Guide to Dieting: Navigating the world of diets can feel overwhelming, with countless options promising quick fixes and drastic results. However, achieving lasting health and well-being requires a more nuanced approach. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of dieting, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health journey.
We will explore the fundamentals of dieting, delve into various popular approaches, and emphasize the importance of personalized plans. We will also discuss setting realistic goals, creating healthy eating plans, managing cravings, and staying motivated for long-term success. Ultimately, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge and tools to embark on a sustainable and fulfilling journey towards a healthier you.
Understanding Dieting
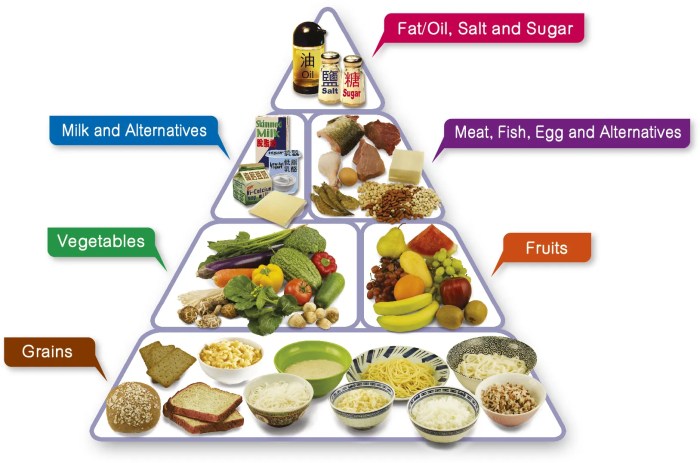
Dieting is a popular topic, often associated with weight loss, but it’s crucial to understand that dieting is more than just restricting calories. It’s about making conscious and informed choices about your food intake to achieve specific health goals. This guide will explore the fundamentals of dieting, different diet types, their potential benefits and risks, and the importance of individual needs and goals.
Fundamental Principles of Dieting
Dieting involves modifying your eating habits to achieve a specific goal. This might involve reducing calorie intake, increasing nutrient density, or altering the composition of your diet. The primary principle is to create a calorie deficit or surplus depending on your goal.
A calorie deficit is when you consume fewer calories than you burn, leading to weight loss. A calorie surplus is when you consume more calories than you burn, potentially leading to weight gain.
Dieting also emphasizes making sustainable lifestyle changes. Focusing on whole foods, regular physical activity, and mindful eating can contribute to long-term success.
Different Types of Diets, Guide to dieting
Various diets cater to different needs and preferences. Some popular examples include:
- Ketogenic Diet: This diet emphasizes high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate intake. The goal is to force the body to burn fat for energy instead of carbohydrates, leading to ketosis. This diet can be effective for weight loss but requires careful monitoring and might not be suitable for everyone.
- Mediterranean Diet: This diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and olive oil. It encourages moderate consumption of fish and poultry, while limiting red meat and processed foods. This diet is known for its heart-healthy benefits and has been linked to reduced risk of chronic diseases.
- Intermittent Fasting: This approach involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. Different methods exist, such as time-restricted feeding or alternate-day fasting. It focuses on regulating eating patterns rather than restricting specific foods. While it can be beneficial for weight management and metabolic health, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any fasting regimen.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Diets
Diets can offer various benefits, but it’s essential to be aware of their potential risks:
- Benefits: Weight loss, improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of chronic diseases, increased energy levels, and improved mental clarity.
- Risks: Nutrient deficiencies, digestive issues, fatigue, headaches, mood swings, and social isolation.
Importance of Individual Needs and Goals
Choosing a diet should be a personalized decision based on individual needs and goals. Factors to consider include:
- Health conditions: Certain diets might be unsuitable for individuals with specific health conditions. Consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
- Lifestyle: Consider your lifestyle and daily routine when selecting a diet. Choose a plan that fits your schedule and preferences.
- Personal goals: Whether your goal is weight loss, improved health, or simply a healthier lifestyle, choose a diet that aligns with your objectives.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is crucial for successful and sustainable weight loss or health improvement. When you set achievable goals, you are more likely to stick with your plan, experience positive results, and feel motivated to continue. This section will guide you through setting goals that are tailored to your individual needs and circumstances.
Understanding Personal Circumstances
Your personal circumstances play a vital role in determining realistic goals. Consider your current health status, lifestyle, and any existing health conditions. For example, if you have a busy work schedule, it might be challenging to commit to intense daily workouts. Acknowledging these factors allows you to set goals that are achievable and sustainable in your everyday life.
Creating a Healthy Eating Plan
A well-structured meal plan is the cornerstone of a successful diet. It provides a framework for making healthy choices, ensuring you get the nutrients your body needs while staying within your calorie goals.
Building a Balanced Meal Plan
A balanced meal plan consists of a variety of foods from all food groups in appropriate proportions. It ensures you receive essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for at least five servings per day. They are packed with vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, contributing to overall health and satiety.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains over refined grains whenever possible. Whole grains are a good source of fiber, which aids digestion and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Lean Protein: Include lean protein sources like poultry, fish, beans, lentils, and tofu in your meals. Protein helps build and repair tissues, keeps you feeling full, and supports healthy blood sugar levels.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporate healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats are essential for hormone production, brain function, and cell health.
- Dairy: Choose low-fat or fat-free dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese. Dairy provides calcium and vitamin D, crucial for bone health.
Healthy Recipe Examples
- Grilled Salmon with Roasted Vegetables: This meal is rich in protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins. Roast your favorite vegetables like broccoli, carrots, and bell peppers with olive oil, salt, and pepper. Grill salmon fillets with lemon juice and herbs. Serve with a side of quinoa or brown rice.
- Chicken Stir-Fry with Brown Rice: This is a quick and easy meal packed with lean protein and vegetables. Stir-fry chicken breast with chopped vegetables like broccoli, carrots, onions, and peppers. Add a low-sodium soy sauce and serve over brown rice.
- Lentil Soup with Whole Wheat Bread: This hearty soup is a great source of protein, fiber, and vitamins. Simmer lentils with chopped vegetables like carrots, celery, and onions. Add a flavorful broth and season with herbs and spices. Serve with a slice of whole wheat bread.
Portion Control and Mindful Eating
Portion control is crucial for managing calorie intake and achieving weight loss.
Mindful eating involves paying attention to your hunger and fullness cues, savoring your food, and eating slowly.
This practice helps prevent overeating and promotes a healthy relationship with food.
- Use smaller plates: This visual trick can help you feel satisfied with smaller portions.
- Read food labels: Pay attention to serving sizes and calorie counts.
- Eat slowly and savor your food: This allows your body time to register fullness.
- Avoid distractions: Don’t eat in front of the TV or while working. Focus on your meal and enjoy it.
Incorporating Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for overall health and weight management. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Find activities you enjoy: This will make it more likely you’ll stick with it.
- Start gradually: If you’re new to exercise, start with short sessions and gradually increase the duration and intensity.
- Make it a habit: Schedule exercise into your day, just like any other important appointment.
- Vary your routine: Keep your workouts interesting by trying different activities.
Managing Food Cravings and Emotional Eating
Food cravings and emotional eating are common experiences that can make it challenging to maintain a healthy diet. Understanding the triggers behind these behaviors is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage them.
Identifying Common Triggers
Understanding the factors that contribute to food cravings and emotional eating is essential for developing effective strategies to manage them.
- Boredom: When we are bored, we may seek stimulation, and food can provide a temporary distraction or sense of pleasure.
- Stress: Stress can trigger the release of hormones that increase appetite and cravings for comfort foods.
- Emotions: Emotional states like sadness, anxiety, or loneliness can lead to emotional eating, where we use food to cope with difficult feelings.
- Social cues: Seeing or smelling food, or being around others who are eating, can trigger cravings.
- Hormonal fluctuations: Hormonal changes, particularly during menstruation or pregnancy, can impact appetite and cravings.
- Sleep deprivation: Lack of sleep can disrupt hormone levels that regulate appetite, leading to increased cravings.
Strategies for Managing Cravings
Once you’ve identified your triggers, you can develop strategies to manage cravings and prevent emotional eating.
- Distraction: Engage in activities you enjoy, such as reading, exercising, or spending time with loved ones, to redirect your attention away from food.
- Delay: Wait for 15-20 minutes before giving in to a craving. Often, the urge will pass.
- Mindful eating: Pay attention to your hunger and fullness cues. Eat slowly and savor each bite.
- Healthy alternatives: When you crave unhealthy foods, opt for healthier alternatives that satisfy your cravings without compromising your diet.
- Hydration: Sometimes, thirst is mistaken for hunger. Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Regular meals: Eating regular, balanced meals can help prevent extreme hunger and cravings.
- Identify your emotional triggers: Journaling can help you understand the emotions that lead to emotional eating.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Find alternative ways to manage stress and emotions, such as exercise, meditation, or talking to a therapist.
Reducing Stress and Promoting Emotional Well-being
Stress and emotional distress can significantly impact eating habits.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects and can reduce stress.
- Meditation and mindfulness: These practices can help calm the mind and reduce stress levels.
- Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Social connections: Strong social relationships provide support and can reduce stress.
- Hobbies: Engaging in enjoyable activities can help you relax and de-stress.
Mindfulness and Self-Compassion
Mindfulness and self-compassion play a crucial role in managing eating habits.
- Mindfulness: Pay attention to your thoughts, feelings, and sensations without judgment. This can help you identify and manage cravings.
- Self-compassion: Treat yourself with kindness and understanding, especially when you make mistakes. Avoid self-criticism.
Maintaining Motivation and Long-Term Success
Dieting is a marathon, not a sprint. Maintaining motivation and achieving long-term success requires a strategic approach that focuses on building sustainable habits and fostering a positive mindset.
Building a Support System and Finding Accountability Partners
Having a strong support system is crucial for staying motivated and accountable. Surround yourself with people who understand your goals and encourage you along the way. This could include friends, family, or even a support group.
- Share your goals: Let your support system know about your dieting journey and what you hope to achieve. This helps them understand your struggles and offer encouragement.
- Find an accountability partner: Partnering with someone who shares similar goals can provide motivation and support. You can check in with each other regularly, share progress, and hold each other accountable.
- Join a support group: Online forums or in-person support groups offer a sense of community and shared experiences. Connecting with others who are going through similar challenges can provide valuable insights and encouragement.
Staying Motivated and Overcoming Setbacks
Maintaining motivation over the long term can be challenging. There will be days when you feel discouraged or tempted to give up. It’s important to have strategies in place to overcome these setbacks.
- Focus on non-scale victories: Don’t solely rely on the scale for motivation. Celebrate smaller achievements, such as increased energy levels, improved sleep, or fitting into clothes that were previously too tight.
- Practice self-compassion: Be kind to yourself when you make mistakes or experience setbacks. Everyone makes mistakes, and it’s important to learn from them and move forward.
- Reward yourself: Set up a reward system for reaching milestones. This could include a non-food reward, such as a new workout outfit or a massage.
Tracking Progress and Celebrating Achievements
Tracking your progress is a powerful tool for staying motivated. It allows you to see how far you’ve come and identify areas where you can improve.
- Keep a food journal: Recording what you eat can help you identify patterns and make adjustments to your diet.
- Measure your progress: Track your weight, body measurements, and other relevant metrics to see how your body is changing.
- Celebrate your successes: Acknowledge your accomplishments, big or small. This will help you stay motivated and reinforce positive behaviors.
Motivational Checklist
Here’s a motivational checklist to help you stay on track:
- Set realistic goals: Aim for gradual, sustainable changes.
- Find a support system: Surround yourself with people who encourage you.
- Track your progress: Monitor your weight, body measurements, and food intake.
- Celebrate your achievements: Acknowledge your successes, no matter how small.
- Stay positive: Focus on the benefits of your healthy lifestyle.
- Be patient: Remember that lasting change takes time.
Consulting Professionals: Guide To Dieting
Embarking on a diet journey can be overwhelming, and seeking guidance from qualified professionals can significantly enhance your chances of success. Consulting with experts like registered dietitians and doctors provides personalized support, evidence-based information, and a comprehensive approach to achieving your health goals.
Finding a Reputable Professional
Finding a reputable and experienced professional is crucial for receiving accurate and effective guidance. Consider the following tips:
- Look for credentials: Ensure the professional holds the appropriate certifications and licenses. For instance, registered dietitians (RDs) are qualified to provide nutrition counseling, while doctors (MDs) can address underlying health conditions that may influence your diet.
- Check experience and specialization: Explore the professional’s experience in working with individuals with similar dietary goals and health conditions as yours. Some dietitians specialize in specific areas, such as weight management, sports nutrition, or diabetes management.
- Read reviews and testimonials: Look for feedback from previous clients to gain insights into the professional’s approach, communication style, and effectiveness.
- Schedule a consultation: A brief consultation allows you to assess the professional’s communication style, approach, and whether you feel comfortable working with them.
Role of Professionals in Diet Planning
Professionals play a vital role in creating personalized diet plans and monitoring your progress:
- Assessment and Goal Setting: Professionals conduct a thorough assessment of your health history, dietary habits, and goals. They work with you to set realistic and achievable targets based on your individual needs and preferences.
- Personalized Diet Plan: Based on the assessment, professionals develop a tailored diet plan that aligns with your goals, health conditions, and lifestyle. They provide guidance on portion sizes, food choices, and meal frequency.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular follow-up appointments allow professionals to monitor your progress, address any challenges, and make adjustments to your plan as needed. They provide ongoing support and motivation to help you stay on track.
Resources for Finding Health and Nutrition Professionals
Several resources can help you find qualified health and nutrition professionals:
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (AND): The AND website offers a directory of registered dietitians in your area. You can search by specialty, location, and other criteria.
- American Medical Association (AMA): The AMA website provides a directory of doctors in your area, allowing you to search by specialty, insurance coverage, and other factors.
- Local hospitals and clinics: Many hospitals and clinics have nutrition departments or offer services from registered dietitians.
- Your primary care physician: Your doctor can recommend qualified dietitians or other health professionals who can support your dietary goals.
Conclusion
Dieting doesn’t have to be a restrictive or daunting experience. By understanding the principles, setting realistic goals, and creating a personalized plan, you can embark on a journey toward healthier habits and improved well-being. Remember to prioritize your individual needs, consult professionals when necessary, and celebrate your progress along the way. This guide is your roadmap to navigating the world of dieting with confidence and achieving sustainable results.
User Queries
What are some common diet myths?
Many diet myths perpetuate unrealistic expectations and unhealthy practices. For example, the idea that “fat is bad” is outdated and ignores the essential role of healthy fats in our diet. Additionally, fad diets that promise rapid weight loss often lack scientific evidence and can be unsustainable in the long run.
How can I prevent weight regain after dieting?
Weight regain is a common challenge after dieting. To prevent this, focus on making sustainable lifestyle changes rather than short-term restrictions. This includes incorporating healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and managing stress levels.
What are some healthy snack options?
Healthy snack options should be nutrient-rich and satisfying. Consider fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, yogurt, or hard-boiled eggs. Avoid processed snacks that are high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and calories.
A guide to dieting can be overwhelming, with so many different approaches and opinions. One thing to consider is the impact of your beverage choices. Some research suggests a possible link between artificial sweeteners and kidney stones, so it’s worth looking into the evidence.
You can learn more about this potential connection by visiting can diet soda cause kidney stones. Ultimately, making informed choices about your diet and hydration is crucial for overall health and well-being.
A guide to dieting often emphasizes nutrient intake, and magnesium plays a crucial role in many bodily functions. If you’re looking to boost your magnesium levels, check out this helpful resource on how to add magnesium to diet. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet can support energy production, muscle function, and even sleep quality, all of which can contribute to a successful and sustainable weight management plan.
A guide to dieting can be overwhelming, with so many different approaches and plans to choose from. It’s helpful to understand the current trends and see what popular diets are out there. You can find a comprehensive list of popular diets right now , which can help you decide which approach might be best for your individual needs and goals.
























