Best diet when pregnant? Think of it as building a super-powered spaceship for your little astronaut! You’re not just eating for one, you’re fueling a whole new world of growth and development. From the moment that positive pregnancy test pops up, your body needs a turbocharged nutrition plan to keep you and your baby thriving.
Pregnancy is a time of incredible transformation, and a healthy diet plays a vital role in supporting both your well-being and your baby’s development. Imagine your body as a bustling construction site, building a tiny human from scratch! This requires a steady supply of essential nutrients, like vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats, to ensure everything is built to perfection.
But don’t worry, you don’t need to become a nutrition expert overnight. This guide will walk you through the key dietary guidelines, essential foods, and common concerns, helping you navigate the exciting journey of pregnancy with confidence and a well-nourished tummy.
Importance of a Healthy Diet During Pregnancy

A healthy diet is not just about maintaining a healthy weight during pregnancy; it’s about providing your growing baby with the essential nutrients they need to develop properly. Eating a balanced diet is crucial for both your and your baby’s well-being.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Their Risks
Nutritional deficiencies during pregnancy can lead to various health complications for both the mother and the developing fetus. These deficiencies can affect the baby’s growth, development, and overall health.
- Iron deficiency: Can lead to anemia in the mother, causing fatigue, shortness of breath, and increased risk of premature birth and low birth weight.
- Iodine deficiency: Can cause intellectual disabilities and developmental delays in the baby.
- Folate deficiency: Can lead to neural tube defects, such as spina bifida, in the baby.
- Vitamin D deficiency: Can increase the risk of preeclampsia, a serious pregnancy complication.
- Calcium deficiency: Can affect the baby’s bone development and increase the risk of osteoporosis in the mother.
Essential Nutrients for a Healthy Pregnancy
Eating a variety of nutrient-rich foods is crucial for a healthy pregnancy. Here’s a breakdown of some essential nutrients and their sources:
Iron
Iron is essential for carrying oxygen to the baby and is crucial for red blood cell production.
- Red meat: Beef, lamb, and pork are excellent sources of iron.
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey are good sources of iron.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, and sardines are rich in iron.
- Beans and lentils: These are good plant-based sources of iron.
- Fortified cereals: Some cereals are fortified with iron.
Folate
Folate is essential for cell growth and development, especially during the first trimester when the baby’s neural tube is forming.
Pregnancy is a time for nourishing both yourself and your little one, but let’s be real, sometimes cravings hit harder than a baby’s first kick. If you’re looking to shed those extra pounds after the baby arrives, consider checking out this free diet plan for weight loss.
Just remember, once you’re back on your feet, your prenatal vitamins are still your best friend, and those cravings might just morph into a love for broccoli.
- Leafy green vegetables: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in folate.
- Citrus fruits: Oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are good sources of folate.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are good sources of folate.
- Fortified cereals: Some cereals are fortified with folate.
Calcium
Calcium is essential for the development of the baby’s bones and teeth, as well as for the mother’s bone health.
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese are excellent sources of calcium.
- Leafy green vegetables: Kale, collard greens, and bok choy are good sources of calcium.
- Fortified foods: Some plant-based milks, juices, and cereals are fortified with calcium.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption and bone health.
- Sunlight exposure: The body produces vitamin D when exposed to sunlight.
- Fatty fish: Salmon, tuna, and mackerel are good sources of vitamin D.
- Fortified foods: Some milk, yogurt, and cereals are fortified with vitamin D.
Iodine
Iodine is essential for the baby’s brain development and thyroid function.
- Seafood: Fish, shellfish, and seaweed are good sources of iodine.
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese are good sources of iodine.
- Iodized salt: Using iodized salt in cooking is a good way to get iodine.
Key Dietary Guidelines for Pregnant Women
The journey of pregnancy is a beautiful and transformative experience, and it’s crucial to nourish your body and your growing baby with the right nutrients. This section will Artikel essential dietary guidelines that can help you thrive during this special time.
Recommended Daily Intake of Nutrients
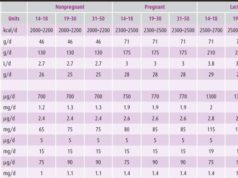
A balanced diet during pregnancy ensures you and your baby receive the essential nutrients for healthy development. Let’s delve into the recommended daily intake of key nutrients:
- Calories:The recommended daily calorie intake for pregnant women varies based on their pre-pregnancy weight and activity level. Generally, an additional 300-450 calories per day is recommended during the second and third trimesters. For example, a woman who consumed 2,000 calories per day before pregnancy might need around 2,300-2,450 calories during pregnancy.This additional calorie intake is crucial to support your baby’s growth and your increased energy needs.
- Protein:Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, including your baby’s organs, muscles, and bones. The recommended daily protein intake increases to 71 grams during pregnancy. Lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, eggs, and dairy products are excellent sources of protein.Think of protein as the building blocks for your little one’s growth!
- Carbohydrates:Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. During pregnancy, it’s important to choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, over refined carbohydrates like white bread and sugary drinks. These complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy and essential fiber for digestion.Pregnancy cravings are real, but remember, you’re not eating for two, you’re eating for a tiny human who’s basically a living, breathing avocado. So, eat your veggies, get your protein, and maybe indulge in a little extra cheese. But after the baby arrives, you might find yourself wondering how to shed those extra pounds.
That’s where the concept of “reverse dieting” comes in handy. How to reverse diet can help you gradually increase your calorie intake to avoid the dreaded yo-yo effect. And remember, breastfeeding is a calorie burner, so don’t be afraid to enjoy those extra snacks while you’re at it! Just be sure to choose nutritious options to keep your energy levels up and your milk supply flowing.
Think of carbohydrates as the fuel for your pregnancy journey!
- Fats:Fats are vital for hormone production, brain development, and cell function. Aim for healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, fatty fish, and olive oil. Limit saturated and trans fats, which can increase the risk of heart disease.Think of fats as the building blocks for your baby’s brain and nervous system!
Hydration: The Elixir of Pregnancy
Staying hydrated is crucial during pregnancy, as it plays a vital role in many bodily functions, including blood circulation, temperature regulation, and waste removal. The recommended daily water intake for pregnant women is around 10 glasses (80 ounces). You can also include other fluids like milk, juice, and herbal teas in your daily intake.
Think of water as the lifeblood for both you and your baby!
Managing Pregnancy Cravings and Aversions
Pregnancy can bring about a rollercoaster of cravings and aversions. While it’s okay to indulge in your cravings occasionally, it’s important to maintain a balanced diet. Here are some tips for managing these changes:
- Listen to Your Body:If you’re craving something specific, try to identify the nutrient you might be lacking. For example, if you’re craving salty foods, you might be low on sodium. Instead of reaching for processed snacks, opt for healthier alternatives like nuts, seeds, or homemade popcorn.
- Seek Alternatives:If you’re experiencing aversions, try to find healthy substitutes. For instance, if you can’t stomach meat, try incorporating more plant-based protein sources like beans, lentils, or tofu.
- Don’t Force It:If you truly can’t stomach something, don’t force it. Focus on eating what you can tolerate and make sure you’re getting a variety of nutrients from other sources.
- Stay Hydrated:Sometimes, cravings and aversions can be related to dehydration. Make sure you’re drinking enough water throughout the day.
- Snack Smart:Keep healthy snacks on hand to avoid reaching for unhealthy options when cravings hit. Some healthy snack ideas include fruit, yogurt, nuts, and seeds.
Foods to Include in a Pregnancy Diet
A balanced and nutritious diet is crucial for both your health and the development of your baby. By incorporating a variety of foods rich in essential nutrients, you can ensure you’re providing your little one with the building blocks they need to grow and thrive.
Foods Rich in Essential Nutrients for Pregnancy
Here’s a table outlining essential food groups, their benefits, and serving suggestions to guide you on your journey to a healthy pregnancy:
| Food Group | Examples | Benefits | Serving Suggestions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fruits | Berries, oranges, apples, bananas, kiwi, mangoes | Rich in vitamins C, A, and folate, which are crucial for cell growth and development. Also provide fiber, which aids digestion and prevents constipation. | Aim for 2-3 servings of fruits daily. You can enjoy them as snacks, add them to yogurt or oatmeal, or incorporate them into smoothies. |
| Vegetables | Leafy greens (spinach, kale), broccoli, carrots, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, bell peppers | Packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support immune function, cell growth, and vision development. | Include 3-5 servings of vegetables daily. Enjoy them steamed, roasted, or as part of salads. |
| Whole Grains | Brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, oats | Provide complex carbohydrates for energy, fiber for digestion, and B vitamins essential for cell growth and development. | Choose whole grains over refined grains whenever possible. Incorporate them into meals and snacks. |
| Protein | Lean meats (chicken, turkey, fish), beans, lentils, eggs, tofu, nuts, seeds | Essential for building and repairing tissues, producing hormones, and supporting the development of your baby’s brain and nervous system. | Aim for 2-3 servings of protein daily. Choose lean protein sources and incorporate plant-based options. |
| Dairy | Milk, yogurt, cheese | Rich in calcium, which is crucial for bone development and growth. Also provide vitamin D, which aids in calcium absorption. | Include 2-3 servings of dairy daily. Choose low-fat or fat-free options for a healthier choice. |
| Healthy Fats | Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel) | Provide essential fatty acids, such as omega-3s, which are vital for brain development and vision. Also support hormone production and cell growth. | Incorporate healthy fats into your diet in moderation. Enjoy them as snacks, add them to salads, or use them for cooking. |
Foods to Limit or Avoid During Pregnancy: Best Diet When Pregnant
Pregnancy is a time of incredible change and growth, and it’s essential to fuel your body with the right nutrients to support both you and your developing baby. While a healthy diet is crucial, there are certain foods that should be limited or avoided altogether during pregnancy.
These foods may pose risks to you or your baby’s health, and it’s important to be aware of them.
Common Food Allergens and Their Impact on Pregnancy
Food allergies can develop at any time, but they are particularly common during pregnancy. While most food allergies are mild and manageable, some can have serious consequences. It’s crucial to be aware of common food allergens and their potential impact on pregnancy.
- Peanuts:Peanut allergy is one of the most common and severe food allergies. It can cause a range of reactions, from mild skin rashes to life-threatening anaphylaxis. If you have a peanut allergy, it’s important to avoid all peanut products, including peanut butter, peanut oil, and peanut-containing snacks.
- Tree Nuts:Tree nuts, such as almonds, walnuts, and cashews, are another common allergen. Reactions to tree nuts can range from mild to severe. If you have a tree nut allergy, avoid all tree nut products.
- Dairy:Lactose intolerance, a common condition that makes it difficult to digest lactose, is not the same as a dairy allergy. However, some people may experience allergic reactions to dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt. If you suspect you have a dairy allergy, it’s essential to consult with a doctor.
- Eggs:Egg allergies can cause a range of reactions, from mild skin rashes to anaphylaxis. If you have an egg allergy, avoid all egg products, including raw eggs, cooked eggs, and egg-containing foods.
- Soy:Soy is a common allergen, and reactions can range from mild to severe. If you have a soy allergy, avoid all soy products, including soy milk, tofu, and soy sauce.
- Wheat:Wheat allergy is less common than other food allergies, but it can cause a range of reactions. If you have a wheat allergy, avoid all wheat products, including bread, pasta, and pastries.
Risks Associated with Consuming Raw or Undercooked Meat, Fish, and Eggs, Best diet when pregnant
Raw or undercooked meat, fish, and eggs can harbor harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella, Listeria, and Toxoplasma, which can cause foodborne illness. These illnesses can be particularly dangerous during pregnancy, as they can lead to miscarriage, premature birth, or other complications.
- Meat:Raw or undercooked meat, such as steak, chicken, and pork, should be avoided during pregnancy. Always cook meat thoroughly to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to kill harmful bacteria.
- Fish:Raw or undercooked fish, such as sushi and sashimi, should be avoided during pregnancy. These foods can contain high levels of mercury, which can be harmful to the developing fetus.
- Eggs:Raw or undercooked eggs should be avoided during pregnancy. Raw eggs can contain Salmonella bacteria, which can cause food poisoning.
Importance of Limiting Caffeine, Alcohol, and Processed Foods During Pregnancy
Caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods should be limited or avoided during pregnancy. These substances can have negative effects on both you and your developing baby.
- Caffeine:High levels of caffeine can increase the risk of miscarriage, premature birth, and low birth weight. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) recommends limiting caffeine intake to 200 milligrams per day, which is about the amount in one 12-ounce cup of coffee.
- Alcohol:Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can cause fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs), which are a range of birth defects that can affect a child’s physical, mental, and behavioral development. There is no safe level of alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
- Processed Foods:Processed foods are often high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. These foods can contribute to weight gain, high blood pressure, and other health problems during pregnancy.
Addressing Common Pregnancy-Related Dietary Concerns
Pregnancy can be a whirlwind of emotions and physical changes, and navigating the world of food during this time can feel like a whole new adventure. From morning sickness to heartburn, weight gain to cravings, there are a lot of dietary concerns that come up during pregnancy.
Let’s dive into some common issues and explore ways to address them.
Prenatal Vitamins and Supplements
Prenatal vitamins are your pregnancy superheroes! They’re packed with essential nutrients like iron, folic acid, and calcium, which are crucial for your baby’s development and your own health. While a balanced diet is ideal, prenatal vitamins can help fill in any nutritional gaps.
It’s important to talk to your doctor about which prenatal vitamin is right for you, as they can guide you based on your individual needs.
Managing Morning Sickness and Heartburn
Morning sickness, despite its name, can strike at any time of day, and heartburn can make even the simplest meal feel like a challenge. Don’t worry, you’re not alone! These are common pregnancy discomforts. Here are some dietary tips to help manage these symptoms:
- Eat small, frequent meals: Instead of three large meals, try snacking on small, bland foods throughout the day. This can help prevent an empty stomach, which can trigger nausea. Think crackers, toast, or fruit.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can worsen nausea and heartburn. Sip on water, herbal teas, or ginger ale throughout the day. Avoid sugary drinks, as they can exacerbate heartburn.
- Avoid trigger foods: Pay attention to foods that seem to make your nausea or heartburn worse. For example, greasy foods, spicy foods, and acidic fruits can often be culprits. Eliminate these from your diet for a while and see if your symptoms improve.
- Elevate your head while sleeping: This can help reduce acid reflux and heartburn at night.
Weight Gain During Pregnancy
Gaining weight during pregnancy is normal and healthy. Your body needs extra calories and nutrients to support your growing baby. However, it’s important to gain weight within a healthy range. Your doctor can help you determine a healthy weight gain goal based on your pre-pregnancy weight and other factors.
- Focus on nutritious foods: Choose foods rich in nutrients like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are crucial for both you and your baby’s health.
- Limit processed foods and sugary drinks: These foods are high in calories and low in nutrients. They can contribute to unhealthy weight gain and may not provide the nourishment you need during pregnancy.
- Stay active: Regular physical activity can help you manage your weight and improve your overall health. Talk to your doctor about safe exercise options during pregnancy. Even gentle activities like walking or swimming can make a difference.
The Role of a Healthcare Professional
Navigating the world of pregnancy nutrition can feel overwhelming, especially with the constant stream of conflicting advice. That’s why it’s crucial to have a trusted healthcare professional in your corner. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure your dietary choices support both your well-being and your baby’s growth.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
Your primary healthcare provider, usually an obstetrician or a midwife, is your first point of contact for all pregnancy-related matters, including nutrition. They’ll monitor your overall health, assess your individual needs, and recommend a balanced diet tailored to your specific circumstances.
They’ll also address any concerns you have about your diet and guide you towards healthy choices.
The Role of a Registered Dietitian
For more in-depth nutrition guidance, consider consulting a registered dietitian (RD). RDs are experts in food and nutrition, and they specialize in creating customized meal plans for various health conditions, including pregnancy. They can help you understand the nutritional requirements of pregnancy, identify potential deficiencies, and develop a personalized eating plan that meets your individual needs.
Forget kale smoothies and chia seed pudding – pregnancy cravings are a whole different beast! While indulging in the occasional cookie is totally fine, it’s crucial to fuel your growing bump with the right nutrients. That’s where the recommended dietary allowance comes in, giving you a roadmap to a balanced diet for both you and your little one.
So, ditch the restrictive diet plans and embrace a balanced approach that includes all the good stuff your body needs, including a healthy dose of chocolate chip cookies!
Resources for Nutrition Support
If you’re seeking additional support or have specific dietary concerns, various resources can help:
- The American Pregnancy Association:Provides comprehensive information on pregnancy nutrition, including articles, recipes, and a helpline for answering questions.
- The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics:Offers a directory of registered dietitians who specialize in prenatal nutrition. You can find a qualified RD in your area through their website.
- Local community health centers:Often offer nutrition counseling and support groups for pregnant women.
Summary
So, remember, pregnancy is a time to celebrate the amazing power of your body and the incredible journey of creating life. Nourishing yourself with a healthy diet is the best way to support this journey, ensuring both you and your little one are happy, healthy, and ready to embark on a new adventure together.
Don’t hesitate to consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support. After all, you deserve to feel your best, and so does your little bundle of joy!
Commonly Asked Questions
What if I’m craving something unhealthy?
Cravings are normal during pregnancy, but try to satisfy them with healthier alternatives. For example, instead of ice cream, opt for frozen yogurt or a fruit smoothie. Remember, moderation is key!
Is it okay to eat sushi during pregnancy?
Raw fish, especially sushi, can carry parasites that are harmful to both you and your baby. It’s best to avoid raw fish altogether during pregnancy. If you’re craving sushi, opt for cooked rolls or vegetable-based options.
How much weight should I gain during pregnancy?
The amount of weight you should gain during pregnancy varies depending on your pre-pregnancy weight. Your healthcare provider can give you personalized recommendations. Aim for a steady, healthy weight gain throughout your pregnancy.