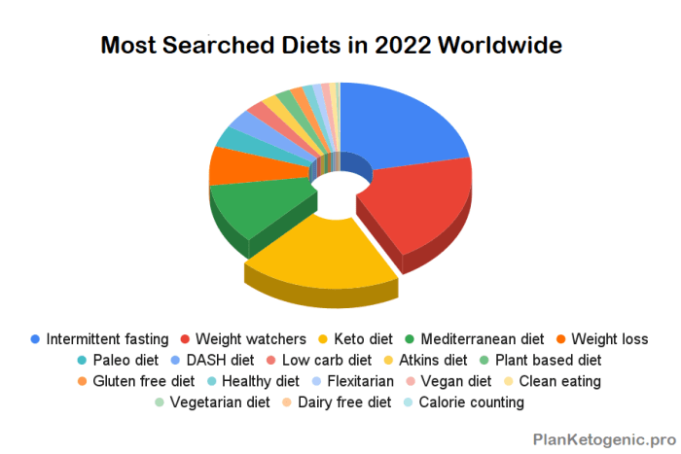
Popular diets 2022 take center stage, with a plethora of options promising weight loss, improved health, and enhanced well-being. This year, we see a convergence of trends, from the tried-and-true Mediterranean diet to the emerging popularity of intermittent fasting. Understanding the principles and potential benefits of these diets can empower individuals to make informed choices about their dietary journey.
The allure of these diets lies in their promise of quick results and a sense of control over one’s health. However, it’s crucial to approach them with a critical eye, considering individual needs, potential risks, and long-term sustainability. This guide delves into the key characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks of the most popular diets in 2022, providing a comprehensive overview to aid in making informed decisions.
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of health and wellness, popular diets have become a constant source of discussion and debate. These dietary trends, often driven by media hype and celebrity endorsements, promise rapid weight loss, improved health, and enhanced well-being. While some diets may offer short-term benefits, it is crucial to understand the underlying principles, potential risks, and long-term sustainability of these popular approaches.
Factors Influencing Diet Trends
The popularity of certain diets is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Media and Social Influence: The media, including magazines, television, and social media platforms, plays a significant role in promoting and shaping dietary trends. Celebrities, influencers, and media outlets often endorse specific diets, contributing to their widespread appeal.
- Scientific Research and Innovation: Advances in nutrition science and research often lead to new dietary recommendations and trends. For example, the discovery of the gut microbiome’s impact on health has fueled interest in diets that promote gut health.
- Cultural and Societal Values: Cultural beliefs, societal norms, and food traditions influence dietary choices. For instance, the rise of veganism and vegetarianism reflects growing concerns about animal welfare and environmental sustainability.
- Personal Experiences and Testimonials: Anecdotal evidence and personal success stories shared online and through word-of-mouth can contribute to the popularity of certain diets.
Understanding Popular Diets in 2022
Navigating the vast array of popular diets can be overwhelming. It is essential to critically evaluate these trends, considering their scientific basis, potential health risks, and long-term feasibility. Understanding the underlying principles and potential downsides of popular diets in 2022 empowers individuals to make informed choices that align with their health goals and lifestyle.
Top Popular Diets in 2022
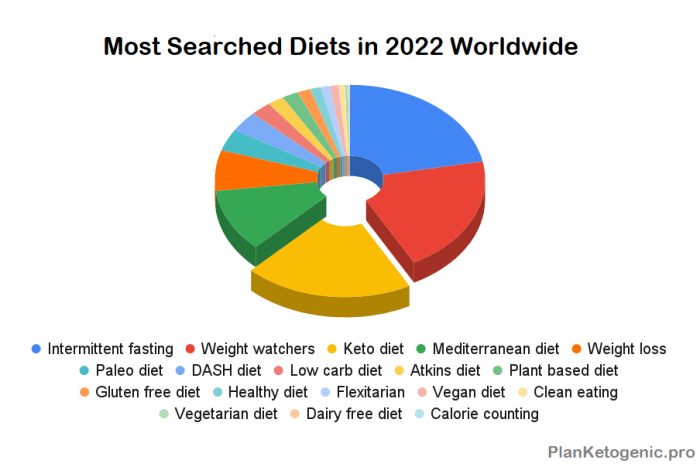
The diet industry is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging each year. 2022 saw the rise of several popular diets that promised weight loss, improved health, and enhanced well-being. This section will explore some of the top diets that gained traction in 2022, delving into their key principles, potential benefits, and potential risks.
Top Diets of 2022
Here is a list of some of the most popular diets in 2022:
- Intermittent Fasting
- Ketogenic Diet
- Mediterranean Diet
- DASH Diet
- Flexitarian Diet
- Vegan Diet
It is important to note that these diets are not necessarily the “best” or most effective for everyone. Individual needs and preferences vary, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any new diet.
Detailed Overview of Popular Diets
A comprehensive overview of each diet is provided below:
| Diet Name | Key Principles | Potential Benefits | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intermittent Fasting | Cyclical pattern of eating and fasting, typically involving periods of restricted calorie intake or complete abstinence from food. | Weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation, and potential for longevity. | Nutrient deficiencies, fatigue, headaches, and potential for disordered eating. |
| Ketogenic Diet | High-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that forces the body to enter a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for energy instead of glucose. | Rapid weight loss, improved blood sugar control, reduced seizures in individuals with epilepsy. | Nutrient deficiencies, constipation, fatigue, and potential for kidney stones. |
| Mediterranean Diet | Emphasis on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, olive oil, fish, and moderate consumption of red wine. | Reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some cancers. | May be difficult to maintain long-term due to its emphasis on fresh, unprocessed foods. |
| DASH Diet | Focus on reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium, magnesium, and calcium consumption. | Lower blood pressure, reduced risk of stroke, and improved heart health. | May require significant dietary changes and can be challenging to maintain. |
| Flexitarian Diet | Semi-vegetarian approach that allows for occasional consumption of meat and animal products. | Increased intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which can improve overall health. | May not provide adequate protein for some individuals, particularly athletes or those with specific dietary needs. |
| Vegan Diet | Elimination of all animal products, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy. | Reduced risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some cancers. | Nutrient deficiencies, particularly vitamin B12, iron, and calcium. |
It is essential to understand that these diets are just a starting point. The best diet for an individual will depend on their specific needs, goals, and preferences.
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) is an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting. It does not specify *what* you should eat, but rather *when* you should eat. This approach to eating has become increasingly popular in recent years, with proponents claiming various health benefits.
Different Methods of Intermittent Fasting, Popular diets 2022
Intermittent fasting has various methods, each with its unique schedule and approach. The most common methods include:
- The 16/8 method (also known as the “Leangains protocol”): This involves fasting for 16 hours each day, typically by skipping breakfast and limiting your eating window to 8 hours. This is one of the most popular methods, as it is relatively easy to follow.
- The 5:2 diet: This method involves eating normally for five days a week and restricting your calorie intake to 500-600 calories on two non-consecutive days.
- Eat Stop Eat: This method involves fasting for 24 hours once or twice a week.
- Alternate-day fasting (ADF): This method involves fasting every other day, with no calorie restriction on eating days.
Potential Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting has been linked to several potential health benefits, including:
- Weight loss: Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can be an effective way to lose weight and reduce body fat. This is likely due to its effect on calorie restriction and hormonal changes.
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Intermittent fasting can improve insulin sensitivity, which is the ability of cells to use glucose for energy. This can help prevent type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
- Reduced inflammation: Studies have shown that intermittent fasting can reduce inflammation throughout the body, which may contribute to its protective effects against chronic diseases.
- Improved brain function: Intermittent fasting has been linked to improved cognitive function, including memory and learning. This may be due to its effects on brain cell growth and survival.
- Increased lifespan: Some studies have shown that intermittent fasting may increase lifespan in animals, although more research is needed to confirm this in humans.
Potential Drawbacks of Intermittent Fasting
While intermittent fasting offers potential benefits, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks:
- Hunger and fatigue: Intermittent fasting can lead to hunger and fatigue, especially during the initial stages.
- Headaches and dizziness: Some people may experience headaches or dizziness during the fasting periods.
- Nutrient deficiencies: If not planned carefully, intermittent fasting can lead to nutrient deficiencies. It is important to ensure that you are getting all the nutrients your body needs.
- Not suitable for everyone: Intermittent fasting is not suitable for everyone, including pregnant or breastfeeding women, people with diabetes, eating disorders, or those taking certain medications.
Examples of Intermittent Fasting Schedules
Here are some examples of common intermittent fasting schedules:
- The 16/8 method: Fast for 16 hours each day, eating only during an 8-hour window. For example, you could eat from 12 pm to 8 pm and fast from 8 pm to 12 pm the next day.
- The 5:2 diet: Eat normally for five days a week and restrict your calorie intake to 500-600 calories on two non-consecutive days. For example, you could eat normally from Monday to Friday and restrict your calories on Tuesday and Thursday.
- Eat Stop Eat: Fast for 24 hours once or twice a week. For example, you could fast from dinner on Wednesday to dinner on Thursday.
Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, is a high-fat, very low-carbohydrate diet that forces the body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis. This diet has gained significant popularity in recent years as a weight loss strategy and for its potential health benefits.
Ketosis and its role in the ketogenic diet
Ketosis is a metabolic state where the body primarily uses fat as its primary source of energy instead of glucose (sugar). This happens when carbohydrate intake is drastically reduced, forcing the body to break down fat into ketones, which are then used as fuel. Ketones are produced in the liver and can be used by the brain and other tissues as an alternative energy source.
Potential health benefits of the ketogenic diet
The ketogenic diet has been associated with several potential health benefits, including:
- Weight loss: The keto diet’s emphasis on fat and restriction of carbohydrates can lead to significant weight loss. By reducing carbohydrate intake, the body burns stored fat for energy, leading to a calorie deficit and weight loss.
- Improved blood sugar control: The ketogenic diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Reduced inflammation: The ketogenic diet has been linked to a reduction in inflammation throughout the body, which may contribute to improved overall health.
- Improved cognitive function: Some studies suggest that the ketogenic diet may enhance cognitive function, potentially improving memory and focus.
Potential risks of the ketogenic diet
While the ketogenic diet offers potential benefits, it also carries certain risks, including:
- Nutrient deficiencies: The ketogenic diet’s strict restrictions on certain food groups can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients, such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Gastrointestinal issues: The keto diet can cause digestive issues, including constipation, diarrhea, and nausea.
- Kidney stones: The ketogenic diet can increase the risk of kidney stones, especially in individuals with a history of kidney problems.
- Keto flu: The keto flu is a common side effect of starting the ketogenic diet, characterized by fatigue, headache, and nausea. This usually subsides within a few days as the body adapts to ketosis.
Sample ketogenic meal plan
Here’s an example of a ketogenic meal plan for a day:
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with avocado and bacon
- Lunch: Salad with grilled chicken or fish, topped with avocado and cheese
- Dinner: Salmon with roasted vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus)
- Snacks: Nuts, seeds, cheese, or keto-friendly protein bars
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet, inspired by the traditional eating patterns of people living in the Mediterranean region, has gained immense popularity for its focus on wholesome foods and potential health benefits. This dietary approach emphasizes plant-based foods, healthy fats, and moderate consumption of animal products, all while promoting a lifestyle rich in physical activity and social interaction.
Key Components of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is characterized by its emphasis on specific food groups and their relative proportions. The diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and healthy fats like olive oil. It also includes moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and dairy products, while limiting red meat and processed foods.
- Fruits and Vegetables: The cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, these foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. Aim for at least five servings of fruits and vegetables daily, including a variety of colors and types.
- Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, whole-wheat bread, and pasta, which are rich in fiber and nutrients. These grains provide sustained energy and support digestive health.
- Legumes: Lentils, beans, chickpeas, and peas are excellent sources of protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. Incorporate them into soups, stews, salads, and vegetarian dishes.
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil is the primary fat source in the Mediterranean diet. It is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. Other healthy fats include those found in nuts, seeds, and avocados.
- Fish: Aim for at least two servings of fish per week, including fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids have been linked to reduced inflammation and improved heart health.
- Poultry and Eggs: Moderate consumption of poultry and eggs is encouraged. Choose lean poultry and limit the intake of processed meats.
- Dairy Products: Include moderate amounts of dairy products like yogurt, cheese, and milk, preferably low-fat or fat-free options.
- Red Meat and Processed Foods: These foods are limited in the Mediterranean diet. Red meat is typically consumed in small portions, and processed foods are generally avoided.
Potential Health Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
Numerous studies have shown that adhering to the Mediterranean diet can have significant positive effects on overall health and well-being. These benefits include:
- Improved Heart Health: The Mediterranean diet’s emphasis on healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants contributes to lowering blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and the risk of heart disease.
- Reduced Risk of Stroke: The diet’s beneficial effects on blood pressure, cholesterol, and inflammation contribute to reducing the risk of stroke.
- Lower Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: The Mediterranean diet’s focus on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Improved Cognitive Function: The diet’s rich antioxidant content and healthy fats may contribute to protecting brain health and reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
- Weight Management: The Mediterranean diet’s focus on whole, unprocessed foods and healthy fats can help promote satiety and support weight management.
- Reduced Risk of Certain Cancers: Some studies suggest that the Mediterranean diet may lower the risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Potential Risks of the Mediterranean Diet
While the Mediterranean diet is generally considered safe and beneficial, some potential risks are associated with it.
- Potential for Nutrient Deficiencies: If not carefully planned, the Mediterranean diet may not provide adequate amounts of certain nutrients, such as vitamin B12, iron, and calcium. This is particularly important for individuals following a vegetarian or vegan version of the diet. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure adequate nutrient intake.
- Potential for Weight Gain: While the Mediterranean diet can promote weight management, it’s essential to be mindful of portion sizes and overall calorie intake. Overconsumption of olive oil and other healthy fats can contribute to weight gain.
- Potential for Allergies: Some individuals may have allergies to specific foods commonly included in the Mediterranean diet, such as nuts, seafood, or dairy products. It’s important to be aware of potential allergies and adjust the diet accordingly.
Typical Foods Included in the Mediterranean Diet
- Fruits: Apples, bananas, berries, citrus fruits, grapes, melons, peaches, pears, pomegranates
- Vegetables: Asparagus, broccoli, carrots, cucumbers, eggplant, garlic, green beans, lettuce, onions, peppers, spinach, tomatoes
- Legumes: Beans (kidney, black, pinto, etc.), chickpeas, lentils, peas
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, whole-wheat bread, pasta, oats
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, nuts (almonds, walnuts, pistachios, etc.), seeds (chia, flax, sunflower), avocados
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, mackerel, sardines, trout
- Poultry: Chicken, turkey
- Dairy Products: Yogurt, cheese (feta, mozzarella), milk (low-fat or fat-free)
- Herbs and Spices: Basil, oregano, rosemary, thyme, garlic, onions
Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets have gained significant popularity in recent years due to their potential health benefits and ethical considerations. These diets emphasize the consumption of plant-based foods while varying in their restrictions on animal products.
Types of Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets encompass a spectrum of dietary approaches, each with its unique characteristics and restrictions.
- Veganism: A vegan diet excludes all animal products, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, and honey. Vegans rely solely on plant-based sources for their nutrition.
- Vegetarianism: Vegetarian diets vary in their restrictions on animal products.
- Lacto-ovo vegetarianism: This type of vegetarianism allows for the consumption of dairy products and eggs, but excludes meat, poultry, and fish.
- Lacto vegetarianism: Lacto vegetarians consume dairy products but exclude eggs, meat, poultry, and fish.
- Ovo vegetarianism: Ovo vegetarians consume eggs but exclude dairy products, meat, poultry, and fish.
- Flexitarianism: Flexitarianism is a more flexible approach that emphasizes plant-based foods but allows for occasional consumption of animal products. Flexitarians aim to reduce their meat consumption but do not entirely eliminate it.
Nutritional Benefits of Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets are often associated with a range of health benefits, including:
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Studies have linked plant-based diets to a lower risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. This is attributed to the high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, which are rich in antioxidants, fiber, and other beneficial nutrients.
- Weight Management: Plant-based diets can aid in weight management due to their lower calorie density and higher fiber content. Fiber helps promote satiety and slows down digestion, leading to a feeling of fullness and reduced calorie intake.
- Improved Digestive Health: The high fiber content in plant-based diets promotes digestive health by increasing stool bulk, regulating bowel movements, and supporting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Increased Nutrient Intake: Plant-based diets are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are crucial for overall health and well-being.
Challenges of Plant-Based Diets
While plant-based diets offer numerous health benefits, they also present some challenges:
- Nutrient Deficiencies: It’s crucial to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients, particularly vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are typically found in animal products. Careful planning and supplementation may be necessary to address these potential deficiencies.
- Social and Cultural Barriers: Adopting a plant-based diet can be challenging in social situations where meat and other animal products are prevalent. Navigating dining out, social gatherings, and cultural traditions can require extra effort and planning.
- Limited Food Choices: While plant-based food options are expanding, some individuals may find it challenging to access a wide variety of plant-based foods, particularly in certain geographic locations or with limited budgets.
Pros and Cons of Plant-Based Diet Types
| Diet Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Vegan |
|
|
| Vegetarian |
|
|
| Flexitarian |
|
|
The DASH Diet: Popular Diets 2022
The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is a flexible and balanced eating plan designed to help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease. It emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products while limiting saturated and unhealthy fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
Benefits of the DASH Diet for Blood Pressure Management
The DASH diet has been scientifically proven to effectively lower blood pressure. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Reduced Sodium Intake: The DASH diet restricts sodium intake, which is a major contributor to high blood pressure. By limiting sodium, the body can better regulate fluid balance, leading to lower blood pressure.
- Increased Potassium Intake: The diet encourages consumption of potassium-rich foods, which help counter the effects of sodium and promote healthy blood pressure levels. Potassium helps relax blood vessels, leading to better blood flow.
- Rich in Magnesium: The DASH diet includes foods rich in magnesium, a mineral that plays a vital role in regulating blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels and reducing inflammation.
- Increased Calcium Intake: The diet emphasizes calcium-rich foods, which have been shown to help lower blood pressure. Calcium contributes to healthy blood vessel function and may also reduce the risk of stroke.
Sample DASH Diet Meal Plan
Here’s a sample meal plan for a day following the DASH diet:
| Meal | Food Choices |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | 1 cup oatmeal with 1/2 cup berries and 1/4 cup low-fat milk, 1 slice whole-wheat toast with 1 tablespoon peanut butter |
| Lunch | Tuna salad sandwich on whole-wheat bread with lettuce and tomato, 1 cup fruit salad |
| Dinner | Grilled chicken breast with 1 cup steamed broccoli and 1/2 cup brown rice, 1 cup lentil soup |
| Snacks | 1/2 cup low-fat yogurt, 1/4 cup trail mix, 1 piece of fruit |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Diet
Choosing the right diet can be a daunting task, with numerous options and conflicting information available. It’s essential to approach this decision with careful consideration, taking into account your individual needs, goals, and preferences.
Understanding Your Goals
It’s crucial to define your reasons for embarking on a new diet. Are you aiming for weight loss, improved health, or both? Identifying your goals will help you narrow down your choices and select a diet that aligns with your aspirations. For example, if your goal is weight loss, a calorie-restricted diet like the DASH diet might be suitable. However, if you’re looking to manage blood pressure, the DASH diet might be a better choice.
Lifestyle Considerations
A successful diet is one that you can sustain over the long term. Consider your lifestyle and how easily you can adapt to the dietary restrictions and meal plans. If you’re someone who travels frequently or has a busy schedule, a diet that requires extensive meal preparation might not be practical.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before making any significant changes to your diet, it’s highly recommended to consult with a registered dietitian or your doctor. They can assess your individual health needs, provide personalized guidance, and help you determine the most appropriate diet for you. They can also identify any potential risks or interactions with existing medical conditions or medications.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new diet, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Sustainability and Long-Term Health
Ultimately, the most effective diet is one that you can maintain for the long haul. Avoid fad diets that promise quick results but are often unsustainable. Instead, focus on making gradual, realistic changes to your eating habits that you can incorporate into your lifestyle. A sustainable diet should promote long-term health and well-being.
Conclusion
The journey through the world of popular diets in 2022 has revealed a diverse landscape of approaches, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. From the time-restricted approach of intermittent fasting to the fat-focused ketogenic diet, and the plant-based philosophy of veganism, there’s a diet for every lifestyle and goal.
Key Takeaways
The analysis highlights the importance of individual needs and goals in selecting a diet. What works for one person may not work for another, and it’s crucial to understand your own body, health status, and dietary preferences.
Closing Notes
In the ever-evolving landscape of dietary trends, popular diets 2022 offer a diverse array of approaches to health and well-being. While some may appeal to specific needs and preferences, it’s essential to prioritize individual health goals, consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice, and embrace sustainable practices for long-term success. Remember, the journey to a healthier lifestyle is unique to each individual, and finding a diet that aligns with personal needs and preferences is key to achieving lasting results.
Popular Questions
What is the best diet for weight loss?
There is no single “best” diet for weight loss, as individual needs and preferences vary. It’s important to choose a diet that aligns with your lifestyle, provides adequate nutrition, and promotes sustainable habits. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can help you determine the most appropriate approach.
Are all popular diets safe?
Not all popular diets are safe for everyone. Some diets may lack essential nutrients or promote unhealthy eating habits. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new diet, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
How long should I follow a popular diet?
The duration of a diet depends on individual goals and health status. Some diets are intended for short-term use, while others are designed for long-term lifestyle changes. It’s essential to discuss the appropriate duration with a healthcare professional.
From the keto craze to the Mediterranean lifestyle, 2022 saw a variety of popular diets. But what about those looking to gain weight? If you’re aiming for healthy weight gain, finding the best diet to gain weight can be just as important as finding a diet for weight loss.
Remember, regardless of your goals, consulting a healthcare professional is always a good idea before making drastic changes to your diet.
From keto to intermittent fasting, 2022 saw a plethora of popular diets vying for attention. But amidst the buzz, a growing number of individuals are turning to a more holistic approach – the clean diet plan. This focuses on whole, unprocessed foods, prioritizing nutrient density and mindful eating.
As people become more aware of the impact of food on their overall well-being, the clean diet plan is poised to become a significant trend in the world of popular diets in 2023.
From the keto craze to the rise of plant-based eating, 2022 saw a diverse range of popular diets. While some focused on cutting carbs, others emphasized whole foods and mindful consumption. One question that often arises, especially for those trying to limit their caffeine intake, is is diet coke caffeine free ?
Understanding the nutritional content of popular beverages can be crucial when navigating any diet plan, as even seemingly “diet” options can contain surprising ingredients.