How to get nutritional facts for my product – How to get nutritional facts for your product is a crucial step in bringing your food or beverage to market. Understanding the nutritional content of your product not only ensures compliance with regulations but also empowers consumers to make informed choices. This comprehensive guide will delve into the methods, procedures, and considerations involved in obtaining accurate and reliable nutritional information for your product.
Whether you’re a small-scale entrepreneur or a large food manufacturer, having access to accurate nutritional data is essential. This information allows you to develop a clear and concise nutritional label, making it easy for consumers to understand the nutritional profile of your product. Moreover, knowing the nutritional content of your product can help you optimize its recipe, formulate new products, and make informed decisions about marketing and branding.
Understanding Nutritional Labeling Requirements
Nutritional labeling is a crucial aspect of food safety and consumer information. It provides consumers with essential details about the nutritional content of food products, enabling them to make informed choices about their diet. This information helps consumers manage their health, prevent nutritional deficiencies, and make informed decisions about their dietary choices.
Legal Requirements for Nutritional Labeling
Nutritional labeling requirements vary across different countries and regions, reflecting their unique regulatory frameworks and consumer needs. Here are some examples:
- United States: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mandates nutritional labeling for most packaged foods. The Nutrition Facts label provides information on serving size, calories, macronutrients (fat, carbohydrates, protein), added sugars, vitamins, and minerals. The FDA also requires specific labeling for certain categories of food, such as low-fat, low-sodium, and organic products.
- European Union: The European Union (EU) has implemented a standardized nutritional labeling system for pre-packaged foods. The EU’s Nutrition Information Regulations require manufacturers to provide information on energy value, fat, saturated fat, carbohydrates, sugars, protein, salt, and certain vitamins and minerals.
- Canada: Health Canada regulates food labeling in Canada. The Nutrition Facts table provides information on serving size, calories, macronutrients, added sugars, and certain vitamins and minerals. The Canadian government also requires specific labeling for certain categories of food, such as low-fat, low-sodium, and gluten-free products.
Purpose of Nutritional Labels
Nutritional labels serve several key purposes:
- Provide Consumers with Nutritional Information: Labels enable consumers to compare the nutritional content of different food products, helping them make informed choices about their diet.
- Promote Healthy Eating Habits: By highlighting key nutrients, such as calories, fat, and sugar, labels encourage consumers to make healthier choices and manage their calorie intake.
- Assist with Dietary Management: Nutritional labels are particularly helpful for individuals with specific dietary needs, such as those managing diabetes, high blood pressure, or allergies.
- Support Public Health Initiatives: Nutritional labeling contributes to public health initiatives by promoting awareness of healthy eating habits and reducing the prevalence of chronic diseases related to diet.
Key Components of a Standard Nutritional Label
A standard nutritional label typically includes the following components:
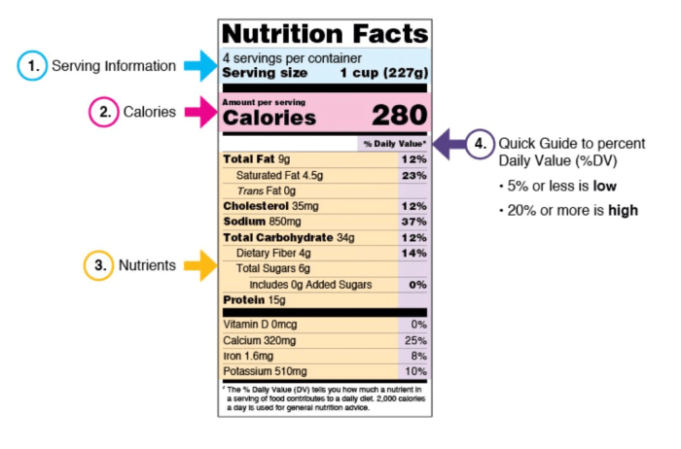
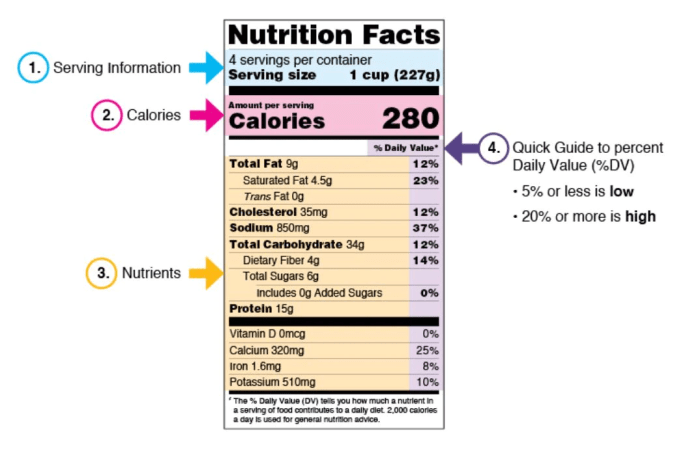
- Serving Size: This indicates the amount of food that is considered a single serving. It is essential for accurately comparing the nutritional content of different products.
- Calories: This represents the amount of energy in a serving.
- Macronutrients: These include fat, carbohydrates, and protein. The label typically lists the total amount of each macronutrient, as well as the amount of saturated fat, cholesterol, and dietary fiber.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Nutritional labels often include information on vitamins and minerals that are considered essential for health, such as vitamin A, vitamin C, calcium, and iron.
- Percent Daily Value (%DV): This represents the percentage of a nutrient in a serving relative to the recommended daily intake for an average adult. It helps consumers understand the contribution of each food to their overall daily nutrient needs.
Methods for Obtaining Nutritional Information
Knowing the nutritional content of your product is essential for accurate labeling and promoting its health benefits. There are several methods to obtain this information, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Laboratory Analysis
Laboratory analysis is the most accurate method for determining the nutritional content of a product. It involves sending a sample of your product to a certified laboratory for testing. The laboratory will use standardized methods to analyze the sample for various nutrients, such as protein, carbohydrates, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
- Accuracy: Laboratory analysis is considered the gold standard for nutritional analysis due to its high accuracy and reliability. It uses standardized methods and equipment to ensure precise measurements.
- Cost: Laboratory analysis can be expensive, especially for multiple tests and complex analyses. The cost depends on the number of nutrients being analyzed, the complexity of the analysis, and the laboratory’s fees.
- Time: Laboratory analysis can take several days or weeks, depending on the complexity of the analysis and the laboratory’s workload.
Using Existing Databases
Several publicly available databases contain nutritional information for a wide range of foods. The USDA Food Composition Database is a comprehensive database that provides nutritional information for thousands of foods, including ingredients and common food preparations.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of existing databases depends on the quality of the data collected and the reliability of the sources. It’s important to choose reputable databases and verify the information before using it for labeling.
- Cost: Using existing databases is typically free or low-cost, making it a cost-effective option for obtaining nutritional information.
- Time: Accessing and retrieving data from existing databases is generally quick and efficient, saving time compared to laboratory analysis.
Consulting with a Food Scientist or Nutritionist
Food scientists and nutritionists have specialized knowledge and experience in food composition and nutritional labeling. They can help you understand the nutritional requirements for your product and provide guidance on how to obtain accurate nutritional information.
- Accuracy: Consulting with a food scientist or nutritionist can ensure that the nutritional information is accurate and meets regulatory requirements.
- Cost: Consulting fees can vary depending on the expertise and experience of the professional.
- Time: Consulting with a food scientist or nutritionist can take some time to schedule appointments and receive their recommendations.
Utilizing Food Composition Software, How to get nutritional facts for my product
Food composition software programs can help you calculate the nutritional content of your product based on its ingredients. These programs use databases of food ingredients and their nutritional values to calculate the overall nutritional profile.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of food composition software depends on the completeness and accuracy of the underlying databases. It’s important to choose reputable software programs that use reliable data sources.
- Cost: Food composition software can range from free to expensive, depending on the features and functionality offered.
- Time: Using food composition software can be relatively quick and efficient, especially for products with simple ingredient lists.
Closure
By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently obtain accurate nutritional facts for your product, ensuring compliance with regulations and providing valuable information to consumers. Remember, understanding the nutritional composition of your product is essential for its success in the marketplace. Whether you choose to utilize laboratory analysis, existing databases, or professional expertise, the journey towards accurate nutritional labeling is an investment in the quality and transparency of your product.
Helpful Answers: How To Get Nutritional Facts For My Product
How do I find a food laboratory for analysis?
You can search online directories for food laboratories in your area or contact your local university or agricultural extension office for recommendations.
What if my product contains ingredients that are not listed in existing databases?
If you have unique or proprietary ingredients, you will need to conduct laboratory analysis to determine their nutritional content.
Are there any free online tools for calculating nutritional information?
Yes, there are several free online tools available, but their accuracy may vary. It’s important to consult with a food scientist or nutritionist to verify the results.
What are the potential consequences of inaccurate or non-compliant nutritional labeling?
Inaccurate or non-compliant labeling can result in fines, product recalls, and damage to your brand reputation.
Figuring out the nutritional facts for your product can be a bit of a puzzle, especially if you’re trying to align it with a specific dietary approach. To make sure your product fits your goals, it’s helpful to first understand what type of diet is best for you – whether it’s a Mediterranean diet, a vegan diet, or something else entirely.
What type of diet is best for me ? Once you have a clearer picture of your dietary needs, you can focus on finding products that align with your choices and provide the necessary nutrients.
Figuring out the nutritional facts for your product can be a bit of a puzzle, especially if you’re aiming for a specific dietary profile. For example, if you’re looking to create a vegetarian-friendly product, you’ll need to make sure it’s packed with protein.
There are lots of great vegetarian protein sources out there, and you can find some helpful tips on how to increase protein intake in vegetarian diet. Once you’ve got a good understanding of the protein content, you can move on to analyzing other nutrients and ensuring your product meets your target audience’s needs.
Finding out the nutritional facts for your product is crucial, especially if you’re aiming for a healthier lifestyle. You can often find this information on the product packaging, or by searching online. If you’re concerned about cholesterol levels, it’s important to be mindful of your diet.
Check out this resource on how to reduce cholesterol with diet for helpful tips and advice. Armed with the right nutritional information and a smart dietary plan, you can make informed choices about your food and overall well-being.