How do keto diet work – How do keto diets work? It’s a question that has captured the attention of health enthusiasts and dieters alike. This low-carb, high-fat approach promises to revolutionize your metabolism, leading to weight loss, improved energy, and even enhanced cognitive function. But how does it actually work?
The answer lies in a fascinating metabolic shift called ketosis, where your body learns to burn fat for fuel instead of relying on carbohydrates.
Imagine your body as a powerful engine, capable of running on different types of fuel. Typically, it relies on carbohydrates for energy. However, the ketogenic diet forces your body to switch gears, transforming fat into ketones, which then become the primary energy source.
This process can lead to a remarkable transformation, with potential benefits ranging from weight loss to improved brain function.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the “keto diet,” has gained significant popularity in recent years as a weight-loss strategy and for its potential health benefits. But what exactly is it, and how does it work?
The Core Principles of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet revolves around a fundamental shift in how your body uses fuel. Instead of relying primarily on glucose (sugar) from carbohydrates, it forces your body to burn fat for energy. This process, known as ketosis, is achieved by drastically reducing carbohydrate intake while increasing the consumption of healthy fats.
Macronutrient Ratios in a Keto Diet
The hallmark of a ketogenic diet lies in its strict macronutrient ratios. Typically, a keto diet consists of:
- High Fat:60-80% of your daily calories should come from healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish.
- Moderate Protein:Protein intake should be moderate, accounting for 15-25% of your daily calories. This ensures adequate protein for muscle maintenance and repair.
- Very Low Carbohydrates:Carbohydrates are severely restricted, making up only 5-10% of your daily calorie intake. This limitation forces your body to switch its primary energy source from glucose to ketones.
History and Origins of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet has a fascinating history, dating back to the early 20th century. It was initially developed as a treatment for epilepsy in children, as it was observed to significantly reduce seizure frequency. While its use for epilepsy has persisted, the ketogenic diet has since been explored for a range of other health benefits, including weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and reduced inflammation.
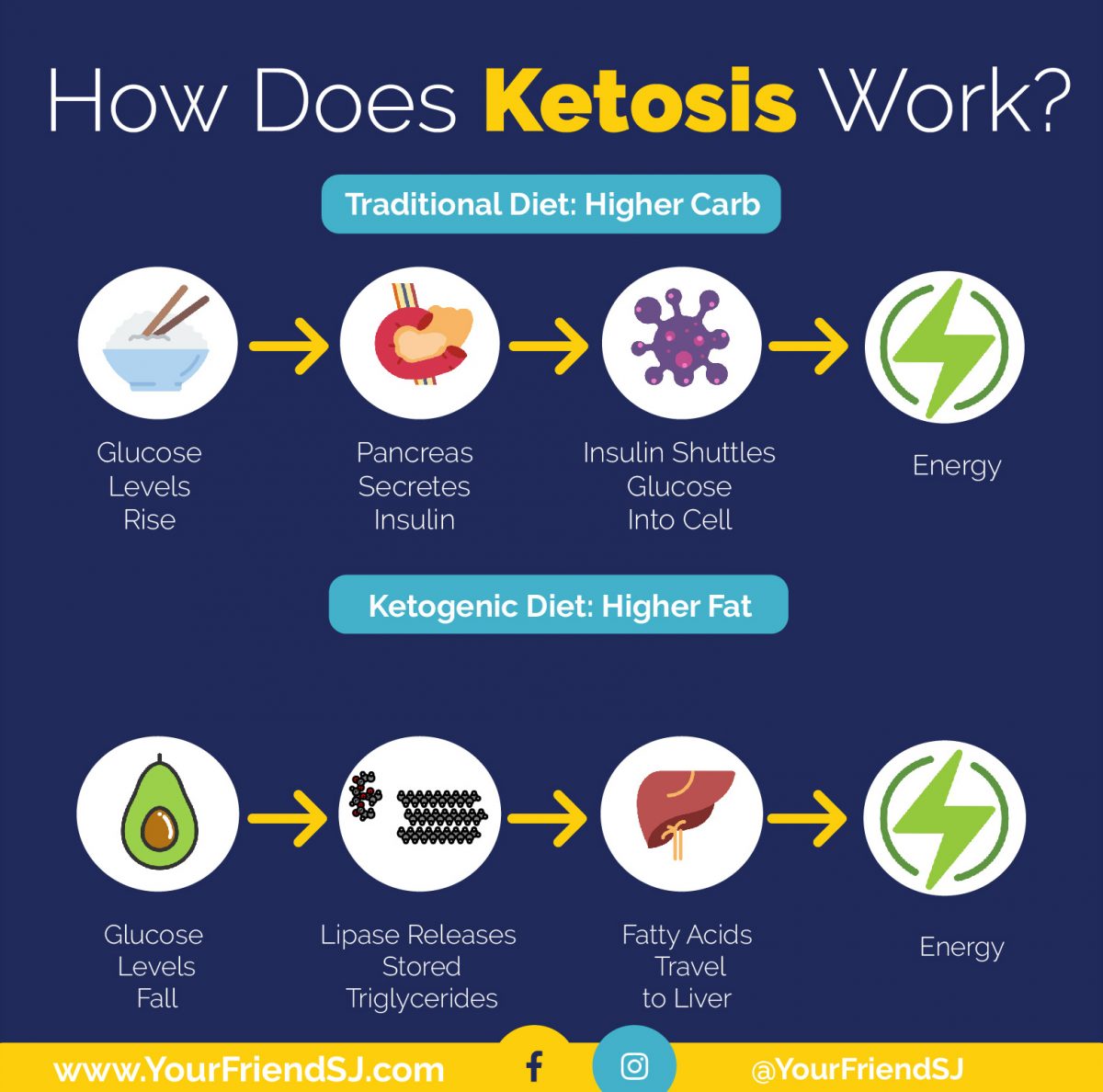
How Ketosis Works
Imagine your body as a fancy car with two fuel tanks: one for regular gasoline (glucose) and one for high-octane racing fuel (ketones). The ketogenic diet is like switching your car to run on that high-octane fuel, which is made from fat.
The Process of Ketosis
When you drastically reduce your carbohydrate intake, your body enters a state of ketosis. This happens because your body is no longer getting its primary energy source from glucose, which is typically broken down from carbohydrates. To compensate, your liver starts converting fat into ketones.
These ketones are then released into your bloodstream and used as an alternative energy source by your brain, muscles, and other organs.
The Role of Ketones in Energy Production
Ketones are like tiny, efficient energy packets. They are a more stable and efficient fuel source than glucose, especially for your brain. They provide a steady supply of energy, which can be beneficial for mental clarity and focus.
Comparison of Glucose and Ketone Metabolism
- Glucose Metabolism:When you eat carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose. This glucose is then transported to your cells and used as energy. This process is called glycolysis.
- Ketone Metabolism:When you are in ketosis, your body uses fat as its primary energy source. This fat is converted into ketones by your liver. These ketones are then transported to your cells and used as energy. This process is called ketogenesis.
Think of it this way: glucose is like a quick burst of energy, but it can lead to sugar crashes. Ketones are like a long-lasting, steady stream of energy that keeps you going throughout the day.
Foods to Include and Avoid
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as keto, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that forces your body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis. Ketosis is a natural process where your body starts burning fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
To achieve this, you need to make strategic choices about the foods you include and exclude from your diet.
The keto diet is all about tricking your body into burning fat for fuel instead of carbs. It’s like telling your metabolism, “Hey, buddy, we’re out of sugar, so let’s start burning that extra belly fat!” And guess what? This fat-burning fiesta can actually help lower your cholesterol levels, too.
If you’re interested in learning more about how to lower your cholesterol with diet, check out this helpful guide: how to low the cholesterol with diet. So, basically, the keto diet is like a double whammy for your health – it helps you lose weight AND improves your cholesterol! Who knew fat could be so fabulous?
Foods to Include
Foods to include on a keto diet are those that are low in carbohydrates and high in fat. These foods help you stay in ketosis and provide essential nutrients for your body.
- Healthy Fats:Olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil, butter, ghee, and fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna. These fats are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial for brain health and heart health.
- Meat and Poultry:Beef, chicken, turkey, lamb, and pork. Choose lean cuts whenever possible to minimize saturated fat intake.
- Eggs:Eggs are a versatile and nutritious source of protein, healthy fats, and vitamins.
- Dairy:Full-fat cheese, yogurt, and cream. Opt for full-fat dairy products as they contain more fat and fewer carbohydrates.
- Non-Starchy Vegetables:Broccoli, cauliflower, spinach, kale, Brussels sprouts, asparagus, and zucchini. These vegetables are low in carbohydrates and rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Nuts and Seeds:Almonds, walnuts, pecans, chia seeds, and flaxseeds. These are excellent sources of healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Berries:Strawberries, raspberries, and blueberries. While these berries contain some carbohydrates, they are low in net carbs and high in antioxidants.
Foods to Avoid
The keto diet emphasizes avoiding foods high in carbohydrates, as they can hinder your body’s ability to enter ketosis.
- Sugary Foods and Drinks:Soda, candy, cakes, pastries, and processed foods containing added sugar. These foods are loaded with carbohydrates and can quickly spike your blood sugar levels.
- Grains:Bread, pasta, rice, cereals, and other grain-based products. These foods are high in carbohydrates and can disrupt your ketosis.
- Starchy Vegetables:Potatoes, corn, peas, and parsnips. These vegetables are high in carbohydrates and should be limited or avoided.
- Legumes:Beans, lentils, and chickpeas. Legumes are high in carbohydrates and can also cause digestive issues for some people.
- Fruit:Most fruits, including bananas, oranges, apples, and grapes. While some berries are allowed in moderation, most fruits are high in carbohydrates and should be avoided on a keto diet.
- Alcohol:Alcohol can hinder ketosis and should be consumed in moderation or avoided altogether.
Keto-Friendly Recipes and Meal Plans
- Breakfast:Keto omelets with cheese and spinach, avocado toast with smoked salmon, keto pancakes made with almond flour, and chia pudding with berries.
- Lunch:Keto salads with grilled chicken or fish, avocado and bacon wraps, cauliflower rice bowls with meat and vegetables, and keto soup.
- Dinner:Keto lasagna made with zucchini noodles, keto chili, salmon with roasted vegetables, and chicken stir-fry with cauliflower rice.
- Snacks:Keto cheese balls, almond butter and celery sticks, hard-boiled eggs, and keto-friendly nuts and seeds.
Nutritional Benefits and Potential Deficiencies
The keto diet can provide several nutritional benefits, including:
- Weight Loss:The keto diet can help you lose weight by reducing your carbohydrate intake and increasing your fat intake, leading to a calorie deficit.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control:By reducing carbohydrate intake, the keto diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, making it beneficial for people with type 2 diabetes.
- Increased Energy Levels:While some people may experience initial fatigue during the transition to ketosis, many report increased energy levels and improved mental clarity once adapted.
- Reduced Inflammation:The keto diet can help reduce inflammation in the body, which may be beneficial for conditions like arthritis and heart disease.
However, the keto diet also has potential deficiencies:
- Nutrient Deficiencies:The restrictive nature of the keto diet can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It is crucial to ensure adequate intake of these nutrients through supplements or carefully planned meals.
- Digestive Issues:Some people may experience digestive issues like constipation, diarrhea, or bloating during the initial phase of the keto diet. These symptoms usually subside as your body adjusts to the diet.
- Kidney Stones:The high intake of protein and fat in the keto diet can increase the risk of kidney stones in some individuals. It is essential to stay hydrated and consult with a healthcare professional if you have a history of kidney stones.
- Long-Term Sustainability:The keto diet can be challenging to maintain long-term due to its restrictive nature and the potential for nutrient deficiencies. It is essential to work with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to create a sustainable plan that meets your individual needs.
The keto diet, for those who haven’t heard, is like a culinary game of tag where your body chases after fat for energy instead of carbs. But if you’ve got PCOS, you might want to check out the best diet with pcos for a more personalized approach.
After all, even keto needs a little help sometimes, especially when it comes to hormonal harmony. So, while the keto diet can be a great tool for weight loss, understanding your individual needs is key, and that’s where a specialized diet can really shine.
Potential Benefits and Risks: How Do Keto Diet Work
The ketogenic diet, while gaining popularity for its weight-loss potential, is not without its pros and cons. Understanding the potential benefits and risks is crucial before embarking on this dietary journey.
Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet’s primary mechanism for weight loss is its ability to induce ketosis, a metabolic state where the body primarily utilizes fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This can lead to several potential benefits.
- Weight Loss:Studies have shown that the ketogenic diet can lead to significant weight loss compared to traditional calorie-restricted diets. This is attributed to its appetite-suppressing effects and increased fat burning.
- Improved Metabolic Health:The ketogenic diet has been associated with improvements in blood sugar control, insulin sensitivity, and cholesterol levels. This can benefit individuals with type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
- Cognitive Function:Some research suggests that the ketogenic diet might improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease. This is based on the brain’s ability to utilize ketones as an alternative energy source.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While the ketogenic diet offers potential benefits, it’s essential to be aware of its potential risks and side effects.
- Keto Flu:This is a common side effect during the initial transition to a ketogenic diet. Symptoms include fatigue, headache, nausea, and constipation. These symptoms usually subside within a few days as the body adapts to using ketones for energy.
- Nutrient Deficiencies:Restricting certain food groups can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This can be mitigated by carefully planning meals and supplementing when necessary.
- Long-Term Health Implications:The long-term health implications of the ketogenic diet are still under investigation. Some studies suggest potential risks, including kidney stones, bone loss, and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. However, more research is needed to fully understand these risks.
Adapting the Keto Diet
The ketogenic diet, while effective for weight loss and other health benefits, requires careful consideration when adapting it for individuals with specific health conditions. The diet’s impact on blood sugar levels, for instance, can be significant, necessitating adjustments for people with diabetes.
Adapting the Keto Diet for Diabetes
Individuals with diabetes need to carefully manage their blood sugar levels. The ketogenic diet can impact these levels due to its low carbohydrate content, potentially leading to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Therefore, close monitoring and adjustments are crucial.
The keto diet, in a nutshell, is like a stubborn toddler who only wants to eat butter and cheese. It forces your body to burn fat for fuel, which can lead to weight loss, but let’s be honest, it’s not for the faint of heart.
If you’re looking for a more balanced approach to weight loss, you might want to check out some other options like the best diet for weight loss. Just remember, even with the keto diet, you’ll still need to eat enough calories to keep your body from thinking it’s being starved and holding onto every ounce of fat like a precious treasure.
- Consulting a Healthcare Professional:It is paramount to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an endocrinologist or registered dietitian, before embarking on the ketogenic diet if you have diabetes. They can help create a personalized plan that aligns with your individual needs and medications.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels:Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential to ensure your levels remain within a safe range. Frequent checks, especially during the initial adaptation period, are recommended.
- Adjusting Insulin Dosage:Individuals on insulin therapy may need to adjust their dosage based on their blood sugar readings. This adjustment should be done in close collaboration with their healthcare provider.
- Slow and Gradual Transition:Transitioning to a ketogenic diet should be gradual to minimize the risk of adverse effects. Introducing keto-friendly foods slowly and monitoring blood sugar levels throughout the process is recommended.
Adapting the Keto Diet for Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet has been used for decades as a treatment for epilepsy, particularly in children. It is believed that the diet’s high-fat, low-carbohydrate content alters brain metabolism, reducing seizures.
- Strict Adherence:The ketogenic diet for epilepsy requires strict adherence to the prescribed macro ratios. Deviation from the plan can negatively impact seizure control.
- Monitoring and Adjustments:Close monitoring of seizure frequency and blood sugar levels is essential. Adjustments to the diet, including the addition of specific foods or supplements, may be necessary based on individual responses.
- Collaboration with a Healthcare Team:Working with a healthcare team, including a neurologist, dietitian, and possibly a pharmacist, is crucial to ensure proper implementation and management of the diet.
Personalized Nutrition Plans
The ketogenic diet is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Individual needs, health conditions, and lifestyle factors should be considered when designing a personalized nutrition plan.
- Dietary Preferences:A successful ketogenic diet incorporates foods that align with your preferences and lifestyle.
- Health Goals:Whether your goal is weight loss, improved blood sugar control, or seizure management, your personalized plan should cater to these objectives.
- Caloric Needs:The ketogenic diet should meet your individual caloric needs to support your overall health and well-being.
The Role of a Healthcare Professional
A healthcare professional plays a vital role in guiding individuals through the ketogenic diet, especially those with health conditions.
- Personalized Guidance:They can provide personalized recommendations based on your health status, medications, and lifestyle.
- Monitoring and Adjustments:They can monitor your progress, make necessary adjustments to the diet, and address any potential side effects.
- Safety and Efficacy:They can ensure the safety and efficacy of the ketogenic diet for your specific situation.
Exercise and Physical Activity on the Keto Diet
Exercise is an essential part of a healthy lifestyle, and it can be incorporated into a ketogenic diet.
- Impact on Ketone Production:Exercise can increase ketone production, providing an additional source of energy for your body.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity:Regular physical activity can enhance insulin sensitivity, potentially improving blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes.
- Weight Management:Exercise plays a crucial role in weight management, complementing the calorie restriction aspect of the ketogenic diet.
The Ketogenic Diet and Long-Term Sustainability
The ketogenic diet, with its focus on fat and minimal carbohydrates, has gained immense popularity for its potential weight loss benefits. But can this restrictive approach to eating be maintained long-term, and what are the potential consequences for both physical and mental well-being?
Maintaining a Keto Lifestyle
Sustaining a ketogenic diet over the long term requires a mindful approach and a deep understanding of the lifestyle changes involved. Here are some practical tips for maintaining a keto lifestyle and avoiding dietary burnout:
- Focus on Whole Foods:Prioritize nutrient-rich foods like leafy greens, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats. These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are crucial for overall health and well-being.
- Plan Your Meals:Planning meals ahead of time can help you avoid impulsive choices and ensure you have access to keto-friendly options. This also helps in staying organized and preventing cravings.
- Experiment with Recipes:Explore a variety of keto-friendly recipes to prevent monotony and keep your meals interesting. There are countless resources available online and in cookbooks that offer delicious and satisfying keto-friendly dishes.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Cheat Occasionally:Strict adherence to the keto diet can be challenging, and occasional indulgences can help prevent feelings of deprivation and make the lifestyle more sustainable. Just be sure to choose your cheat meals wisely and keep them in moderation.
- Seek Support:Connect with others who follow a ketogenic diet, either online or in person. Sharing experiences, tips, and recipes can provide valuable support and motivation.
The Keto Diet and Mental Well-being, How do keto diet work
While the ketogenic diet can be effective for weight management, it’s essential to consider its potential impact on mental well-being. The restrictive nature of the diet can lead to:
- Nutrient Deficiencies:The keto diet’s focus on fat can limit the intake of essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This can potentially lead to fatigue, mood swings, and impaired cognitive function.
- Social Challenges:Eating out and attending social gatherings can be difficult when following a keto diet. This can lead to feelings of isolation and social exclusion, which can negatively impact mental health.
- Cognitive Changes:The initial “keto flu” phase can cause brain fog, headaches, and fatigue, which can impact mood and cognitive function. While these symptoms usually subside within a week, some individuals may experience persistent cognitive changes.
- Dietary Burnout:Strict adherence to a restrictive diet can lead to feelings of deprivation and exhaustion. This can result in disordered eating patterns and a negative relationship with food.
Long-Term Sustainability: The Verdict
While the ketogenic diet can be effective for short-term weight loss, its long-term sustainability is debatable. The restrictive nature of the diet can lead to nutrient deficiencies, social challenges, and potential negative impacts on mental well-being. It’s crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks and to adopt a balanced approach that prioritizes overall health and well-being.
Last Point
Embarking on a keto journey is a fascinating adventure into the world of metabolic adaptation. By understanding the science behind it and embracing a balanced approach, you can harness the power of ketosis to achieve your health and wellness goals.
Remember, it’s not just about restricting carbohydrates; it’s about embracing a lifestyle that fuels your body with the right nutrients and empowers you to thrive. So, are you ready to unlock the secrets of fat-burning success? The journey begins with a single, delicious keto meal!
Q&A
Is the keto diet safe for everyone?
While the keto diet can be beneficial for many, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
How long does it take to enter ketosis?
It typically takes 2-7 days to enter ketosis, depending on individual factors like metabolism and dietary habits.
What are the common side effects of the keto diet?
Some common side effects include keto flu, headaches, fatigue, and constipation. These usually subside within a few days as your body adapts.
Can I exercise while on a keto diet?
Yes, exercise is encouraged on the keto diet. However, it’s important to listen to your body and adjust your workout intensity as needed.