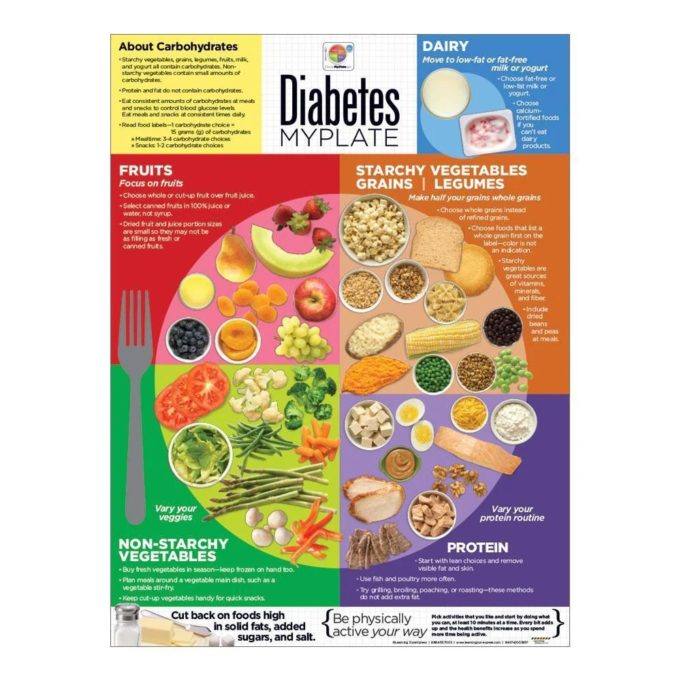
How to eat like a diabetic? It’s a question that many individuals with diabetes ask themselves, seeking guidance on managing their condition through diet. This guide explores the intricate relationship between diabetes and diet, providing a comprehensive understanding of how food choices can impact blood sugar levels and overall well-being. From the fundamentals of a diabetic-friendly diet to meal planning strategies and addressing common concerns, this resource empowers individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions about their nutrition.
Living with diabetes requires a mindful approach to eating, focusing on balanced meals, portion control, and regular blood sugar monitoring. This guide delves into the specific dietary principles that support blood sugar control, highlighting the importance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in a diabetic diet. We’ll explore recommended and discouraged food choices, providing a framework for making healthy decisions that promote optimal health.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
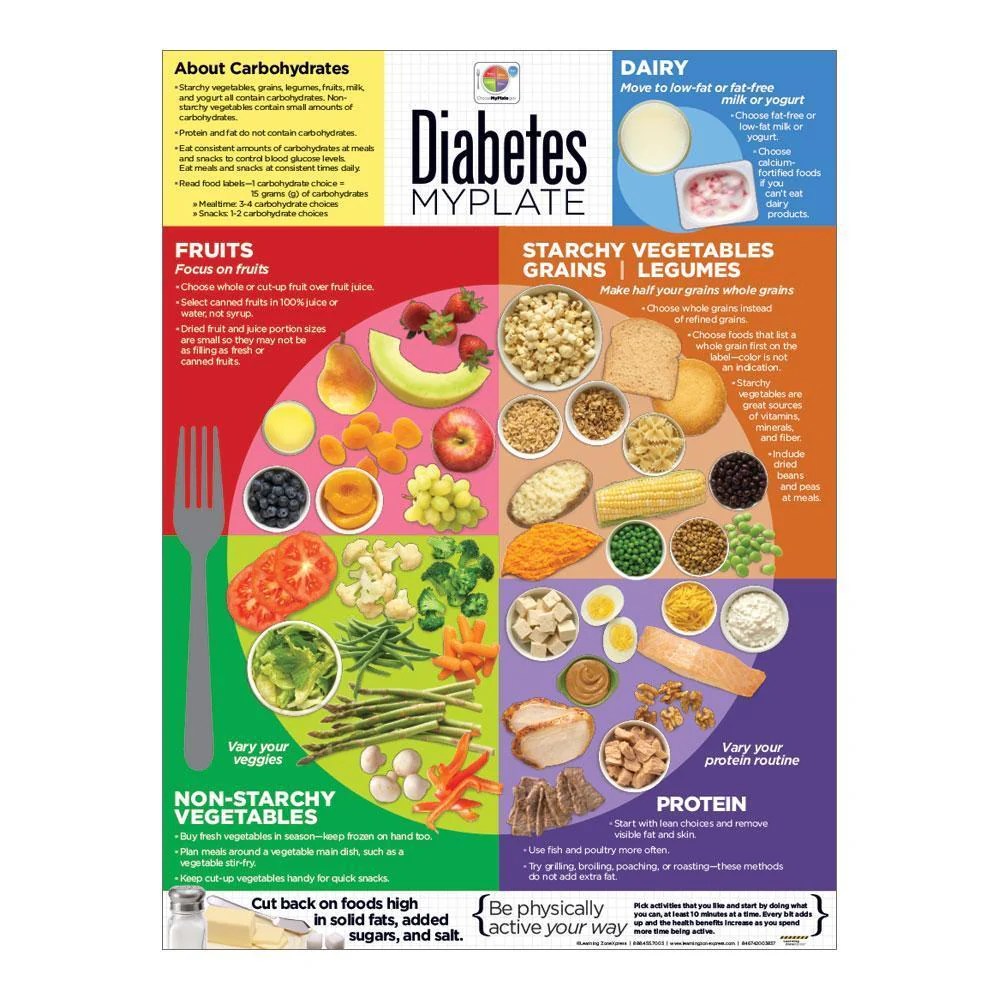
Managing blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of living with diabetes. It involves monitoring your blood sugar, understanding the factors that influence it, and making lifestyle adjustments to maintain a healthy range.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for managing diabetes. It helps you understand how your body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. There are various methods for monitoring blood sugar:
- Finger-prick blood glucose meters: These devices require a small blood sample from your fingertip. They provide quick and accurate readings, making them ideal for frequent monitoring.
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs): These devices continuously measure your blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. They provide real-time data, allowing you to see trends and patterns in your blood sugar levels.
Interpreting blood sugar readings is important for making informed decisions about your diabetes management.
- Target blood sugar range: Your healthcare provider will set a target blood sugar range for you based on your individual needs and goals.
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia): Readings above your target range indicate high blood sugar. This can be caused by various factors, including eating too many carbohydrates, not taking enough insulin, or being physically inactive.
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia): Readings below your target range indicate low blood sugar. This can be caused by taking too much insulin, skipping meals, or exercising more than usual.
Adjusting Meal Plans
Your meal plan should be tailored to your individual needs and blood sugar readings.
- Carbohydrate counting: Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. Learning to count carbohydrates in your meals can help you control your blood sugar.
- Portion control: Eating appropriate portion sizes is crucial for managing blood sugar. Consult your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized recommendations.
- Timing of meals: Eating meals and snacks at regular intervals can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Food choices: Choosing nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help improve blood sugar control.
Role of Physical Activity
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in blood sugar management. It helps your body use glucose for energy, improving insulin sensitivity.
- Type of activity: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Examples include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing.
- Timing of activity: Exercise can help lower blood sugar levels, so it’s beneficial to engage in physical activity shortly after meals.
- Monitoring blood sugar: It’s essential to monitor your blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise, as it can fluctuate.
The Role of Nutrition Professionals
Navigating the world of diabetes and its dietary requirements can feel overwhelming, but you don’t have to go it alone. Registered dietitians (RDs) and nutritionists are trained professionals who can provide invaluable support in managing your diabetes and achieving your health goals.
Consulting a nutrition professional can be a game-changer for people with diabetes. They possess the expertise to help you understand the complex relationship between food and blood sugar levels, and they can guide you in making informed choices about your diet.
Eating like a diabetic requires careful planning and consistency, focusing on whole foods, portion control, and regular exercise. It’s important to remember that quick fixes like diet pills dangerous can be harmful and don’t address the underlying issues of managing diabetes.
A healthy lifestyle is the key to successful diabetes management, so consult with a healthcare professional to create a personalized plan that works best for you.
Personalized Meal Planning
One of the primary benefits of working with a nutrition professional is the development of a personalized meal plan. This plan is tailored to your individual needs, taking into account factors such as your current diet, activity level, medical history, and medication. A personalized meal plan can help you:
- Control your blood sugar levels: By understanding the glycemic index (GI) and glycemic load (GL) of different foods, you can make choices that minimize blood sugar spikes and crashes. A dietitian can help you identify foods that are low in GI and GL, which are generally better for blood sugar management.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Weight management is crucial for people with diabetes, as excess weight can increase insulin resistance and worsen blood sugar control. A nutritionist can help you create a balanced diet that promotes healthy weight loss or maintenance.
- Reduce your risk of complications: Following a diabetes-friendly diet can lower your risk of developing long-term complications, such as heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, and kidney disease. A dietitian can help you identify foods that can help prevent these complications.
Ongoing Support
Beyond meal planning, nutrition professionals offer ongoing support and guidance to help you maintain healthy eating habits over the long term. They can:
- Address your concerns: You can discuss any questions or challenges you face regarding your diet and diabetes management.
- Provide education and resources: Nutrition professionals can share the latest information about diabetes nutrition and connect you with reliable resources. They can also help you understand the impact of different foods and meal preparation techniques on your blood sugar levels.
- Monitor your progress: They can track your blood sugar levels and make adjustments to your meal plan as needed to ensure you’re on track to meet your goals.
- Help you overcome barriers: They can provide strategies for managing cravings, dealing with social situations, and making healthy choices when dining out.
Finding Qualified Nutrition Professionals
There are several ways to find a qualified nutrition professional:
- Ask your doctor for a referral: Your doctor can recommend a registered dietitian or nutritionist who specializes in diabetes management.
- Search online databases: The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (AND) offers a searchable database of registered dietitians on its website. You can also search for nutritionists in your area using online directories.
- Contact local hospitals or clinics: Many hospitals and clinics have nutrition departments that offer diabetes education and counseling services.
- Check with your insurance provider: Your insurance plan may cover some or all of the costs associated with seeing a nutrition professional.
Addressing Common Concerns
Living with diabetes can be challenging, and it’s natural to have questions and concerns. Let’s address some common misconceptions and explore ways to manage your condition effectively.
Debunking Common Misconceptions, How to eat like a diabetic
Many misconceptions surround diabetes and its management. It’s essential to separate fact from fiction to make informed decisions about your health.
- “I can’t eat anything sweet.” While sugary foods and drinks should be limited, a diabetic diet doesn’t mean you can never enjoy treats. The key is moderation and choosing healthier alternatives when possible.
- “All carbohydrates are bad.” Not all carbs are created equal. Complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are essential for energy and provide valuable nutrients. It’s crucial to focus on these while limiting simple carbohydrates like refined sugars and processed foods.
- “Diabetes is a death sentence.” While diabetes can have serious complications, it’s manageable with proper care and lifestyle changes. With regular monitoring, medication, and a healthy diet, you can live a long and fulfilling life.
Managing Weight and Preventing Complications
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications. Here are some strategies:
- Regular physical activity: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. This can include brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Balanced diet: Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. Limit saturated and trans fats, added sugars, and processed foods.
- Portion control: Be mindful of serving sizes and avoid overeating. Use smaller plates and measure out your food.
Navigating Social Events and Dining Out
It’s important to enjoy social gatherings and dining out without compromising your diabetes management. Here are some tips:
- Plan ahead: Check the menu in advance and choose healthier options. Consider bringing your own snacks or drinks if needed.
- Communicate with your server: Inform them about your dietary needs and ask for modifications to dishes. For example, request grilled instead of fried options or ask for sauces on the side.
- Mindful choices: Opt for smaller portions, share dishes with friends, and choose grilled, baked, or steamed foods over fried or heavily sauced options.
Wrap-Up: How To Eat Like A Diabetic
By understanding the principles of a diabetic diet, embracing healthy food choices, and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals with diabetes can take control of their condition and live fulfilling lives. This guide serves as a starting point for a journey toward improved health and well-being, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their nutrition and manage their diabetes effectively. Remember, consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide personalized guidance and support for managing diabetes through diet.
Expert Answers
What are the best snacks for diabetics?
Healthy snack options for diabetics include fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and yogurt. These snacks provide essential nutrients and can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Can diabetics eat sweet potatoes?
Yes, sweet potatoes can be included in a diabetic diet in moderation. They are a good source of fiber and vitamins, but they also contain carbohydrates. It’s important to monitor portion sizes and consider their impact on blood sugar levels.
What are some common misconceptions about diabetic diets?
One common misconception is that diabetics can’t eat any sweets. While it’s true that sugary foods should be limited, individuals with diabetes can still enjoy occasional treats in moderation. Another misconception is that all carbohydrates are bad. Complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains and legumes, are beneficial for diabetics.
Eating like a diabetic often means focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, managing portion sizes, and limiting saturated and trans fats. This can also help in reducing cholesterol levels, which is crucial for overall heart health. You can learn more about how to reduce cholesterol with diet and find tips on incorporating healthy fats and fiber into your meals.
By adopting a heart-healthy approach to your diet, you’re not only managing diabetes but also promoting overall well-being.
Eating like a diabetic often means making smart choices to manage blood sugar levels. One key aspect is incorporating plenty of fiber into your meals. Fiber helps slow down the absorption of sugar, keeping blood sugar levels stable. There are numerous creative ways to add fiber to your diet, like swapping white bread for whole grains or adding more fruits and vegetables to your meals.
Check out these tips for adding fiber to your diet. This can help you feel fuller for longer and better manage your diabetes.