbohydrates.
Snacks
- Fruit: Apples, oranges, bananas, berries, and grapes are all good sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are good sources of healthy fats, protein, and vitamin E.
- Yogurt: Yogurt is a good source of probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria that support gut health.
Benefits of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources offers numerous benefits for your immune system. These benefits include:
- Provides Essential Nutrients: A balanced diet ensures you receive the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to support immune function. These nutrients are essential for the production of white blood cells, which are responsible for fighting infections.
- Supports Gut Health: A diet rich in fiber and probiotics helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which plays a vital role in immune function. The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem of bacteria that helps regulate immune responses.
- Reduces Inflammation: Some foods, like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce chronic inflammation, which can weaken the immune system.
- Boosts Antioxidant Defenses: Antioxidants help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, which can contribute to inflammation and weaken the immune system. Fruits, vegetables, and certain spices are rich in antioxidants.
Tips for Incorporating Immune-Boosting Nutrients
Here are some practical tips for incorporating immune-boosting nutrients into your everyday meals and snacks:
- Eat the Rainbow: Choose a variety of fruits and vegetables in different colors, as each color offers unique nutrients.
- Include Whole Grains: Choose whole-grain breads, cereals, and pasta for fiber and complex carbohydrates.
- Choose Lean Protein Sources: Include lean protein sources like chicken, fish, beans, lentils, and tofu in your meals.
- Snack Smart: Opt for healthy snacks like fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds instead of processed foods.
- Cook at Home: Cooking at home allows you to control the ingredients and portion sizes, making it easier to create healthy meals.
- Read Food Labels: Pay attention to food labels and choose options that are low in sugar, saturated fat, and sodium.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated, as dehydration can weaken the immune system.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Immune Function

Beyond diet, various lifestyle factors significantly influence your immune system’s ability to function effectively. These factors are interconnected and play a crucial role in maintaining your overall health and resilience.
Lifestyle Factors and Immune Function
Lifestyle factors, such as sleep, stress, and physical activity, can have a profound impact on your immune system’s ability to function optimally.
| Factor | Impact on Immune Function | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep | Adequate sleep is crucial for immune system function. During sleep, your body produces cytokines, proteins that help regulate inflammation and fight infection. Sleep deprivation can suppress your immune system, making you more susceptible to illness. | Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimize your sleep environment for optimal sleep. |
| Stress | Chronic stress can weaken your immune system. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones like cortisol, which can suppress immune function. This can make you more susceptible to infections and illnesses. | Practice stress management techniques like deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature. Engage in activities you enjoy and seek support from friends, family, or a therapist. |
| Physical Activity | Regular physical activity boosts your immune system. Exercise promotes blood circulation, which helps deliver immune cells throughout your body. It also reduces inflammation and improves your body’s response to infections. | Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Include strength training exercises at least twice a week. |
Dietary Supplements for Immune Support
While a balanced diet rich in whole foods is the foundation for a healthy immune system, dietary supplements can play a supporting role in bolstering immune function. They can help bridge nutritional gaps and provide concentrated doses of specific nutrients that may be lacking in the diet.
Understanding Dietary Supplements
Dietary supplements are products that contain vitamins, minerals, herbs, or other substances that are intended to supplement the diet. They are not intended to replace a healthy diet, but rather to provide additional nutrients that may be beneficial for immune health.
Common Immune-Boosting Supplements
A variety of supplements have been studied for their potential to support immune function. Here are some of the most commonly used:
- Vitamin C: A powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. It also plays a role in the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections.
- Zinc: An essential mineral that is involved in many immune functions, including the production of white blood cells and the activation of immune cells.
- Elderberry: A plant extract that has been traditionally used to support immune health. Studies suggest that elderberry may help reduce the duration and severity of colds and flu.
- Vitamin D: A fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for immune function. Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of infections.
- Probiotics: Live microorganisms that are similar to those found in the gut. Probiotics may help to improve gut health, which is essential for immune function.
Choosing Appropriate Supplements
When choosing dietary supplements, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Dosage: The recommended dosage for each supplement varies depending on the specific product and individual needs. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
- Quality: Look for supplements that are manufactured in a GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) facility. This ensures that the products meet quality standards and are safe for consumption.
- Interactions: Certain supplements can interact with medications. It’s important to inform your doctor about all supplements you are taking, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking prescription medications.
Potential Interactions with Medications
Some dietary supplements can interact with medications, potentially leading to adverse effects. For example, vitamin K supplements can interfere with the effectiveness of blood thinners, and zinc supplements can reduce the absorption of certain antibiotics. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, especially if you are taking medications.
The Role of Probiotics and Gut Health
Your gut is home to trillions of bacteria, collectively known as the gut microbiome. This diverse community plays a vital role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for a robust immune system.
The Connection Between Gut Health and Immune Function
The gut microbiome is intimately linked to the immune system. Approximately 70% of the body’s immune cells reside in the gut, forming a crucial barrier against pathogens. The gut microbiota helps regulate immune responses by:
* Producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs): SCFAs like butyrate have anti-inflammatory properties and contribute to the integrity of the gut lining, preventing harmful bacteria from entering the bloodstream.
* Stimulating the development of immune cells: The gut microbiota interacts with immune cells, triggering their maturation and differentiation.
* Competing with harmful bacteria: Beneficial bacteria in the gut microbiome compete with pathogens for resources, limiting their growth and preventing infections.
The Role of Probiotics in Supporting a Healthy Gut Microbiome
Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, provide health benefits to the host. They are often referred to as “good” bacteria. Probiotics help maintain a balanced gut microbiome by:
* Replenishing beneficial bacteria: Probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut, increasing their numbers and promoting a healthy balance.
* Producing antimicrobial compounds: Some probiotics produce substances that inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria, contributing to a healthy gut environment.
* Modulating immune responses: Probiotics can influence immune cell activity, promoting a balanced and effective immune response.
Food Sources and Supplement Options for Increasing Probiotic Intake
Food Sources
- Fermented Foods: Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso are rich in probiotics. Look for varieties that contain live and active cultures.
- Tempeh: Tempeh is a fermented soybean product that is a good source of probiotics and protein.
- Kombucha: Kombucha is a fermented tea drink that contains a variety of beneficial bacteria.
Supplement Options
- Probiotic Supplements: Probiotic supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders. Choose supplements containing strains that have been scientifically proven to be beneficial for gut health.
Importance of Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining optimal immune function. Just like a well-oiled machine, your body needs sufficient fluids to operate effectively, and this includes your immune system.
Impact of Dehydration on Immune Function
Dehydration can significantly hinder your immune system’s ability to fight off infections and diseases. When you’re dehydrated, your body’s fluids become concentrated, which can affect the function of immune cells.
- Reduced Immune Cell Activity: Dehydration can lead to a decrease in the production and activity of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections. White blood cells are responsible for identifying and destroying pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses. When they are not functioning optimally due to dehydration, your body becomes more susceptible to infections.
- Impaired Immune Response: Dehydration can also impair the overall immune response by slowing down the circulation of immune cells throughout the body. This can delay the delivery of immune cells to areas where they are needed to fight infections, making it harder for your body to effectively combat pathogens.
Staying Hydrated
Here are some tips for staying hydrated throughout the day:
- Drink water regularly: Aim to drink water throughout the day, even when you’re not thirsty.
- Carry a water bottle: Keep a reusable water bottle with you and refill it frequently.
- Eat fruits and vegetables: Many fruits and vegetables contain high water content, such as watermelon, cucumber, and spinach.
- Limit sugary drinks: Sugary drinks, such as soda and juice, can actually dehydrate you.
Individualized Dietary Needs
While the general recommendations Artikeld in this guide provide a valuable framework for supporting immune health, it’s crucial to understand that dietary needs can vary significantly from person to person. Factors such as age, gender, health status, lifestyle, and genetics all play a role in determining the optimal dietary intake for each individual.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
To ensure you’re meeting your specific nutritional requirements and optimizing your immune function, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or registered dietitian. These professionals can assess your individual needs, consider any existing health conditions or medications, and provide personalized dietary guidance.
Identifying and Addressing Specific Dietary Needs
Here are some key areas to discuss with your healthcare professional to identify and address your individual dietary needs related to immune health:
- Dietary restrictions or allergies: Discuss any food allergies, intolerances, or restrictions you may have. This information will help determine appropriate food choices and ensure you’re getting the necessary nutrients from other sources.
- Existing health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or autoimmune disorders, may require specific dietary modifications. Your healthcare professional can advise on appropriate dietary adjustments to support your immune function while managing your condition.
- Medication interactions: Some medications can interact with certain nutrients, affecting their absorption or effectiveness. Your healthcare professional can advise on potential interactions and recommend dietary strategies to minimize these effects.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the nutritional needs of both mother and baby increase. Your healthcare professional can provide guidance on specific nutrient requirements and recommend foods to support both your immune system and that of your child.
- Age-related changes: As we age, our nutritional needs and metabolism change. Your healthcare professional can help you identify any age-related dietary modifications to support your immune function and overall health.
A balanced diet is crucial for a robust immune system, and understanding the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is key. While the RDA applies to everyone, vegetarians need to pay special attention to certain nutrients, like vitamin B12 and iron.
You can find a detailed breakdown of the RDA for vegetarians on this website: Recommended Dietary Allowance for vegetarians. By following these guidelines, vegetarians can ensure they are getting the nutrients they need to maintain a strong immune system.
While focusing on a healthy immune system, it’s important to remember that a balanced diet also plays a role in weight management. You can learn more about the Recommended Dietary Allowance for weight management here. By understanding both, you can create a meal plan that strengthens your immunity and supports your overall health.
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system. However, it’s important to remember that dietary needs can vary based on individual health conditions. For those with specific medical conditions, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate Recommended Dietary Allowance.
By tailoring your diet to your individual needs, you can support both your overall health and your immune system.