Can you diet while pregnant? This question is a common one for expectant mothers who are concerned about their weight and the health of their baby. While it’s essential to maintain a healthy weight during pregnancy, dieting in the traditional sense is often discouraged. Pregnancy requires increased nutrient intake to support the growing fetus, and restrictive diets can put both mother and baby at risk.
This article explores the complexities of nutrition during pregnancy, delving into the importance of balanced eating, the potential dangers of restrictive diets, and how to manage weight gain safely and effectively. We’ll also discuss common pregnancy cravings, food safety concerns, and the role of healthcare professionals in guiding your nutritional journey.
Importance of Proper Nutrition During Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time of significant physical and hormonal changes, and it is crucial for women to prioritize their nutrition to support their own health and the healthy development of their baby. A balanced and nutritious diet during pregnancy provides the essential nutrients required for fetal growth, development, and overall maternal well-being.
Nutritional Needs During Pregnancy
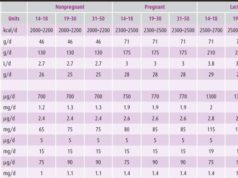
The nutritional needs of pregnant women are significantly higher than those of non-pregnant women. This is due to the increased demands of supporting fetal growth, development, and the physiological changes associated with pregnancy.
- Calories: Pregnant women require an additional 300-500 calories per day, particularly in the second and third trimesters. These extra calories are essential for fetal growth and development, as well as for meeting the increased energy demands of the mother’s body.
- Protein: Protein is crucial for the growth and development of the fetus, including the placenta, amniotic fluid, and maternal tissues. Pregnant women require an additional 25 grams of protein per day. This can be obtained from various sources, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and dairy products.
- Iron: Iron is essential for red blood cell production and oxygen transport. Pregnant women require an increased amount of iron to meet the demands of their growing body and the developing fetus. Iron deficiency anemia can lead to fatigue, shortness of breath, and complications during pregnancy and delivery.
- Folic Acid: Folic acid is a B vitamin that plays a vital role in cell division and growth. It is essential for the development of the baby’s brain and spinal cord. Inadequate folic acid intake during pregnancy can increase the risk of neural tube defects, such as spina bifida.
- Calcium: Calcium is essential for bone development and growth. Pregnant women require an increased amount of calcium to support the growth of the baby’s bones and teeth. Calcium deficiency can lead to weak bones and osteoporosis.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D plays a role in calcium absorption and bone health. Pregnant women need adequate vitamin D to support the development of the baby’s bones and teeth. Vitamin D deficiency can increase the risk of rickets in the baby.
Understanding “Dieting” During Pregnancy

The term “dieting” often conjures images of restrictive eating plans aimed at weight loss. However, during pregnancy, the concept of dieting takes on a different meaning. It’s crucial to understand that “dieting” in the context of pregnancy should never involve deprivation or drastic calorie restriction. Instead, it’s about making mindful and healthy food choices that support both the mother’s and the baby’s well-being.
Dieting during pregnancy is generally not recommended, as your body needs extra nutrients to support both you and your growing baby. However, making healthy choices is always important. A vegetarian diet, which focuses on plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and grains, what’s vegetarian diet can be a nutritious option during pregnancy, as long as you ensure you’re getting enough essential nutrients like iron and vitamin B12.
It’s always best to consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized advice on healthy eating during pregnancy.
Potential Risks of Restrictive Diets During Pregnancy
While some women might be tempted to diet during pregnancy, especially if they are concerned about weight gain, it’s essential to recognize the potential risks associated with restrictive diets.
It’s crucial to remember that dieting during pregnancy is generally not recommended. Instead of focusing on strict restrictions, consider exploring healthy ideas for diet that emphasize nutrient-rich foods and portion control. This approach can help you maintain a healthy weight while ensuring your baby receives the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and development.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Restrictive diets can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients like iron, folic acid, calcium, and vitamin D, which are crucial for the baby’s growth and development. These deficiencies can result in various health complications for both the mother and the baby.
- Low Birth Weight: Inadequate nutrient intake during pregnancy can lead to low birth weight, increasing the risk of health problems for the newborn, including respiratory distress syndrome and developmental delays.
- Premature Birth: Some studies suggest a link between restrictive diets and an increased risk of premature birth. This can lead to various complications for the baby, including respiratory problems and developmental challenges.
- Maternal Health Issues: Restrictive diets can negatively impact the mother’s health, leading to fatigue, weakness, and an increased risk of complications like anemia and gestational diabetes.
Weight Management and Pregnancy
Gaining weight during pregnancy is normal and necessary for the healthy development of your baby. However, excessive weight gain can lead to complications like gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and difficulty delivering.
Recommended Weight Gain Guidelines
The recommended weight gain during pregnancy varies depending on your pre-pregnancy Body Mass Index (BMI). BMI is a measure of body fat based on height and weight. The following table Artikels the recommended weight gain ranges for different BMI categories:
| Pre-Pregnancy BMI | Recommended Weight Gain (lbs) |
|---|---|
| Underweight (<18.5) | 28-40 lbs |
| Normal weight (18.5-24.9) | 25-35 lbs |
| Overweight (25-29.9) | 15-25 lbs |
| Obese (≥30) | 11-20 lbs |
Role of Exercise and Healthy Eating
Maintaining a healthy weight during pregnancy is crucial for both you and your baby. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can help you achieve this.
Exercise
Exercise during pregnancy has numerous benefits, including:
- Improved mood and energy levels
- Reduced risk of gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and other pregnancy complications
- Easier labor and delivery
- Faster postpartum recovery
It is important to choose safe and effective exercises that are suitable for pregnancy. Some examples include:
- Low-impact aerobics: Walking, swimming, water aerobics
- Strength training: Light weights, resistance bands, bodyweight exercises
- Yoga and Pilates: These exercises can improve flexibility, strength, and balance
Healthy Eating
A balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is essential for both you and your baby. It is important to avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of caffeine.
Addressing Specific Dietary Concerns
Pregnancy can bring a whirlwind of changes, including shifts in taste and appetite. It’s common to experience intense cravings and aversions, making it crucial to navigate these changes while prioritizing your health and that of your growing baby.
Managing Cravings and Aversions
Pregnancy cravings and aversions are often driven by hormonal fluctuations and the body’s increased need for certain nutrients. While indulging in occasional cravings is fine, it’s important to prioritize healthy choices. Here’s how to manage cravings and aversions:
- Identify Triggers: Pay attention to what triggers your cravings and aversions. Certain smells, sights, or times of day might contribute to these changes.
- Healthy Substitutions: When craving unhealthy foods, find healthier alternatives. For example, if you crave chocolate, opt for dark chocolate or a small piece of fruit instead.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can sometimes mimic cravings. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help reduce cravings and aversions.
- Listen to Your Body: If you have a strong aversion to a particular food, don’t force yourself to eat it. Your body might be trying to tell you something. However, consult your doctor if you’re concerned about nutritional deficiencies.
Safety and Risks of Specific Foods and Beverages
While enjoying a varied diet during pregnancy is essential, it’s important to be mindful of certain foods and beverages that can pose risks to you and your baby.
Caffeine
- Moderate Intake: Limiting caffeine intake to less than 200 milligrams per day is generally considered safe during pregnancy. This is roughly equivalent to one 12-ounce cup of coffee.
- Potential Risks: Excessive caffeine consumption during pregnancy has been linked to a higher risk of miscarriage, premature birth, and low birth weight.
- Alternatives: Consider switching to decaffeinated coffee or tea, or opting for other beverages like water or herbal teas.
Alcohol
- No Safe Amount: There is no safe amount of alcohol consumption during pregnancy. Alcohol can cross the placenta and harm the developing fetus.
- Risks: Alcohol consumption during pregnancy can lead to fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs), a range of physical, mental, and behavioral problems that can last a lifetime.
- Avoidance: It’s essential to abstain from alcohol completely during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
Raw Seafood
- Risk of Foodborne Illness: Raw seafood can contain harmful bacteria, parasites, and viruses that can cause foodborne illness, potentially affecting both you and your baby.
- Examples: Avoid sushi, sashimi, and other raw seafood dishes.
- Cook Thoroughly: If you choose to eat seafood, ensure it is cooked thoroughly to kill any harmful organisms.
Navigating Food Allergies and Intolerances
If you have food allergies or intolerances, it’s essential to manage them carefully during pregnancy.
- Identify Triggers: Work with your doctor or a registered dietitian to identify your specific food triggers and create a safe and nutritious eating plan.
- Read Labels Carefully: Pay close attention to food labels and avoid ingredients that can trigger your allergies or intolerances.
- Inform Restaurants: When dining out, inform restaurant staff about your allergies or intolerances to ensure your food is prepared safely.
- Carry Emergency Medications: Keep your prescribed allergy medications, such as an epinephrine auto-injector, readily available in case of an emergency.
Resources and Support for Pregnant Women
Navigating pregnancy can be overwhelming, especially when it comes to making healthy choices for you and your growing baby. You’re not alone! Numerous resources and support systems are available to help you make informed decisions and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Reputable Resources and Organizations
These organizations provide evidence-based information and guidance on healthy eating during pregnancy:
| Organization | Website | Description |
|---|---|---|
| American Pregnancy Association | https://americanpregnancy.org/ | Offers comprehensive information on all aspects of pregnancy, including nutrition, with a focus on evidence-based recommendations. |
| Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics | https://www.eatright.org/ | Provides resources on healthy eating for all life stages, including pregnancy, with a focus on practical tips and recipes. |
| March of Dimes | https://www.marchofdimes.org/ | A leading non-profit organization dedicated to preventing birth defects, premature birth, and infant mortality, offering information on prenatal care and nutrition. |
Healthcare Professionals, Can you diet while pregnant
Consulting with a qualified healthcare professional specializing in nutrition during pregnancy can provide personalized guidance and address your specific needs:
- Registered Dietitian (RD) or Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN): These professionals are experts in nutrition and can provide personalized advice on healthy eating during pregnancy, addressing any dietary concerns or restrictions.
- Obstetrician-Gynecologist (OB/GYN): Your primary care provider during pregnancy can offer general nutrition guidance and refer you to a specialist if needed.
- Certified Lactation Consultant (CLC): These professionals can provide expert advice on breastfeeding and nutrition for both you and your baby.
Accessing Reliable Information and Support
- Consult your healthcare provider: Your doctor or midwife is your primary source of information and can provide personalized advice based on your individual needs and medical history.
- Seek out credible sources: Refer to reputable organizations and websites, such as those listed above, for evidence-based information on pregnancy nutrition.
- Join support groups: Connecting with other pregnant women can offer valuable insights, emotional support, and shared experiences.
- Don’t hesitate to ask for help: If you have any concerns or questions about your diet or pregnancy, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider or a qualified nutrition professional.
Closing Notes: Can You Diet While Pregnant
Pregnancy is a time of incredible change and growth, both for the mother and the developing baby. Nourishing your body with the right nutrients is crucial for a healthy pregnancy and a healthy start for your little one. While “dieting” might not be the right approach, focusing on a balanced and nutrient-rich diet will help you thrive throughout your pregnancy journey. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.
FAQ Corner
Can I eat sushi during pregnancy?
It’s best to avoid raw seafood, including sushi, during pregnancy. Raw fish can contain parasites that can be harmful to both you and your baby. Cooked seafood is generally safe to eat in moderation.
What about caffeine during pregnancy?
Limiting caffeine intake during pregnancy is recommended. Too much caffeine can increase the risk of miscarriage and premature birth. Moderate consumption (up to 200mg per day) is generally considered safe, but it’s best to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Is it safe to exercise during pregnancy?
Regular exercise is beneficial during pregnancy, but it’s important to choose safe activities and listen to your body. Talk to your doctor about appropriate exercise routines for your individual situation.
While it’s generally not recommended to go on a restrictive diet during pregnancy, it’s important to make healthy choices. If you’re curious about popular diet trends, you can check out a list of popular diets in 2022. However, remember that these diets might not be suitable for pregnant women, and it’s always best to consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.