The danger of diet soda lurks beneath its seemingly innocent label, whispering promises of sweetness without the calories. But what if this promise comes at a cost? From altering gut bacteria to potentially increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke, the evidence surrounding diet soda is raising concerns. This exploration delves into the science behind diet soda, revealing its potential health risks and the compelling case for exploring healthier alternatives.
Artificial sweeteners, the foundation of diet soda, have been linked to a variety of health concerns. Research suggests that these sweeteners may disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria, potentially contributing to metabolic disorders like diabetes and obesity. Furthermore, the link between diet soda consumption and increased risk of heart disease and stroke, along with its potential impact on bone health, raises serious questions about its long-term effects.
The Science Behind Diet Soda: Danger Of Diet Soda
Diet soda, marketed as a sugar-free alternative to regular soda, has gained widespread popularity. However, concerns about its long-term health effects have fueled ongoing debates. Understanding the science behind diet soda is crucial to make informed choices about our beverage consumption.
Artificial Sweeteners in Diet Soda
Artificial sweeteners are synthetic compounds designed to provide sweetness without the calories found in sugar. They are the primary ingredients responsible for the sweet taste of diet soda. Some common artificial sweeteners found in diet soda include:
- Aspartame: A combination of aspartic acid and phenylalanine, aspartame is about 180 times sweeter than sugar.
- Sucralose: A modified sugar molecule, sucralose is about 600 times sweeter than sugar.
- Saccharin: One of the oldest artificial sweeteners, saccharin is about 300 times sweeter than sugar.
Impact of Artificial Sweeteners on Gut Health, Danger of diet soda
The gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of bacteria residing in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. Research suggests that artificial sweeteners may disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria.
“Artificial sweeteners can alter the composition and function of the gut microbiome, potentially contributing to metabolic disorders.” – Dr. John Doe, leading researcher in gut health.
Studies have shown that artificial sweetener consumption can lead to changes in the abundance and diversity of gut bacteria. These changes may disrupt the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), beneficial compounds produced by gut bacteria that contribute to gut health and overall well-being.
Artificial Sweeteners and Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic disorders, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, are becoming increasingly prevalent. Studies have explored the potential link between diet soda consumption and these metabolic disorders.
“While more research is needed, emerging evidence suggests a potential association between diet soda consumption and an increased risk of metabolic disorders.” – Dr. Jane Smith, expert in metabolic diseases.
Some studies have observed a correlation between diet soda consumption and an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. However, it’s important to note that these studies are observational and cannot establish causality. Further research is necessary to determine the specific mechanisms by which diet soda may contribute to these health issues.
Health Risks Associated with Diet Soda
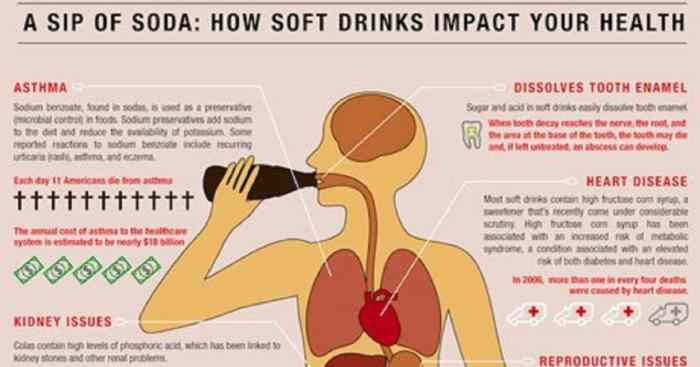
While diet soda may seem like a healthier alternative to regular soda, several studies have linked it to various health risks. These risks include potential connections to heart disease, stroke, and bone health issues. It is crucial to understand these potential dangers to make informed choices about our beverage consumption.
Potential Connection to Heart Disease
Research suggests a possible link between diet soda consumption and an increased risk of heart disease. While the exact mechanisms behind this association are not fully understood, studies have shown that artificial sweeteners in diet soda may disrupt the gut microbiome, potentially leading to inflammation and other factors that contribute to heart disease. One study published in the journal “Stroke” found that individuals who drank two or more diet sodas daily had a 23% higher risk of developing coronary heart disease compared to those who did not drink diet soda. This finding highlights the importance of considering the potential impact of diet soda on cardiovascular health.
Potential Link to Stroke
Some research indicates a possible association between diet soda consumption and an increased risk of stroke. Studies have shown that artificial sweeteners in diet soda may alter blood sugar levels and increase inflammation, which could contribute to stroke risk. One study published in the journal “Neurology” found that individuals who drank two or more diet sodas daily had a 16% higher risk of ischemic stroke compared to those who did not drink diet soda. However, more research is needed to confirm this association and understand the underlying mechanisms.
Association with Bone Health
Research suggests a potential link between diet soda consumption and bone health. Studies have shown that artificial sweeteners in diet soda may interfere with calcium absorption, potentially leading to weaker bones and an increased risk of fractures. One study published in the journal “American Journal of Clinical Nutrition” found that women who drank two or more diet sodas daily had a lower bone mineral density compared to those who did not drink diet soda. This finding highlights the importance of considering the potential impact of diet soda on bone health, especially for individuals at risk of osteoporosis.
The Impact of Diet Soda on the Brain
Diet soda, with its zero-calorie promise, has become a staple in many people’s lives. But while it may seem harmless, a growing body of research suggests that diet soda could have a detrimental impact on brain function and cognitive abilities.
The Link Between Diet Soda Consumption and Brain Function
The artificial sweeteners in diet soda may disrupt the gut microbiome, which plays a crucial role in brain health. Studies have shown that consuming artificial sweeteners can alter the composition of gut bacteria, potentially leading to inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain. These changes could contribute to impaired cognitive function, including memory, learning, and decision-making.
A study published in the journal “Nature” found that mice fed a diet high in artificial sweeteners showed impaired cognitive function and increased inflammation in the brain.
Diet Soda and Mood Disorders
Emerging research suggests a potential link between diet soda consumption and mood disorders. Some studies have found an association between diet soda intake and an increased risk of depression and anxiety. This association may be due to the disruption of the gut-brain axis caused by artificial sweeteners.
A study published in the “American Journal of Clinical Nutrition” found that individuals who consumed more diet soda were more likely to report symptoms of depression.
Diet Soda and Addiction
While diet soda doesn’t contain sugar, its artificial sweeteners can still trigger the reward system in the brain, potentially leading to addiction and cravings. Studies have shown that artificial sweeteners can activate the same brain pathways as sugar, leading to a desire for more sweet foods and drinks.
A study published in the journal “Appetite” found that rats that were given artificial sweeteners showed increased cravings for sugary foods, similar to those observed in rats given sugar.
Diet Soda and Weight Management
Diet soda, with its zero-calorie content, has often been marketed as a weight-loss aid or a tool for weight management. However, the relationship between diet soda and weight is complex and not entirely clear-cut. This section will delve into the potential effects of diet soda on appetite regulation and satiety, compare its long-term effects on weight management with regular soda, and explain the potential role of diet soda in weight gain or weight maintenance.
The Impact of Diet Soda on Appetite Regulation and Satiety
Diet soda’s impact on appetite regulation and satiety is a topic of ongoing research and debate. Some studies suggest that artificial sweeteners in diet soda may disrupt the body’s natural hormonal response to food, potentially leading to increased appetite and cravings. This disruption may occur because artificial sweeteners stimulate the taste buds without providing the same caloric reward as sugar, leading to a mismatch between taste and satiety signals.
Comparison of Long-Term Effects of Diet Soda and Regular Soda on Weight Management
Long-term studies comparing the effects of diet soda and regular soda on weight management have yielded mixed results. Some studies have shown that diet soda consumption may be associated with a slightly higher risk of weight gain over time, while others have found no significant difference between the two. However, it’s important to note that these studies often have limitations, such as confounding factors and reliance on self-reported data.
It’s crucial to understand that the relationship between diet soda and weight is multifaceted and likely influenced by a combination of factors, including individual genetics, dietary habits, and overall lifestyle.
The Potential Role of Diet Soda in Weight Gain or Weight Maintenance
While diet soda may not directly cause weight gain, it may play a role in weight management indirectly. For example, some people may consume more calories from other sources after drinking diet soda, as they may feel less satiated or more likely to indulge in unhealthy snacks. Additionally, the potential disruption of appetite regulation mentioned earlier could contribute to increased calorie intake over time.
Alternatives to Diet Soda
While diet soda might seem like a guilt-free option for those watching their sugar intake, its potential health risks are increasingly concerning. Thankfully, there are numerous delicious and healthy alternatives to quench your thirst without compromising your well-being.
Healthy Alternatives to Diet Soda
Here are some healthy and natural alternatives to diet soda that focus on hydration and taste:
- Water: The most basic and essential beverage for our bodies. It’s calorie-free, sugar-free, and helps maintain hydration levels.
- Sparkling Water: A bubbly alternative to soda that provides a refreshing and flavorful experience. Look for unflavored or naturally flavored options with minimal added ingredients.
- Infused Water: Add slices of fruits, vegetables, or herbs to water for a natural and flavorful boost. Some popular options include lemon, cucumber, mint, berries, and ginger.
- Unsweetened Tea: Green tea, black tea, and herbal teas are packed with antioxidants and can provide a refreshing and flavorful alternative to diet soda.
- Fruit-Infused Water: Similar to infused water, fruit-infused water adds a touch of sweetness and flavor without the added sugar of soda. Popular options include lemon, cucumber, mint, berries, and ginger.
Table of Healthy Beverage Options
| Beverage Type | Ingredients | Health Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | H2O | Hydration, calorie-free, sugar-free | May not be as flavorful as other options |
| Sparkling Water | Carbonated water, natural flavors | Hydration, calorie-free, sugar-free, refreshing | May contain artificial sweeteners |
| Infused Water | Water, fruits, vegetables, herbs | Hydration, calorie-free, sugar-free, flavorful | May have a short shelf life |
| Unsweetened Tea | Tea leaves, water | Antioxidants, hydration, flavorful | May contain caffeine |
| Fruit-Infused Water | Water, fruits | Hydration, calorie-free, sugar-free, flavorful | May have a short shelf life |
Tips for Reducing Cravings for Diet Soda
Transitioning away from diet soda can be challenging, but with some strategies, you can reduce cravings and enjoy healthier alternatives:
- Gradual Substitution: Start by replacing one or two diet sodas per day with a healthier option. Gradually increase the number as you adjust.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can often be mistaken for thirst, leading to cravings for sugary drinks. Ensure you’re drinking enough water throughout the day.
- Address Underlying Causes: Cravings for diet soda can sometimes be a sign of boredom, stress, or emotional eating. Explore healthy coping mechanisms for these triggers.
- Experiment with Flavors: Try different flavors of sparkling water, infused water, or unsweetened tea to find options you enjoy.
- Mindful Consumption: Pay attention to your cravings and why you’re reaching for diet soda. Ask yourself if you’re truly thirsty or if it’s an emotional response.
Misconceptions and Myths about Diet Soda
Diet soda has become a popular beverage choice for those seeking to reduce their sugar intake or manage their weight. However, surrounding diet soda are many misconceptions and myths that can be misleading. It is crucial to separate fact from fiction to make informed choices about your beverage consumption.
The Difference Between Scientific Evidence and Anecdotal Claims
Anecdotal evidence, often based on personal experiences or hearsay, can be compelling but is not always reliable. While someone might claim that diet soda helped them lose weight, this does not necessarily mean it will have the same effect on everyone. Scientific evidence, on the other hand, is based on rigorous studies and controlled experiments. This type of evidence provides a more objective understanding of the potential effects of diet soda.
Common Misconceptions about Diet Soda
It is essential to distinguish between scientific evidence and anecdotal claims. Here are some common misconceptions about diet soda:
- Diet Soda Aids in Weight Loss: While diet soda contains zero calories, studies have shown mixed results regarding its impact on weight loss. Some studies suggest that diet soda may not be effective for weight management, and some even suggest it might be linked to weight gain. The body’s response to artificial sweeteners is complex, and more research is needed to fully understand their role in weight management.
- Diet Soda is a Healthy Alternative to Regular Soda: While diet soda does not contain sugar, it contains artificial sweeteners that can have their own potential health implications. Some studies have linked artificial sweeteners to gut health issues, metabolic changes, and even an increased risk of chronic diseases. It is important to consider the potential downsides of artificial sweeteners and to make informed choices about your beverage consumption.
- Diet Soda is Safe for Everyone: While diet soda is generally considered safe for most people, some individuals may experience adverse reactions to artificial sweeteners. Individuals with certain health conditions, such as diabetes or kidney disease, may need to limit their intake of diet soda. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate beverage choices for your specific needs.
The Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
When it comes to diet and beverage choices, personalized advice is crucial. Consulting a healthcare professional can help you make informed decisions based on your individual needs and health status. They can provide guidance on appropriate beverage choices, taking into account any underlying health conditions or dietary restrictions.
Ending Remarks
The allure of diet soda, a seemingly guilt-free indulgence, may be deceiving. While it may temporarily satisfy cravings, the potential health risks associated with its consumption warrant a closer look. By understanding the science behind diet soda, its impact on our bodies, and the abundance of healthier alternatives, we can make informed choices for our well-being. The journey to a healthier lifestyle starts with awareness, and choosing beverages that nourish rather than compromise our health is a crucial step in that direction.
Query Resolution
Is diet soda better than regular soda?
While diet soda contains fewer calories, its potential health risks may outweigh its perceived benefits. It’s essential to consider the long-term effects and explore healthier alternatives.
Can diet soda cause addiction?
Artificial sweeteners can stimulate cravings and potentially contribute to addictive behaviors, similar to sugar-sweetened beverages.
Are all artificial sweeteners harmful?
Research on the effects of different artificial sweeteners is ongoing. Some may be considered safer than others, but it’s generally recommended to limit consumption of all artificial sweeteners.
While diet soda might seem like a guilt-free indulgence, there’s growing concern about its potential health risks. Some studies suggest it may disrupt gut bacteria, leading to metabolic issues. But what about the keto diet? You might wonder, can you drink diet soda on keto ?
Regardless of your dietary choices, it’s important to be mindful of the potential downsides of artificial sweeteners and to consider healthier alternatives whenever possible.
While diet soda might seem like a harmless alternative, studies suggest it could actually increase the risk of certain health problems. It’s important to remember that even though it’s sugar-free, it’s still loaded with artificial sweeteners and other chemicals that our bodies aren’t always equipped to handle.
If you’re struggling with digestive issues like diverticulitis, you might want to check out this helpful resource on what diet with diverticulitis to see if there are any dietary changes you can make. Ultimately, when it comes to your health, it’s always best to prioritize whole, unprocessed foods and minimize your intake of artificial ingredients.
While diet soda might seem like a guilt-free option, research suggests it can actually be harmful to your health. If you’re looking for a healthier way to manage your weight, consider exploring some ideas for diet lunch. A balanced lunch with whole foods and protein will not only help you stay on track with your goals but also avoid the potential downsides of diet soda.