How long do foods last in the freezer? This question arises frequently, especially when seeking to extend the shelf life of perishable items. Freezing food is a popular method of preservation, allowing us to enjoy fresh ingredients long after their peak season. Freezing not only helps reduce food waste but also provides convenience and access to a variety of culinary options.
The longevity of frozen food depends on several factors, including the type of food, proper packaging, and consistent freezer temperature. Understanding the nuances of freezing and thawing ensures that your frozen treasures remain safe, palatable, and nutritious.
Food Preservation: The Art of Freezing
Food preservation is a vital practice that has been around for centuries, allowing us to enjoy fresh foods beyond their natural shelf life. Freezing is a popular and effective method of food preservation that involves lowering the temperature of food to inhibit the growth of bacteria and slow down enzymatic reactions, thereby extending its lifespan.
Freezing offers several benefits, including:
Benefits of Freezing Food
Freezing is a valuable tool for preserving food, offering several advantages:
- Extended Shelf Life: Freezing significantly extends the shelf life of various foods, allowing you to enjoy them for weeks, months, or even years. This is especially helpful for seasonal fruits and vegetables, reducing food waste.
- Nutritional Preservation: Freezing helps retain essential nutrients in food, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. While some nutrient loss may occur, freezing preserves a significant portion compared to other preservation methods.
- Convenience and Flexibility: Freezing allows you to prepare meals in advance, saving time and effort on busy days. You can freeze individual portions for quick and easy meals or freeze entire dishes for later enjoyment.
- Cost Savings: Freezing allows you to buy food in bulk when it’s on sale, reducing your grocery bills. You can also freeze leftovers to prevent waste and save money.
Factors Influencing Food Longevity in the Freezer
Several factors influence how long food can be safely stored in the freezer:
- Type of Food: Different foods have varying freezing times and storage durations. For example, fruits and vegetables generally have shorter freezer lifespans than meat or poultry.
- Freezing Method: Proper freezing techniques, such as blanching vegetables before freezing, can significantly extend their shelf life.
- Packaging: Using airtight containers or freezer-safe bags helps prevent freezer burn, which can affect the quality and taste of food.
- Freezer Temperature: Maintaining a consistent freezer temperature of 0°F (-18°C) or below is crucial for optimal food preservation.
General Freezer Storage Guidelines
Freezing is an effective method of preserving food for extended periods. To maximize the quality and safety of frozen food, it is essential to follow proper storage guidelines.
Packaging and Labeling
Proper packaging plays a crucial role in preventing freezer burn, which is a condition that occurs when frozen food is exposed to air and moisture. It also helps to maintain the flavor and texture of the food.
- Use freezer-safe containers or bags. These are designed to withstand the cold temperatures and prevent leaks or spills. Choose containers that are airtight and moisture-proof.
- Leave some space at the top of the container or bag to allow for expansion. Frozen food expands as it freezes, so leaving some space prevents the container from bursting or leaking.
- Wrap food tightly in freezer-safe plastic wrap or aluminum foil. This helps to create a barrier against air and moisture.
- Label all packages with the name of the food and the date it was frozen. This will help you keep track of the food’s freshness and prevent waste.
Freezing Temperatures, How long do foods last in the freezer
Freezing temperatures are crucial for slowing down the growth of bacteria and preserving the quality of food.
The recommended freezing temperature for optimal preservation is 0°F (-18°C).
Maintaining this temperature ensures that food stays frozen solid and prevents the formation of ice crystals, which can damage the food’s texture and flavor.
Freezing vs. Deep Freezing
Freezing and deep freezing are both methods of preserving food by lowering its temperature. However, they differ in the rate of freezing and the temperature achieved.
- Freezing refers to the process of lowering the temperature of food to 32°F (0°C) or below. This slows down the growth of bacteria and extends the shelf life of food.
- Deep freezing refers to the process of lowering the temperature of food to 0°F (-18°C) or below. This is the ideal temperature for long-term food preservation and ensures that food stays frozen solid.
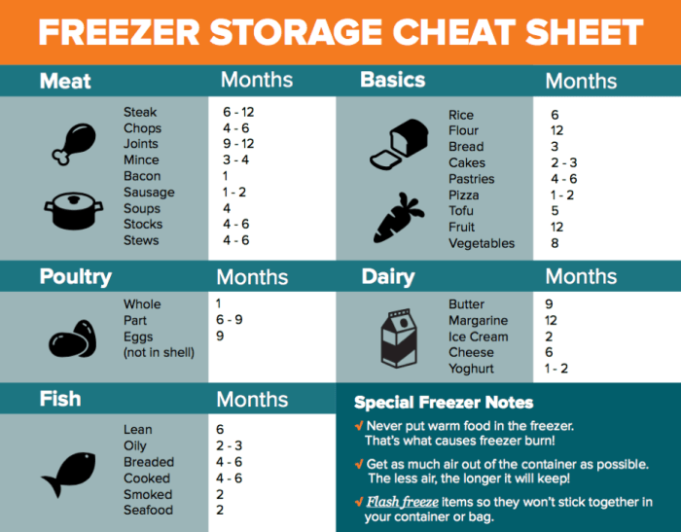
Food Categories and Their Freezer Lifespans
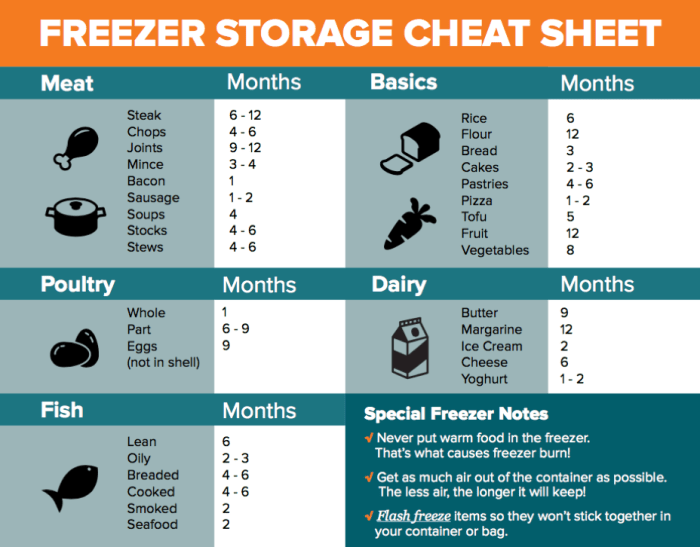
Freezing is a remarkable method for extending the shelf life of various foods. By lowering the temperature, we effectively slow down the growth of bacteria and enzymes, preventing spoilage and preserving the quality of our food. However, it’s important to remember that not all foods freeze equally well, and different categories have varying freezer lifespans.
Freezer Storage Timelines for Different Food Categories
The following table provides a general overview of recommended freezer storage times for various food categories. It’s crucial to note that these are just guidelines, and actual storage times may vary depending on factors such as the quality of the food, packaging methods, and freezer temperature.
| Food Category | Recommended Freezer Storage Time | Tips for Optimal Freezing | Signs of Spoilage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fruits | 8-12 months |
|
|
| Vegetables | 8-12 months |
|
|
| Meat | 4-12 months |
|
|
| Poultry | 9-12 months |
|
|
| Seafood | 3-6 months |
|
|
| Breads | 2-3 months |
|
|
| Dairy Products | 2-3 months |
|
|
| Cooked Meals | 2-3 months |
|
|
Freezing Techniques and Tips
Freezing is a valuable technique for preserving the freshness and nutritional value of food, extending its shelf life, and making meal preparation more efficient. However, proper freezing techniques are crucial to ensure that the quality of the food is maintained and that it is safe to eat.
Blanching Vegetables Before Freezing
Blanching is a crucial step in preparing vegetables for freezing. It involves briefly immersing vegetables in boiling water, followed by a quick plunge into ice water. This process helps to stop enzyme activity that causes deterioration in flavor, color, and texture during freezing. Blanching also helps to shrink the vegetables, making them easier to package and reducing the risk of freezer burn.
- Choose fresh, high-quality vegetables: Start with vegetables that are free of blemishes and signs of spoilage.
- Wash and trim the vegetables: Remove any dirt or debris, and trim off any damaged or unwanted parts.
- Prepare the vegetables: Cut vegetables into appropriate sizes for freezing, such as small pieces or slices.
- Blanch the vegetables: Bring a large pot of water to a rolling boil. Add the vegetables to the boiling water and blanch for the recommended time, which varies depending on the type of vegetable. Consult a reliable source for blanching times.
- Shock the vegetables: Immediately transfer the blanched vegetables to a bowl of ice water to stop the cooking process.
- Drain and dry the vegetables: Remove the vegetables from the ice water and drain them thoroughly. Pat them dry with paper towels to remove excess moisture.
- Package the vegetables: Place the blanched vegetables in freezer-safe bags or containers, leaving some headspace for expansion during freezing.
- Label and date the packages: Label the packages with the name of the vegetable and the date of freezing.
Vacuum Sealing Meat and Seafood
Vacuum sealing is a highly effective technique for preserving the freshness and quality of meat and seafood. It involves removing air from the packaging, creating an airtight seal that prevents freezer burn and oxidation. Vacuum sealing also helps to extend the shelf life of meat and seafood significantly.
- Use a vacuum sealer: Invest in a good quality vacuum sealer for optimal results.
- Prepare the meat or seafood: Trim any excess fat or connective tissue, and cut the meat or seafood into portions as needed.
- Place the meat or seafood in vacuum-seal bags: Choose bags specifically designed for vacuum sealing.
- Seal the bags: Place the bags in the vacuum sealer and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for sealing.
- Label and date the packages: Label the packages with the name of the meat or seafood and the date of freezing.
Freezing Sauces, Soups, and Stews
Freezing sauces, soups, and stews is a convenient way to preserve these dishes for later use. However, it’s important to consider a few key points to ensure that the texture and flavor remain consistent after freezing.
- Cool the sauces, soups, and stews completely: Before freezing, allow the dishes to cool to room temperature. This helps to prevent ice crystals from forming and affecting the texture.
- Use freezer-safe containers: Choose containers that are specifically designed for freezing, as they are less likely to crack or break.
- Leave some headspace: Leave about an inch of headspace at the top of the container to allow for expansion during freezing.
- Label and date the containers: Label the containers with the name of the dish and the date of freezing.
Thawing and Reheating Frozen Foods
Thawing frozen foods is a crucial step in ensuring food safety and quality. Improper thawing can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria, potentially causing foodborne illness. This section will discuss safe thawing methods, emphasize the importance of complete thawing, and provide guidance on reheating frozen foods effectively.
Safe Thawing Methods
Thawing frozen foods safely is essential to prevent bacterial growth. The three primary methods for thawing frozen foods are refrigerator thawing, cold water thawing, and microwave thawing. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the best method depends on the type of food and the time available.
- Refrigerator Thawing: This is the safest and most recommended method for thawing most frozen foods. It involves transferring the frozen food from the freezer to the refrigerator, where it gradually thaws at a safe temperature. Refrigerator thawing typically takes several hours or even overnight, depending on the size and type of food. This method is particularly suitable for large cuts of meat, poultry, and seafood. Refrigerator thawing ensures that the food thaws slowly and evenly, minimizing the risk of bacterial growth.
- Cold Water Thawing: This method involves placing the frozen food in a sealed container or bag submerged in cold water. The water should be changed every 30 minutes to ensure it remains cold. Cold water thawing is faster than refrigerator thawing but still ensures safe thawing. It is particularly suitable for smaller items like individual portions of meat or poultry, as well as frozen vegetables. However, it is essential to ensure the food remains submerged in cold water and is not left at room temperature for extended periods.
- Microwave Thawing: Microwave thawing is the fastest method but is not recommended for all foods. It is best suited for smaller portions of food, such as individual servings of vegetables or meat. When using a microwave to thaw food, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the defrost setting. This setting is designed to thaw food evenly without cooking it. However, it is important to note that some foods, like large cuts of meat or poultry, are not suitable for microwave thawing due to uneven thawing and potential for overcooking in some areas. Additionally, microwave thawing can alter the texture and quality of certain foods.
Importance of Complete Thawing
It is crucial to thaw frozen food completely before cooking. This is because unevenly thawed food can cook unevenly, leading to potential foodborne illness. Additionally, partially thawed food may not reach a safe internal temperature during cooking, increasing the risk of bacterial contamination.
Important Note: Never thaw food at room temperature. This can create a temperature-danger zone where bacteria can multiply rapidly.
Reheating Frozen Foods
Once frozen food has been thawed, it is important to reheat it properly to ensure food safety and quality. The recommended internal temperature for reheating most cooked foods is 165°F (74°C). Here are some tips for reheating frozen foods:
- Reheating in the Oven: This is a good option for reheating large portions of food, such as roasts or casseroles. Preheat the oven to 350°F (175°C) and reheat the food until it reaches an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C). It is essential to use an oven-safe dish and cover the food with aluminum foil to prevent drying.
- Reheating on the Stovetop: This method is suitable for reheating smaller portions of food, such as soups, stews, or sauces. Heat the food over medium heat, stirring occasionally, until it reaches an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C). Be sure to use a pot or pan that is large enough to accommodate the food and prevent splatter.
- Reheating in the Microwave: Microwave reheating is a convenient option for reheating smaller portions of food, such as leftovers or individual meals. However, it is important to use a microwave-safe dish and cover the food to prevent splattering. Reheat the food on high power for a few minutes, stirring or rotating the food halfway through. Use a food thermometer to ensure the food reaches an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C).
Food Safety and Freezer Burn
Freezer burn is a common problem that can affect the quality and safety of frozen foods. It occurs when moisture escapes from food, leaving behind an unpleasant, dried-out appearance and a slightly off flavor. While freezer burn doesn’t necessarily make food unsafe to eat, it significantly impacts its texture, flavor, and nutritional value.
Preventing Freezer Burn
Preventing freezer burn is crucial for maintaining the quality of frozen foods. This can be achieved through proper packaging and storage techniques.
- Airtight Containers: Using airtight containers is the most effective way to prevent freezer burn. These containers prevent air from reaching the food, minimizing moisture loss. Opt for containers made of freezer-safe materials like glass or hard plastic.
- Heavy-Duty Freezer Wrap: Heavy-duty freezer wrap, such as plastic wrap or aluminum foil, provides a good barrier against air and moisture. Ensure you wrap food tightly, leaving minimal air pockets.
- Vacuum Sealing: Vacuum sealing machines remove air from packaging, creating a tight seal that prevents freezer burn. This method is particularly effective for meat, poultry, and fish.
- Freezing in Portions: Freeze food in smaller portions to minimize thawing and refreezing, which can contribute to freezer burn.
Identifying and Avoiding Freezer-Burned Food
Recognizing freezer burn is essential to avoid consuming food that has lost its quality and flavor.
- Appearance: Freezer-burned food often has a grayish or white, dried-out appearance, with ice crystals forming on the surface.
- Texture: The texture of freezer-burned food can become tough, leathery, or dry.
- Taste: The flavor of freezer-burned food can be bland or have an off, slightly metallic taste.
While freezer-burned food is generally safe to eat, it is best to avoid consuming it as the quality and flavor have been compromised. Trimming off the affected portions can sometimes salvage the rest of the food, but the best practice is to prevent freezer burn in the first place.
Conclusion
Freezing food is a valuable tool for extending its shelf life and minimizing food waste. By understanding the proper techniques and guidelines, you can preserve the quality, flavor, and nutritional value of your food.
Freezing is a practical way to store food for extended periods, allowing you to enjoy fresh ingredients even when they’re out of season or unavailable.
Safe Freezing and Thawing Practices
Safe handling of frozen foods is crucial to prevent foodborne illnesses.
- Freeze food at its freshest, as quality degrades over time.
- Package food properly to prevent freezer burn.
- Label and date packages for easy identification and tracking.
- Thaw food in the refrigerator or using the cold water method.
- Never thaw food at room temperature, as this creates a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Cook thawed food thoroughly to ensure safety.
Last Word: How Long Do Foods Last In The Freezer
Freezing food is a valuable tool for preserving freshness and extending the life of perishable items. By following proper freezing techniques, you can enjoy the benefits of a well-stocked freezer, reducing food waste and maximizing your culinary creativity. Remember to practice safe thawing methods and be mindful of freezer burn to ensure that your frozen foods retain their quality and safety.
FAQ Compilation
What is the ideal freezer temperature for optimal food preservation?
The ideal freezer temperature is 0°F (-18°C) or below. This ensures that frozen foods stay at a safe temperature for long-term storage.
Can I freeze food in its original packaging?
It’s generally not recommended to freeze food in its original packaging. Most food packaging isn’t designed for freezer storage and can leak or tear, leading to freezer burn or contamination. Use freezer-safe containers or wrap food tightly in freezer-safe plastic wrap or aluminum foil.
How do I know if frozen food is still safe to eat?
Check for signs of freezer burn, such as discoloration, ice crystals, or a dry, leathery texture. If the food has an off odor or color, it’s best to discard it. Remember to always cook frozen food thoroughly to ensure its safety.
While we’re on the topic of food storage, it’s interesting to note how long various items can last in the freezer. For example, a frozen pizza can hold up for a couple of months, but a delicate fruit like strawberries might only stay fresh for a few weeks.
Speaking of sweet treats, did you know there’s actually a difference between diet pepsi and pepsi zero ? While both are sugar-free, they have slightly different flavor profiles and ingredients. Back to the freezer, remember that proper packaging and freezing techniques are crucial for extending the shelf life of your food.
Knowing how long foods last in the freezer is crucial for planning your meals and reducing food waste. A well-organized freezer can be a great asset to a clean diet plan , allowing you to stock up on healthy ingredients and prepare meals ahead of time.
Remember to label your frozen items with dates to ensure you’re using the oldest items first and maximizing freshness.
Knowing how long foods last in the freezer is essential for any household, especially when considering alternative diets like raw food. If you’re wondering about the benefits of a raw diet for your canine companion, you might want to check out this article on is raw diet good for dogs.
Regardless of your dietary choices, understanding freezer storage times helps ensure food safety and prevents waste.