How does keto diet work – How does the keto diet work? It’s a question that’s been buzzing around the internet and health circles for years, and for good reason! This revolutionary way of eating, with its high-fat, low-carb approach, promises a world of potential benefits, from weight loss to improved brain function.
Imagine this: instead of relying on sugary carbohydrates for energy, your body switches gears, learning to burn fat as its primary fuel source. This process, known as ketosis, is like unlocking a secret energy source within you. But how does this fat-burning magic actually happen?
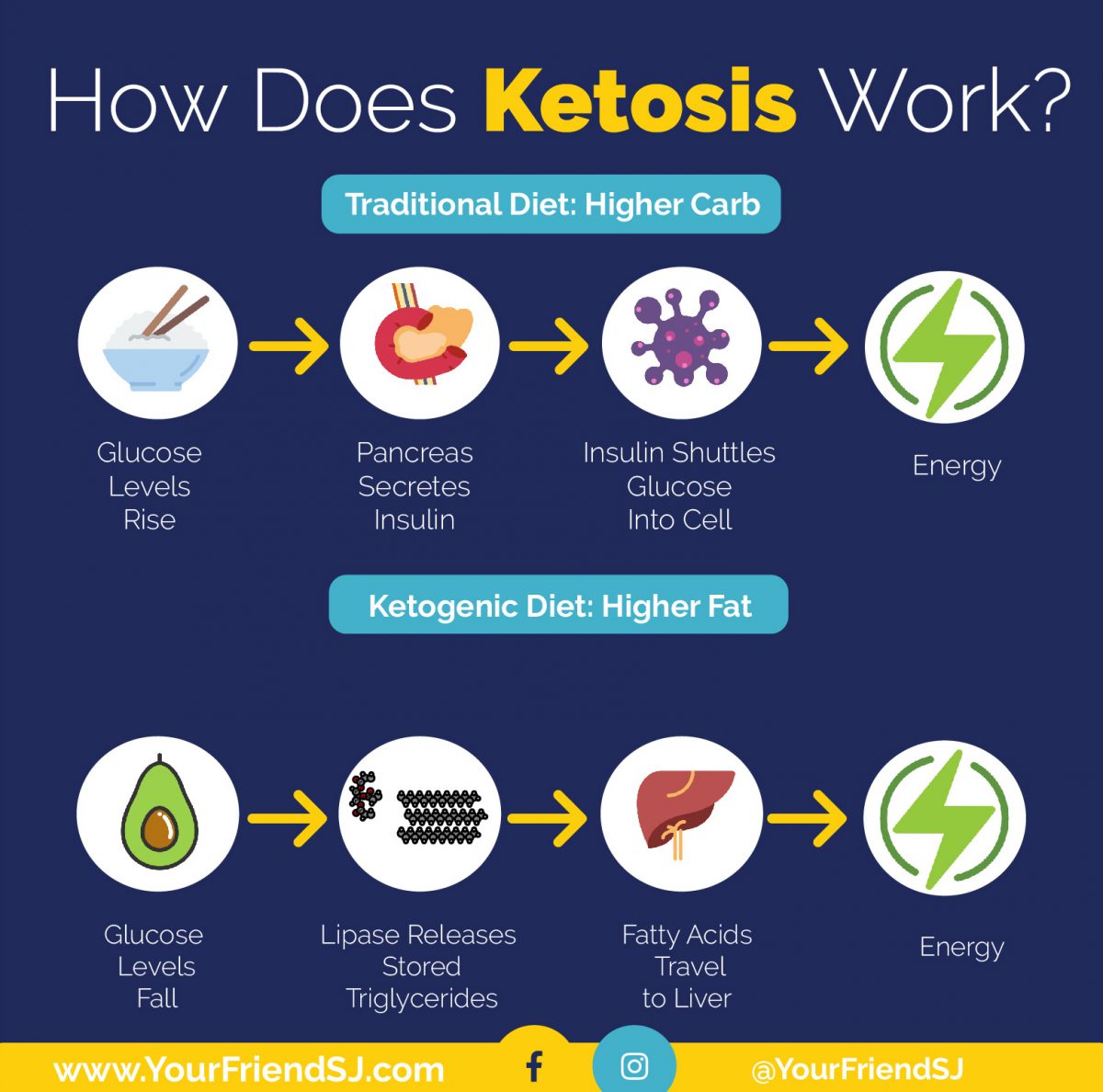
The keto diet, in essence, is a metabolic game changer. By dramatically reducing carbohydrates, you trick your body into a state of nutritional emergency. Since your usual source of fuel (sugar) is unavailable, your liver steps up, transforming fat into ketones, which then become your body’s new energy powerhouse.
This shift in energy production is the key to understanding how the keto diet works its magic.
The Basics of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that forces your body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis. This state is characterized by the burning of fat for energy instead of glucose, the body’s primary fuel source.
Macronutrient Breakdown
The ketogenic diet emphasizes a specific ratio of macronutrients: fat, protein, and carbohydrates. The goal is to significantly reduce carbohydrate intake while increasing fat consumption. This shift in macronutrient ratios triggers the body’s metabolic switch to ketosis.
The keto diet, for those who haven’t been living under a rock, is all about ditching carbs and embracing fat. It’s like a party where the guest of honor is butter, and everyone else is just there to watch the show.
But let’s be real, even keto warriors need a little something sweet sometimes. That’s where a good ol’ diet ginger ale comes in – it’s like a sugary escape for your taste buds without throwing your body’s delicate carb balance out of whack.
So, go ahead, enjoy that fizzy treat, and get back to your fat-fueled adventures!
A typical ketogenic diet breakdown is:
- Fat: 70-80% of daily calories
- Protein: 15-20% of daily calories
- Carbohydrates: 5-10% of daily calories
Metabolic Shifts in Ketosis
When you drastically reduce carbohydrate intake, your body enters a state of ketosis. This occurs because your liver starts to break down fat into ketones, which are used as an alternative fuel source. These ketones are then transported to your brain and other tissues, providing energy in the absence of glucose.
The key metabolic shifts during ketosis include:
- Reduced glucose levels:The body’s primary energy source, glucose, is limited, forcing it to find alternative fuel sources.
- Increased fat burning:Fat is broken down into ketones, which are used as energy.
- Ketone production:The liver produces ketones from fat breakdown, providing an alternative fuel source for the brain and other tissues.
How Ketosis Works
Imagine your body as a car. It needs fuel to run, and that fuel is primarily glucose, a sugar derived from carbohydrates. When you eat a ketogenic diet, you drastically reduce your carbohydrate intake, forcing your body to find an alternative fuel source.
This is where ketosis comes in.
The Process of Entering and Maintaining Ketosis
Ketosis is a metabolic state where your body starts burning fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. To achieve this, your body needs to switch from using glucose as its primary fuel to using ketones. Ketones are produced when your liver breaks down fat.
This process happens in three main stages:
- Carbohydrate Depletion:When you drastically reduce your carbohydrate intake, your body’s glucose stores start to deplete. This triggers the release of hormones like glucagon, which signals to your liver to start breaking down stored fat.
- Fat Breakdown:Your liver breaks down stored fat into fatty acids and glycerol. Fatty acids are then transported to the liver, where they are converted into ketones.
- Ketone Production:Ketones are produced in the liver and released into the bloodstream. They can then be used as an energy source by your brain, muscles, and other tissues.
The Role of Insulin and Glucagon in Regulating Ketosis, How does keto diet work
Insulin and glucagon are two hormones that play a crucial role in regulating ketosis.
The keto diet is like a party where your body is the guest of honor, but the only food on the menu is fat. It’s a bit of a shock to the system, but your body gets used to it and starts burning fat for fuel.
If you’re looking to lose that stubborn belly fat, you might want to check out how to diet to lose belly fat and see if it’s right for you. Just remember, it’s not a magic bullet, and you’ll need to make lifestyle changes to keep the weight off.
But hey, if you’re willing to ditch the carbs and embrace the fat, you might just be surprised by how much better you feel.
- Insulin:Insulin is a hormone that helps your body store glucose. When you eat carbohydrates, your body releases insulin, which signals your cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. In ketosis, insulin levels are low, allowing your body to break down stored fat instead of storing glucose.
- Glucagon:Glucagon is a hormone that helps your body release glucose from storage. When your blood sugar levels are low, your body releases glucagon, which signals to your liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. In ketosis, glucagon levels are high, stimulating the breakdown of stored fat and the production of ketones.
Production and Utilization of Ketones as an Energy Source
When your body is in ketosis, your liver produces three primary types of ketones:
- Acetoacetate:This is the most common ketone produced by the liver.
- Beta-hydroxybutyrate:This is the most abundant ketone in the blood during ketosis.
- Acetone:This is a minor ketone that is primarily exhaled.
These ketones are then released into the bloodstream and can be used as an energy source by various tissues in your body, including your brain, muscles, and heart.
“Ketones are a highly efficient fuel source for the brain and can provide a sustained energy supply during periods of fasting or carbohydrate restriction.”
Potential Benefits of the Keto Diet
The ketogenic diet, with its emphasis on fat and restriction of carbohydrates, has gained significant attention for its potential health benefits. While more research is needed to fully understand its long-term effects, studies have shown promising results in various areas.
The keto diet is like a sneaky ninja, slipping past your body’s usual sugar-burning routine and forcing it to burn fat instead. It’s all about cutting carbs and loading up on healthy fats, tricking your body into thinking it’s in a state of starvation.
But don’t worry, you won’t actually be starving! There are plenty of delicious keto-friendly recipes out there. If you’re looking for more general advice on diet to lose weight , you can find a ton of resources online.
Anyway, back to the keto diet – it’s a bit of a rollercoaster ride, but once your body adjusts, you’ll be feeling energized and shedding those extra pounds like a snake shedding its skin.
Weight Loss and Body Composition
The keto diet can be effective for weight loss due to its ability to induce ketosis, a metabolic state where the body primarily burns fat for energy. This leads to a reduction in appetite and calorie intake, contributing to weight loss.
The diet also promotes the loss of body fat while preserving muscle mass, which is crucial for maintaining metabolism and overall health.
Diabetes Management
The keto diet has shown potential in managing type 2 diabetes. By reducing carbohydrate intake, it can help improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce the need for medication. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any dietary changes, especially if you have diabetes.
Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet has been used for decades as a treatment for epilepsy, particularly in children. It is believed to work by reducing seizures through various mechanisms, including reducing brain inflammation and increasing the production of ketone bodies. While not a cure, the keto diet can be a valuable tool for managing epilepsy, especially in cases where conventional medications are not effective.
Other Potential Benefits
- Improved Cognitive Function:Some studies suggest that the keto diet may improve cognitive function, including memory, focus, and alertness. This may be due to the increased production of ketone bodies, which can provide an alternative energy source for the brain.
- Reduced Inflammation:The keto diet has been linked to reduced inflammation throughout the body, which may play a role in preventing chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Improved Heart Health:The keto diet can lower triglycerides and increase HDL cholesterol, which are beneficial for heart health. However, it is important to note that the diet can also raise LDL cholesterol, so it is essential to monitor cholesterol levels and make adjustments as needed.
- Improved Skin Health:The keto diet may improve skin health by reducing inflammation and promoting the production of collagen. This can lead to clearer skin, fewer wrinkles, and a more youthful appearance.
Potential Risks and Considerations
The keto diet, like any other drastic dietary change, can come with its own set of potential risks and side effects. While it might seem like a magical solution for weight loss, it’s important to understand the potential downsides and take necessary precautions.
Electrolyte Imbalance
Electrolytes are essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium, which play crucial roles in various bodily functions. When you switch to a keto diet, your body starts burning fat for energy, leading to a decrease in carbohydrate intake. This sudden shift can disrupt your electrolyte balance, causing a range of unpleasant symptoms.
It’s crucial to monitor your electrolyte levels and replenish them adequately to prevent potential health issues.
- Dehydration:Since you’re consuming fewer carbohydrates, your body produces less antidiuretic hormone (ADH), leading to increased urination and potential dehydration.
- Hypokalemia (Low Potassium):Potassium is lost through urine during ketosis, potentially causing muscle cramps, fatigue, and weakness.
- Hyponatremia (Low Sodium):Sodium levels can drop due to increased water loss, leading to headaches, nausea, and confusion.
Nutritional Deficiencies
While the keto diet focuses on healthy fats, it can be restrictive in terms of certain essential nutrients. If not carefully planned, you might miss out on vital vitamins and minerals.
- Fiber:A keto diet typically limits high-fiber foods, potentially leading to constipation and digestive issues.
- Vitamins and Minerals:A lack of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can result in deficiencies in essential vitamins like Vitamin C, Vitamin E, and certain B vitamins.
Potential Long-Term Health Effects
The long-term effects of the keto diet are still being studied, and more research is needed to fully understand its impact on overall health.
- Kidney Stones:A keto diet can increase the risk of kidney stones due to its high-fat content and potential dehydration.
- Bone Loss:The restriction of calcium-rich foods can contribute to bone loss, especially in individuals already at risk for osteoporosis.
- Cardiovascular Health:While some studies suggest the keto diet might improve cardiovascular health, others raise concerns about its impact on cholesterol levels and heart health.
Implementing the Keto Diet
Embarking on the ketogenic diet requires a strategic approach to ensure successful adaptation and sustained results. This involves understanding the dietary principles, meal planning, and practical tips for managing cravings and transitioning smoothly into this unique way of eating.
Sample Ketogenic Meal Plan
A well-structured ketogenic meal plan provides a framework for consuming nutrient-rich foods that align with the diet’s principles. Here’s a sample meal plan to illustrate a typical day on keto:
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach and avocado, topped with a drizzle of olive oil and a sprinkle of Himalayan salt. This combination provides a good source of protein, healthy fats, and essential nutrients.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, sliced cucumbers, bell peppers, and a keto-friendly dressing made with olive oil, lemon juice, and Dijon mustard. This meal delivers protein, fiber, and healthy fats while keeping carbohydrates low.
- Dinner: Salmon with roasted asparagus and cauliflower rice. This option provides a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids from the salmon, along with fiber and essential vitamins and minerals from the vegetables.
Keto-Friendly Foods and Nutritional Profiles
Understanding the nutritional profiles of keto-friendly foods is crucial for making informed choices and ensuring adequate nutrient intake. Here’s a table outlining some common keto-friendly foods and their nutritional values:
| Food | Calories | Protein (grams) | Fat (grams) | Carbohydrates (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avocado | 160 | 2 | 15 | 9 |
| Salmon (4 ounces) | 180 | 20 | 10 | 0 |
| Chicken Breast (4 ounces) | 165 | 31 | 3 | 0 |
| Eggs (2 large) | 155 | 12 | 10 | 1 |
| Cauliflower Rice (1 cup) | 25 | 2 | 0 | 5 |
Tips for Transitioning to a Ketogenic Diet
Transitioning to a ketogenic diet can be a gradual process that requires patience and consistency. Here are some tips for a smoother transition:
- Start slowly: Instead of drastically eliminating all carbohydrates, gradually reduce your intake over a few days or weeks. This helps your body adjust to the changes in fuel source and minimizes potential side effects like headaches or fatigue.
- Focus on whole foods: Prioritize unprocessed, nutrient-rich foods like meat, fish, poultry, vegetables, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients and support overall well-being.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential, especially during the initial stages of the ketogenic diet. Water helps flush out excess ketones and supports overall hydration.
- Be patient: It takes time for your body to adapt to burning fat for energy. Be patient with yourself and allow your body to adjust to the new way of eating. Results may take a few weeks or even months to become noticeable.
Managing Cravings
Cravings are a common challenge when transitioning to a ketogenic diet. However, there are strategies to manage them effectively:
- Identify triggers: Pay attention to what triggers your cravings, whether it’s stress, boredom, or specific foods. Once you identify the triggers, you can develop strategies to avoid them or manage them effectively.
- Distract yourself: When cravings strike, distract yourself with activities you enjoy, such as exercise, reading, or spending time with loved ones. This can help shift your focus away from food and reduce cravings.
- Drink water or unsweetened tea: Often, cravings are a sign of dehydration. Drinking water or unsweetened tea can help satiate your thirst and reduce cravings.
- Eat regular meals and snacks: Skipping meals or going too long without eating can increase cravings. Make sure to eat regular meals and snacks throughout the day to maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent cravings.
The Keto Diet and Exercise
The keto diet can significantly impact your exercise performance and recovery. Understanding these impacts and how to adjust your routine can help you maximize your fitness goals while following a ketogenic lifestyle.
Adjusting Exercise Routines During Ketosis
It’s crucial to adapt your exercise routine when transitioning to a keto diet. Ketosis can initially lead to reduced energy levels and potentially impact your endurance.
- Start Slowly:Begin with shorter workouts and gradually increase the intensity and duration as your body adapts. Listen to your body and take rest days when needed.
- Focus on Low-Intensity Exercise:Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling are good options for beginners, as they require less energy and are easier on your muscles.
- Hydrate:Dehydration is common during ketosis, so it’s crucial to stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water throughout the day and before, during, and after exercise.
- Fuel with Electrolytes:Electrolyte depletion can occur on the keto diet, especially during exercise. Consuming electrolyte-rich beverages or supplements can help prevent fatigue and cramping.
Benefits of Combining the Keto Diet with Strength Training
The keto diet, with its emphasis on fat as a primary energy source, can be beneficial for strength training.
- Increased Fat Burning:The keto diet promotes fat burning, which can provide a sustainable source of energy for strength training workouts.
- Improved Muscle Recovery:Studies suggest that keto diets may improve muscle recovery after intense exercise, potentially leading to faster gains in strength and muscle mass.
- Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity:The keto diet can improve insulin sensitivity, which can aid in muscle growth and repair.
Long-Term Sustainability of the Keto Diet: How Does Keto Diet Work
The ketogenic diet, while effective for short-term weight loss, raises questions about its long-term feasibility and potential health implications. Can you truly sustain a keto lifestyle for years on end? Let’s delve into the complexities of long-term keto adherence and explore the potential benefits and drawbacks.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Maintaining a keto diet for an extended period can lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully managed. The strict limitations on carbohydrate intake may restrict the intake of essential vitamins and minerals found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Fiber:A keto diet often restricts fiber intake, which is crucial for digestive health and regulating blood sugar levels.
- Vitamin B:Many B vitamins, such as thiamin (B1), riboflavin (B2), and niacin (B3), are found in carbohydrates, and their deficiency can lead to fatigue, anemia, and neurological problems.
- Potassium:A keto diet may lead to potassium deficiency, which can result in muscle weakness, fatigue, and irregular heartbeat.
- Magnesium:Magnesium deficiency can manifest as headaches, fatigue, and muscle cramps.
Metabolic Adaptations
The body undergoes metabolic adaptations when on a ketogenic diet. While these adaptations can be beneficial for weight loss and metabolic health, they also raise concerns about long-term sustainability.
- Reduced Basal Metabolic Rate:A keto diet can lead to a decrease in the body’s basal metabolic rate (BMR), which is the number of calories burned at rest. This can make weight management more challenging over time.
- Hormonal Changes:The keto diet can influence hormone levels, potentially affecting appetite regulation and leading to hunger and cravings.
- Gut Microbiome:The composition of the gut microbiome can change on a keto diet, which may have implications for overall health and metabolism.
End of Discussion
The keto diet is a fascinating journey into the world of fat-burning, offering a potential path to improved health and well-being. While it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, its ability to tap into your body’s natural fat-burning capabilities makes it a compelling option for many.
So, if you’re ready to explore the world of ketosis and discover its potential benefits, be sure to do your research, consult with a healthcare professional, and embark on this journey with a healthy dose of caution and curiosity.
Remember, like any dietary change, the key to success lies in understanding how your body works and making informed choices that align with your individual needs and goals.
Popular Questions
Is the keto diet safe for everyone?
The keto diet may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new diet.
How long does it take to enter ketosis?
It typically takes 2-4 days to enter ketosis, but this can vary depending on individual factors.
What are some common side effects of the keto diet?
Some common side effects include fatigue, headache, constipation, and bad breath, often referred to as “keto flu.” These symptoms usually subside within a few days.
Can I exercise on the keto diet?
Yes, you can exercise on the keto diet. However, you may need to adjust your exercise routine and fuel intake to accommodate the changes in your body’s energy sources.
Is the keto diet sustainable long-term?
The long-term sustainability of the keto diet depends on individual preferences and lifestyle factors. It’s important to consider potential nutrient deficiencies and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.



















