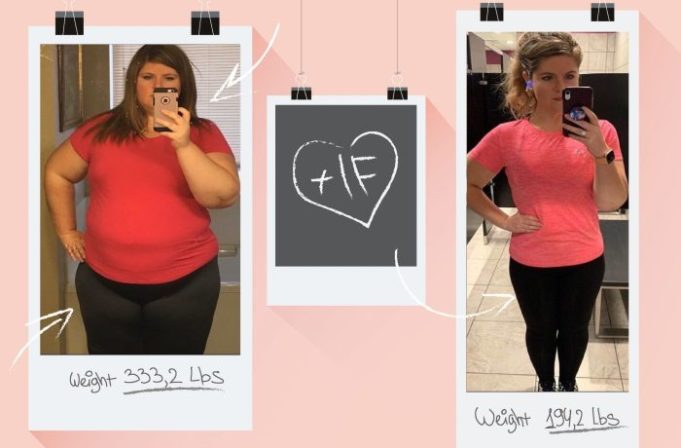
How to lose weight with intermittent fasting is a popular and intriguing topic, with many people seeking to harness the power of this approach to achieve their weight loss goals. Intermittent fasting is a dietary pattern that cycles between periods of eating and fasting, often involving extended periods of abstaining from food.
This method has gained traction for its potential to promote weight loss, improve insulin sensitivity, and enhance overall health.
This guide delves into the different types of intermittent fasting methods, outlining their benefits and potential risks. It provides practical advice on creating a personalized fasting plan, navigating hunger and cravings, and incorporating lifestyle factors to maximize success. Furthermore, we’ll explore the potential interactions between intermittent fasting and specific health conditions, emphasizing the importance of consulting a healthcare professional before embarking on this journey.
Understanding Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) is an eating pattern that cycles between periods of eating and voluntary fasting. It’s not about what you eat, but ratherwhen* you eat. Unlike traditional diets that focus on restricting certain foods, IF involves abstaining from food for specific periods.
This can be done in various ways, leading to different IF methods.
Types of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting methods vary in their approach, offering flexibility to suit individual preferences and lifestyles. Here are some of the most popular methods:
- 16/8 Method:This involves fasting for 16 hours each day and restricting your eating window to 8 hours. It’s a popular method due to its simplicity and effectiveness. For example, you could fast from 8 pm to 12 pm the next day, eating only during the 12 pm to 8 pm window.
- 5:2 Diet:This method involves eating normally for five days a week and restricting calorie intake to 500-600 calories on two non-consecutive days.
- Alternate-Day Fasting:This method involves fasting for a full 24 hours every other day, with normal eating on the other days.
- Eat Stop Eat:This method involves fasting for 24 hours once or twice a week.
Potential Benefits of Intermittent Fasting for Weight Loss
Intermittent fasting can be an effective weight loss strategy due to several mechanisms:
- Reduced Calorie Intake:By limiting the time you can eat, you naturally consume fewer calories, leading to weight loss. For instance, if you typically consume 2,000 calories a day, restricting your eating window to 8 hours could reduce your intake to 1,500 calories, resulting in a 500 calorie deficit.
This deficit can contribute to weight loss over time.
- Increased Fat Burning:When you fast, your body starts breaking down stored fat for energy, leading to increased fat burning. Research suggests that IF can help increase levels of human growth hormone, which can boost metabolism and fat burning.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity:Fasting can improve insulin sensitivity, allowing your body to utilize glucose more efficiently. This can lead to reduced blood sugar levels and a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While intermittent fasting can be beneficial, it’s crucial to understand its potential risks and side effects:
- Headaches and Fatigue:You may experience headaches or fatigue during the initial stages of fasting, as your body adjusts to the new eating pattern. These symptoms usually subside within a few days.
- Irritability and Difficulty Concentrating:Some people experience irritability and difficulty concentrating during fasting periods. This is primarily due to low blood sugar levels, which can be managed by consuming electrolytes.
- Nutrient Deficiencies:If not planned carefully, IF can lead to nutrient deficiencies. It’s essential to ensure a balanced diet with adequate nutrient intake during eating periods.
- Gastrointestinal Issues:Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, constipation, or diarrhea during fasting. These symptoms can be minimized by gradually introducing IF and staying hydrated.
It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting intermittent fasting, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions.
Intermittent fasting is a popular weight loss strategy that involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. It’s not about starving yourself, but rather about creating a calorie deficit. If you’re concerned about feeling hungry during fasting periods, check out How to lose weight without starving yourself for tips on managing hunger.
Intermittent fasting can be a sustainable and effective way to lose weight, but it’s important to listen to your body and adjust the fasting periods to suit your individual needs.
Creating a Fasting Plan

Intermittent fasting isn’t about restricting what you eat, but rather when you eat. There are several methods to choose from, and the best one for you depends on your lifestyle, preferences, and goals.
Choosing the Right Intermittent Fasting Method
Finding the right intermittent fasting method involves considering your individual needs and goals. Some factors to think about include:
- Your daily schedule:How much time can you realistically dedicate to fasting each day?
- Your health and fitness goals:Are you aiming for weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, or better overall health?
- Your current eating habits:Are you already accustomed to eating within a specific window, or do you need to make significant adjustments?
Once you’ve considered these factors, you can start exploring different intermittent fasting methods. Here are a few popular options:
The 16/8 Method
This method involves fasting for 16 hours each day and eating within an 8-hour window. It’s often considered one of the easiest ways to start intermittent fasting, as it requires minimal changes to your daily routine.
Intermittent fasting can be an effective way to lose weight, especially when combined with a healthy diet and exercise. As women age, hormonal changes can make weight loss more challenging, so understanding the unique needs of women over 40 is crucial.
For insights into strategies specifically tailored for this age group, check out this guide on how to lose weight after 40 for women. Returning to intermittent fasting, remember that consistency and listening to your body are key to success.
- Sample 16/8 Fasting Schedule:
- Fasting Window:8:00 PM to 12:00 PM (16 hours)
- Eating Window:12:00 PM to 8:00 PM (8 hours)
- Potential Food Choices:During your eating window, focus on nutrient-rich foods like:
- Breakfast:Oatmeal with berries and nuts, eggs with whole-wheat toast, or Greek yogurt with fruit and granola
- Lunch:Salad with grilled chicken or fish, lentil soup, or a veggie burger on a whole-wheat bun
- Dinner:Salmon with roasted vegetables, chicken stir-fry, or lentil stew
It’s crucial to remember that these are just examples, and you can customize your schedule and food choices based on your preferences and dietary needs.
Listening to Your Body
While there are many established methods, it’s important to listen to your body and adjust your fasting schedule as needed. You may find that you need to start with a shorter fasting window and gradually increase it over time. Pay attention to how you feel during your fasts and make adjustments accordingly.
Some common signs that you may need to adjust your fasting schedule include:
- Extreme hunger:If you’re feeling overly hungry and finding it difficult to concentrate, you may need to shorten your fasting window.
- Headaches:Headaches are a common side effect of fasting, especially in the beginning. If they’re severe or persistent, you may need to adjust your schedule or break your fast.
- Fatigue:If you’re feeling unusually tired or sluggish, you may need to adjust your fasting schedule or ensure you’re getting enough calories and nutrients during your eating window.
It’s also important to note that intermittent fasting may not be suitable for everyone. If you have any underlying health conditions, consult with your doctor before starting an intermittent fasting plan.
Nutrition During Fasting Windows: How To Lose Weight With Intermittent Fasting
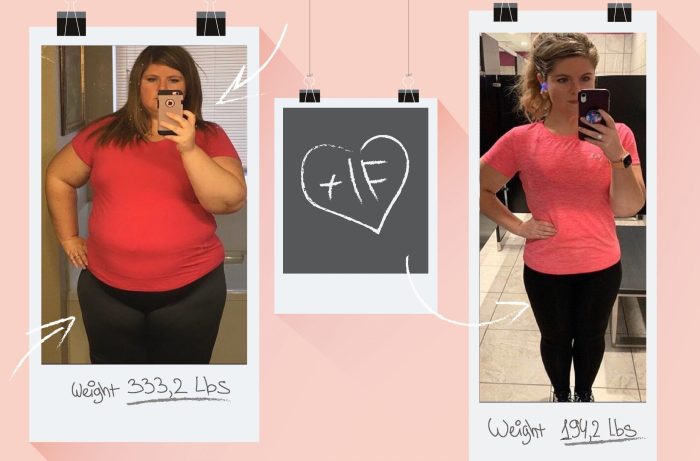

While intermittent fasting focuses on -when* you eat, what you eat during your eating windows is crucial for successful weight loss. By making smart food choices, you can optimize your body’s response to fasting, maximizing fat burning and minimizing hunger.
Food Choices During Eating Windows
Focus on nutrient-dense foods rich in protein, fiber, and healthy fats. These nutrients keep you feeling full and satisfied, preventing overeating and cravings during your eating window. They also help regulate blood sugar levels, which can be particularly important during fasting periods.
- Protein: Protein helps preserve muscle mass during fasting, boosts metabolism, and promotes satiety. Aim for lean protein sources like fish, chicken, turkey, beans, lentils, tofu, and eggs.
- Fiber: Fiber slows down digestion, keeping you feeling full for longer. Choose whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
- Healthy Fats: Healthy fats provide sustained energy and support hormone production. Include avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish in your diet.
Meal Examples, How to lose weight with intermittent fasting
Here are some examples of healthy and nutritious meals for each meal window, incorporating protein, fiber, and healthy fats:
| Meal Window | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16/8 Method (8-hour eating window) | Scrambled eggs with spinach and avocado | Salmon with roasted vegetables and quinoa | Chicken breast with sweet potato and green beans |
| 5:2 Method (2 days of fasting per week) | Greek yogurt with berries and nuts | Lentil soup with whole-grain bread | Tofu stir-fry with brown rice and vegetables |
| Alternate-Day Fasting | Smoothie with protein powder, fruit, and spinach | Tuna salad with whole-wheat crackers | Vegetarian chili with black beans and corn |
Staying Hydrated During Fasting
Staying hydrated is crucial throughout your fasting period. Water helps prevent dehydration, which can lead to headaches, fatigue, and cravings. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during your fasting window. You can also enjoy unsweetened tea or black coffee, as these beverages have minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
Managing Hunger and Cravings
Intermittent fasting, while effective for weight loss, can present challenges like hunger and cravings. These feelings are normal, especially during the initial stages of adapting to a fasting schedule. However, there are strategies you can employ to manage these challenges and ensure a successful fasting journey.
Intermittent fasting is a popular weight loss strategy that involves cycling between periods of eating and fasting. It’s a simple way to manage your calorie intake and can help you lose weight without feeling overly deprived. If you’re looking for more comprehensive guidance on how to shed pounds quickly and healthily from the comfort of your own home, check out this excellent resource: How to lose weight fast and healthy at home.
This website offers valuable tips and strategies for sustainable weight loss, which can complement the benefits of intermittent fasting.
Distraction Techniques
Distraction can be a powerful tool for managing hunger and cravings. When these feelings arise, engaging in activities that divert your attention can help minimize their intensity.
- Engage in Physical Activity:Exercise, whether a brisk walk, yoga, or a workout session, can effectively distract you from hunger pangs. It also helps release endorphins, which can boost your mood and reduce cravings.
- Socialize:Spending time with friends or family can take your mind off food and provide a sense of companionship. It’s a great way to stay occupied and avoid dwelling on hunger.
- Engage in Hobbies:Immerse yourself in activities you enjoy, such as reading, listening to music, or pursuing a creative hobby. This can help take your focus away from food and make the fasting period more enjoyable.
Mindful Eating
Mindful eating involves paying close attention to your eating habits and becoming aware of your hunger and satiety cues. This practice can help you make conscious food choices and avoid overeating during your eating window.
- Slow Down Your Eating:Take your time while eating and savor each bite. This allows your body to register fullness signals and prevents you from consuming more than you need.
- Pay Attention to Hunger and Fullness:Before, during, and after meals, be mindful of your hunger and fullness levels. Eat when you are truly hungry and stop when you feel comfortably satisfied, not overly full.
- Choose Satiating Foods:Opt for foods that are rich in protein, fiber, and healthy fats, as these nutrients promote satiety and keep you feeling fuller for longer. Examples include lean protein sources like chicken, fish, tofu, and beans, as well as vegetables and fruits rich in fiber.
Healthy Snack Options
While it’s best to avoid snacking during fasting periods, there are instances where a healthy snack can help manage hunger and cravings. These options should be low in calories and high in nutrients to support your fasting goals.
- Unsweetened Tea or Coffee:These beverages can provide a caffeine boost and help suppress appetite. Ensure they are unsweetened to avoid consuming unnecessary calories.
- Water-Rich Fruits and Vegetables:Fruits like watermelon and cucumbers, and vegetables like celery and spinach, are low in calories and high in water content, making them filling and hydrating options.
- Nuts and Seeds:A small handful of nuts or seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, or sunflower seeds, can provide healthy fats and fiber to help curb hunger. Choose unsalted and unsweetened varieties for minimal calorie intake.
Electrolyte Importance
Electrolytes are minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium that play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including hydration, nerve function, and muscle contraction. During fasting, electrolyte levels can become depleted, leading to headaches, fatigue, and muscle cramps.
- Electrolyte Depletion:When you fast, your body uses stored glycogen, which releases water and electrolytes. This can lead to electrolyte imbalances, especially if you’re not adequately hydrated.
- Electrolyte Replenishment:To prevent these symptoms, it’s important to replenish electrolytes during your fasting periods. This can be achieved through consuming electrolyte-rich beverages, such as coconut water or sports drinks, or by adding electrolytes to your water.
- Importance of Hydration:Adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining electrolyte balance. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout your fasting periods, especially during exercise or hot weather.
Lifestyle Factors for Success
Intermittent fasting is a powerful tool for weight loss, but to maximize its effectiveness, it’s crucial to integrate it with a holistic approach that addresses other important lifestyle factors. These elements work synergistically to support your weight loss journey and promote overall well-being.
Exercise and Intermittent Fasting
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in weight loss by increasing your calorie expenditure, building muscle mass, and improving insulin sensitivity. Combining intermittent fasting with exercise can amplify these benefits, leading to more significant and sustainable weight loss results.
- Increased Calorie Burn:Exercise burns calories, creating a calorie deficit that contributes to weight loss.
- Enhanced Fat Oxidation:Exercise, particularly during fasting periods, encourages your body to utilize stored fat as energy, leading to greater fat loss.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity:Exercise helps your body respond better to insulin, making it more efficient at utilizing glucose for energy and reducing fat storage.
Incorporating Exercise into a Fasting Plan
The intensity and duration of exercise during intermittent fasting depend on your fitness level and preferences. Here are some recommendations:
- For Beginners:Start with light to moderate-intensity activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling for 30 minutes most days of the week.
- For Intermediate Level:Increase the duration and intensity of your workouts, incorporating activities like jogging, weight training, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
- For Advanced Level:Engage in more challenging activities like running, CrossFit, or competitive sports.
Sleep, Stress Management, and Hydration
Beyond exercise, other lifestyle factors significantly influence your weight loss journey.
- Sleep:Adequate sleep is essential for hormonal balance, appetite regulation, and metabolism. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stress Management:Chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol levels, which can promote fat storage and hinder weight loss. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your routine.
- Hydration:Staying adequately hydrated is crucial for overall health and can help curb hunger during fasting periods. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially during fasting windows.
Intermittent Fasting and Health Conditions
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained popularity as a weight-loss strategy, but it’s crucial to understand its potential interactions with pre-existing health conditions. While IF can be beneficial for some, it might not be suitable for everyone, especially those with specific health concerns.
Potential Interactions with Health Conditions
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting IF, especially if you have any underlying health conditions. IF can potentially interact with certain conditions, impacting their management or exacerbating symptoms.
- Diabetes: IF can affect blood sugar levels, potentially leading to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). It’s crucial to monitor blood sugar levels closely and adjust medications if needed.
- Thyroid Disorders: IF can impact thyroid hormone levels, particularly in individuals with hypothyroidism.
It’s vital to consult with an endocrinologist to ensure proper thyroid management.
- Eating Disorders: IF can trigger or worsen eating disorders, especially in individuals with a history of disordered eating. It’s crucial to seek professional help if you have concerns about your relationship with food.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Consulting a healthcare professional is essential before starting IF, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions. They can:
- Assess Your Individual Health Status: A healthcare professional can evaluate your medical history, current medications, and overall health to determine if IF is safe and appropriate for you.
- Provide Personalized Guidance: They can recommend the best type of IF plan for your needs, considering your health conditions and goals.
- Monitor Your Progress: They can monitor your health during IF and adjust your plan as needed to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Resources for Finding Qualified Healthcare Providers
Several resources can help you find qualified healthcare providers who can provide personalized guidance on IF:
- Your Primary Care Physician: Your primary care physician can refer you to specialists if needed.
- Professional Organizations: Organizations like the American Academy of Family Physicians and the American College of Physicians offer directories of healthcare providers.
- Online Directories: Websites like Zocdoc and Healthgrades allow you to search for healthcare providers based on your location, specialty, and insurance coverage.
Epilogue
Intermittent fasting can be a powerful tool for weight loss and overall well-being, but it’s crucial to approach it with a balanced perspective. By understanding the different methods, creating a personalized plan, and managing potential challenges, you can embark on a journey toward a healthier lifestyle.
Remember, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions. With careful planning and guidance, you can unlock the potential benefits of intermittent fasting and achieve your health and weight loss goals.
Popular Questions
Is intermittent fasting safe for everyone?
Intermittent fasting may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain health conditions. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting intermittent fasting, particularly if you have diabetes, thyroid disorders, eating disorders, or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
What are some common side effects of intermittent fasting?
Common side effects of intermittent fasting include headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and irritability. These side effects are usually mild and tend to subside as your body adapts to the fasting periods. Staying hydrated, consuming electrolytes, and gradually increasing the duration of fasting periods can help minimize these side effects.
How much weight can I expect to lose with intermittent fasting?
The amount of weight you can lose with intermittent fasting depends on various factors, including your starting weight, diet, exercise habits, and overall lifestyle. Intermittent fasting can be an effective tool for weight loss, but it’s not a magic bullet.
Combining it with a healthy diet and regular exercise is crucial for achieving sustainable results.