Is keto diet good for diabetics? It’s a question that has sparked a lot of debate in the health and wellness world. The ketogenic diet, with its high-fat, low-carb approach, has gained popularity for weight loss and other health benefits, but its suitability for people with diabetes is a topic that requires careful consideration.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body regulates blood sugar levels. While a keto diet can potentially help manage blood sugar, it’s crucial to understand the potential benefits and risks, as well as the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional before making any drastic dietary changes.
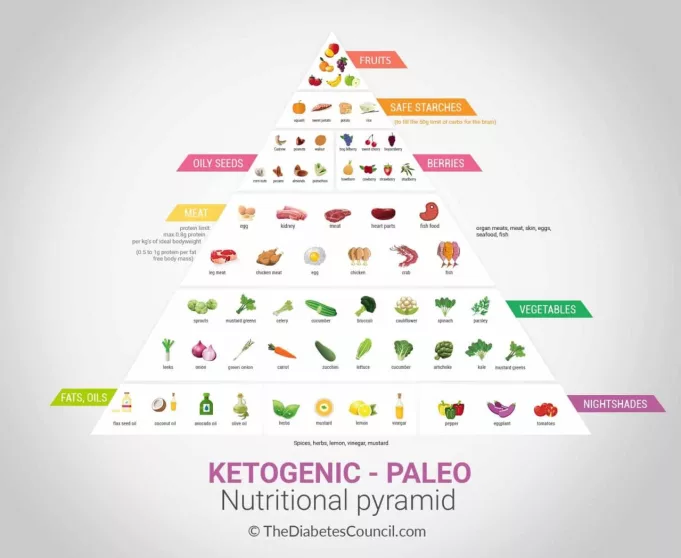
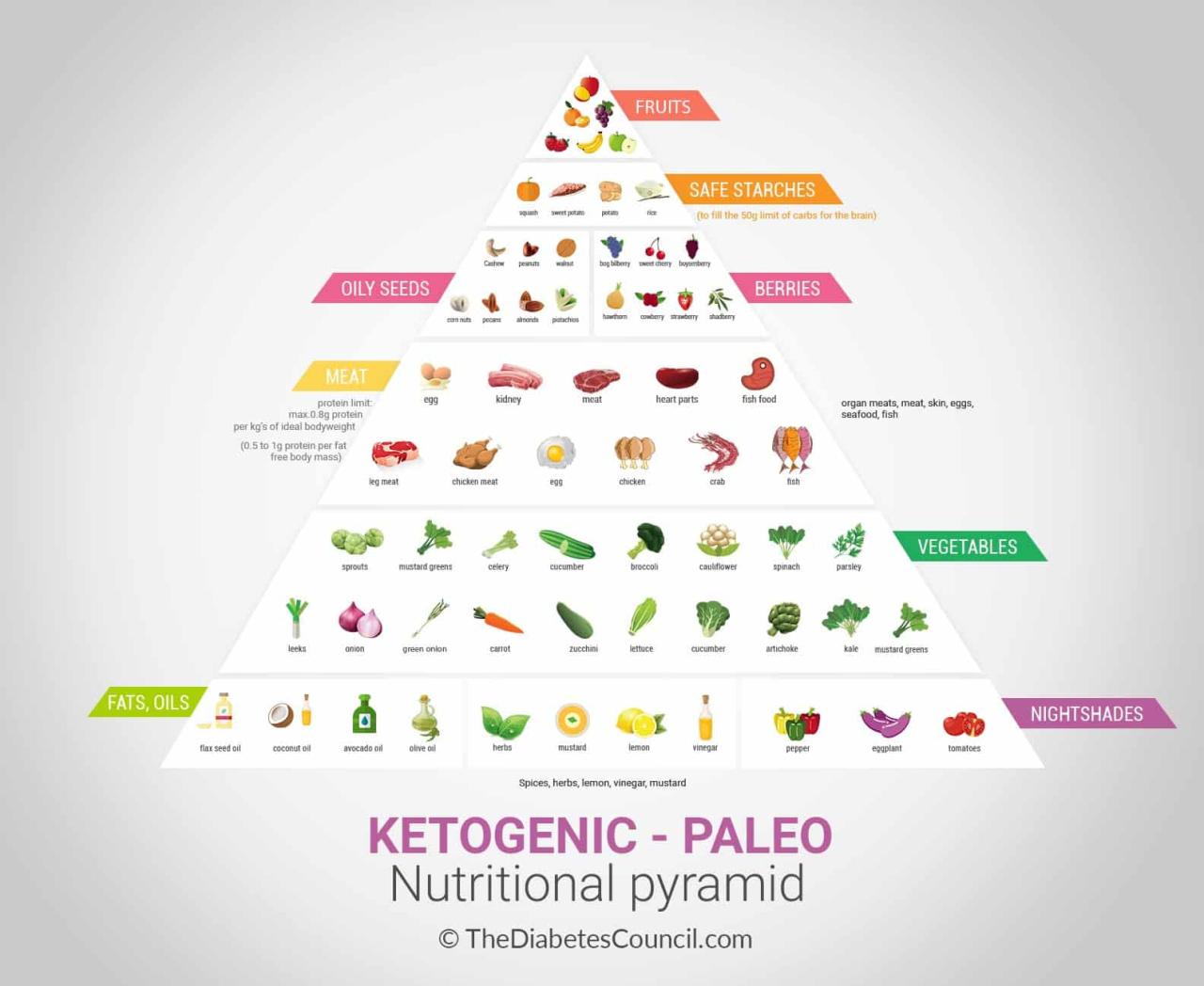
Keto Diet Basics
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that forces your body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis. This diet has gained significant popularity for its potential weight loss benefits and its impact on blood sugar control, making it a topic of interest for individuals with diabetes.
Macronutrient Ratios in a Keto Diet
The keto diet’s success hinges on achieving a specific ratio of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—to trigger ketosis. The typical macronutrient breakdown for a keto diet is:
Fat
The keto diet can be a rollercoaster for diabetics, with its ups and downs in blood sugar. But hey, at least you can be sure your feline friend is eating well! Choosing the right food is crucial for their health, and checking out the best food brands for cats can make all the difference.
Just like a balanced diet is key for a diabetic, it’s essential for your cat’s well-being too. So, while you’re figuring out the keto thing, remember to give your furry friend the best nutrition possible!
70-80% of daily calories
Protein
15-20% of daily calories
Carbohydrates
5-10% of daily calories
This means that a keto diet emphasizes consuming a large portion of calories from healthy fats while significantly limiting carbohydrate intake.
Foods Allowed and Restricted on a Keto Diet
The keto diet restricts foods high in carbohydrates, such as:
- Sugary drinks (soda, juice)
- Refined grains (white bread, pasta)
- Starchy vegetables (potatoes, corn)
- Fruits (bananas, grapes, mangoes)
- Legumes (beans, lentils)
On the other hand, the keto diet encourages the consumption of:
- Healthy fats (olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil)
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
- Meat (chicken, beef, pork)
- Eggs
- Non-starchy vegetables (broccoli, spinach, cauliflower)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia seeds)
Blood Sugar Management in Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, which can lead to various health complications if left unmanaged. Understanding the intricate dance of hormones, particularly insulin and glucagon, is crucial for comprehending how blood sugar levels are regulated.
Insulin and Glucagon: The Sugar Squad
Insulin and glucagon are two key hormones that work in tandem to maintain blood sugar balance. Imagine them as a dynamic duo, each playing a crucial role in ensuring that your blood sugar levels stay within a healthy range.
- Insulin: The Sugar-Lowering Superhero: When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which enters your bloodstream. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, acts like a key that unlocks cells, allowing glucose to enter and provide energy. This lowers blood sugar levels.
- Glucagon: The Sugar-Raising Savior: When blood sugar levels dip too low, for example, between meals, glucagon, also produced by the pancreas, springs into action. It triggers the release of stored glucose from the liver, effectively raising blood sugar levels to maintain energy levels.The keto diet, with its high-fat, low-carb approach, can be a rollercoaster ride for diabetics. While it might initially help manage blood sugar, it’s crucial to remember that the long-term effects are still being studied. Before diving headfirst into this fat-fueled adventure, it’s wise to consider whether the keto diet is safe for you, as you can check out this resource is keto diet safe.Remember, a healthy diet for diabetics should always be tailored to individual needs and monitored closely with a healthcare professional.
The Keto Diet’s Impact on Blood Sugar
The ketogenic diet, or keto diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that forces your body to enter a state of ketosis. In ketosis, your body primarily burns fat for energy instead of glucose. This metabolic shift has a profound impact on insulin and blood sugar levels.
- Reduced Insulin Demand: Because the keto diet restricts carbohydrates, there’s less glucose circulating in your bloodstream. This leads to lower insulin levels and reduced insulin resistance, a condition where cells become less responsive to insulin.
- Stabilized Blood Sugar: The consistent fat intake on a keto diet provides a steady stream of energy, reducing the need for frequent glucose spikes and dips. This can help stabilize blood sugar levels, leading to fewer fluctuations throughout the day.
Keto vs. Other Diabetes Diets
While the keto diet has shown promise in managing blood sugar, it’s important to compare its effects with other popular diabetes diets.
Keto vs. Traditional Diabetes Diet
- Traditional Diabetes Diet: This diet typically emphasizes moderate carbohydrate intake, lean protein, and healthy fats. It aims to manage blood sugar levels by focusing on portion control and choosing nutrient-dense foods.
- Keto Diet: The keto diet takes a more radical approach by drastically reducing carbohydrate intake and replacing it with fat. While it can lead to significant blood sugar improvements, it requires careful planning and adherence to avoid potential side effects.
Keto vs. Mediterranean Diet
- Mediterranean Diet: This diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, olive oil, and lean protein. It’s known for its heart-healthy benefits and can also help manage blood sugar levels.
- Keto Diet: The keto diet’s focus on fat and low carbohydrate intake differs significantly from the Mediterranean diet’s emphasis on whole grains and fruits. While both diets can be beneficial for diabetes management, their approaches to achieving this are distinct.
Potential Benefits of a Keto Diet for Diabetics
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, has gained significant attention for its potential benefits in managing blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes. This diet focuses on drastically reducing carbohydrate intake while increasing fat consumption, forcing the body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis, where it primarily burns fat for energy instead of glucose.
This shift in energy source can have profound implications for blood sugar control and potentially improve long-term health outcomes for diabetics.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
The keto diet’s primary mechanism for blood sugar management lies in its ability to reduce insulin resistance. Insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar, struggles to effectively do its job when cells become resistant to its effects. This resistance often occurs due to high carbohydrate intake, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
By drastically limiting carbohydrates, the keto diet helps minimize insulin spikes and improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to better utilize glucose and regulate blood sugar more effectively.
Effect on HbA1c Levels, Is keto diet good for diabetics
HbA1c, also known as glycosylated hemoglobin, provides a long-term measure of blood sugar control over the preceding 2-3 months. Elevated HbA1c levels indicate poor blood sugar management and are associated with an increased risk of diabetic complications. Studies suggest that the keto diet can lead to significant reductions in HbA1c levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
This reduction is attributed to the diet’s impact on insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control. Lower HbA1c levels translate to better blood sugar management and a reduced risk of developing long-term complications.
Potential Benefits on Long-Term Complications
The keto diet’s positive effects on blood sugar control extend beyond immediate benefits. Long-term blood sugar management is crucial for preventing or delaying the onset of diabetic complications, such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, and kidney disease. By improving insulin sensitivity and reducing HbA1c levels, the keto diet can contribute to better long-term health outcomes for diabetics.
Research Supporting the Keto Diet’s Benefits for Diabetes
Numerous studies have investigated the keto diet’s impact on diabetes management. A 2018 study published in the journal
- Diabetes Care* found that individuals with type 2 diabetes who followed a keto diet for 12 weeks experienced significant reductions in HbA1c levels, fasting blood sugar, and body weight compared to those who followed a standard diabetes diet. Another study published in the journal
- Nutrients* in 2020 demonstrated that a keto diet was effective in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood sugar fluctuations in individuals with type 2 diabetes. These studies, along with others, provide evidence that the keto diet holds promise as a potential therapeutic approach for managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of long-term complications in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Potential Risks and Considerations: Is Keto Diet Good For Diabetics
While the keto diet can offer potential benefits for managing blood sugar levels in people with diabetes, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential risks and considerations associated with this approach. Like any dietary change, transitioning to a ketogenic lifestyle requires careful planning, monitoring, and individual adjustments.
Potential Side Effects
Adopting a keto diet can lead to certain side effects, particularly during the initial adaptation phase. These are often temporary and tend to subside as your body adjusts to the new dietary pattern.
- Keto Flu:This is a common experience during the first few days or weeks of the keto diet. It can manifest as fatigue, headache, nausea, constipation, and brain fog. These symptoms are usually due to the body’s transition from burning carbohydrates to burning fat for energy.Staying hydrated and consuming electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium can help alleviate these symptoms.
- Nutrient Deficiencies:The restrictive nature of the keto diet can potentially lead to deficiencies in certain essential nutrients. This is especially true for fiber, vitamins (like vitamin C, E, and K), and minerals (like calcium and magnesium). Supplementing with a multivitamin and increasing your intake of nutrient-rich foods can help mitigate these deficiencies.
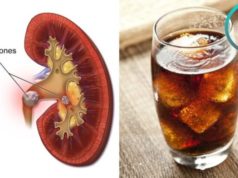
- Kidney Stones:In some individuals, a keto diet can increase the risk of kidney stones. This is primarily due to the increased excretion of ketones, which can lead to a higher concentration of calcium in the urine. Staying hydrated and consuming adequate amounts of potassium can help reduce this risk.
- Digestive Issues:The high fat content of a keto diet can sometimes cause digestive discomfort, including diarrhea, constipation, and bloating. Consuming high-quality fats and gradually increasing fat intake can help minimize these issues.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, regardless of the dietary approach they choose. However, it becomes even more important when following a keto diet.
- Frequent Monitoring:It’s essential to check blood sugar levels frequently, especially during the initial adaptation phase and after significant dietary changes. This helps identify any unexpected fluctuations and adjust the diet accordingly.
- Individualized Adjustments:Each person responds differently to the keto diet. You may need to adjust your carbohydrate intake, exercise routine, or medication based on your individual blood sugar readings. Consulting with a healthcare professional is vital for personalized guidance.
- Potential for Hypoglycemia:While the keto diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, it’s crucial to be aware of the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). This can occur if carbohydrate intake is too low, especially during periods of increased physical activity. It’s important to have a readily available source of carbohydrates to address this potential issue.
Consultation and Guidance
Before embarking on a ketogenic diet, especially if you have diabetes, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess your individual needs, medical history, and current medications to determine if the keto diet is a suitable option for you.
A healthcare professional can help create a personalized ketogenic meal plan tailored to your specific needs and medical conditions. They can also guide you on potential risks and benefits, as well as provide strategies for managing potential side effects and ensuring your overall health and well-being.
So, you’re wondering if the keto diet is a good fit for your diabetes? It’s a hot topic, but honestly, it’s like asking if a unicorn can fly – it’s a complex question with a lot of factors. If you’re looking to shed some pounds without hitting the gym, check out this article on how to lose weight without working out.
But when it comes to diabetes, consult your doctor, because the keto diet isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s all about finding what works best for your unique situation.
Questions to Discuss with a Healthcare Professional
It’s essential to have an open and honest conversation with your doctor or a registered dietitian before starting a keto diet. Here are some key questions to discuss:
| Question | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Are you comfortable with me trying a ketogenic diet? | This allows your healthcare professional to assess your overall health and determine if the keto diet is safe for you. |
| What are the potential risks and benefits of a ketogenic diet for me, given my current health conditions and medications? | This helps you understand the potential impact of the diet on your specific health situation. |
| How can I safely and effectively manage my blood sugar levels while on a ketogenic diet? | This ensures you have a clear understanding of how to monitor and manage your blood sugar levels while on the diet. |
| What specific dietary guidelines should I follow to ensure I’m getting the necessary nutrients while on a ketogenic diet? | This ensures you are consuming a balanced diet that meets your nutritional needs. |
| Are there any medications or supplements I should consider taking while on a ketogenic diet? | This helps you avoid any potential interactions between the diet and your medications. |
| How frequently should I monitor my blood sugar levels while on a ketogenic diet? | This ensures you are closely monitoring your blood sugar levels and making necessary adjustments to your diet. |
| What are the potential side effects of a ketogenic diet, and how can I manage them? | This helps you be prepared for any potential side effects and have strategies in place to manage them. |
| How long should I follow a ketogenic diet, and how can I safely transition back to a regular diet if needed? | This helps you understand the long-term implications of the diet and how to make a safe transition back to a regular diet. |
Outcome Summary
Ultimately, the decision to try a keto diet for diabetes is a personal one. It’s essential to weigh the potential benefits and risks, consider your individual needs and medical history, and consult with a healthcare professional to create a safe and effective plan.
While the keto diet may offer advantages for some individuals with diabetes, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution and should be approached with caution and guidance.
FAQ Insights
Can a keto diet help me lose weight if I have diabetes?
Yes, a keto diet can help you lose weight, which can be beneficial for managing diabetes. However, weight loss should always be supervised by a healthcare professional, especially if you have diabetes.
What are some common side effects of a keto diet?
Common side effects include keto flu (flu-like symptoms like fatigue, headache, and nausea), constipation, and nutrient deficiencies. These side effects are usually temporary and can be managed with proper hydration and dietary adjustments.
Can I eat fruits on a keto diet?
Most fruits are high in carbohydrates and are restricted on a keto diet. However, some low-carb fruits like berries can be enjoyed in moderation.