Is keto diet good for high cholesterol? This question has become increasingly relevant as the popularity of the ketogenic diet, a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan, continues to rise. While the keto diet has been touted for its potential weight loss benefits and its ability to improve certain health conditions, its impact on cholesterol levels remains a subject of debate. This article delves into the intricacies of the keto diet, exploring its effects on cholesterol and providing insights for individuals considering this dietary approach.
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, forces the body to enter a metabolic state known as ketosis. In ketosis, the body primarily burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This shift in energy metabolism leads to a reduction in insulin levels and an increase in ketones, which are produced by the liver from fat. While the keto diet can lead to significant weight loss, it is crucial to understand its potential impact on cholesterol levels and to make informed decisions regarding its suitability for individuals with high cholesterol.
Ketogenic Diet Basics
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate eating plan that forces the body to enter a metabolic state called ketosis. This diet has gained significant popularity in recent years, primarily due to its potential weight loss benefits.
Macronutrient Breakdown
The ketogenic diet emphasizes a significant reduction in carbohydrate intake while increasing the proportion of fat in the diet. This shift in macronutrient ratios leads to a metabolic shift, where the body primarily utilizes fat for energy instead of glucose.
- Carbohydrates: Typically restricted to 20-50 grams per day, with a focus on non-starchy vegetables and low-carb fruits.
- Protein: Moderate intake, typically around 20-30% of daily calories.
- Fat: High intake, comprising 70-80% of daily calories, sourced from healthy fats like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish.
Ketosis and Its Impact
When carbohydrates are restricted, the body begins to break down stored fat for energy. This process produces ketones, which are alternative energy sources that the brain and other organs can utilize. Ketosis is the state where the body primarily relies on ketones for fuel.
- Reduced Insulin Levels: Ketosis leads to a significant reduction in insulin levels, which is the hormone responsible for storing glucose in the body. This can be beneficial for managing blood sugar levels and improving insulin sensitivity.
- Increased Fat Burning: The body’s primary energy source shifts from glucose to fat, leading to increased fat burning and potential weight loss.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Some studies suggest that ketosis may enhance cognitive function and mental clarity, although more research is needed to confirm this effect.
Allowed and Restricted Foods
The ketogenic diet emphasizes foods that are low in carbohydrates and high in fat.
Allowed Foods
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocado oil, coconut oil, butter, ghee, nuts, seeds, fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), and avocados.
- Non-Starchy Vegetables: Spinach, kale, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, asparagus, zucchini, and bell peppers.
- Protein Sources: Meat (beef, chicken, pork), fish, eggs, and low-carb dairy products (cheese, yogurt).
- Low-Carb Fruits: Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries) in moderation.
Restricted Foods
- Sugary Foods and Drinks: Sugary drinks, candies, pastries, and desserts.
- Starchy Foods: Bread, pasta, rice, potatoes, and corn.
- Processed Foods: Packaged snacks, fast food, and processed meats.
- High-Carb Fruits: Bananas, mangoes, grapes, and pineapple.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas.
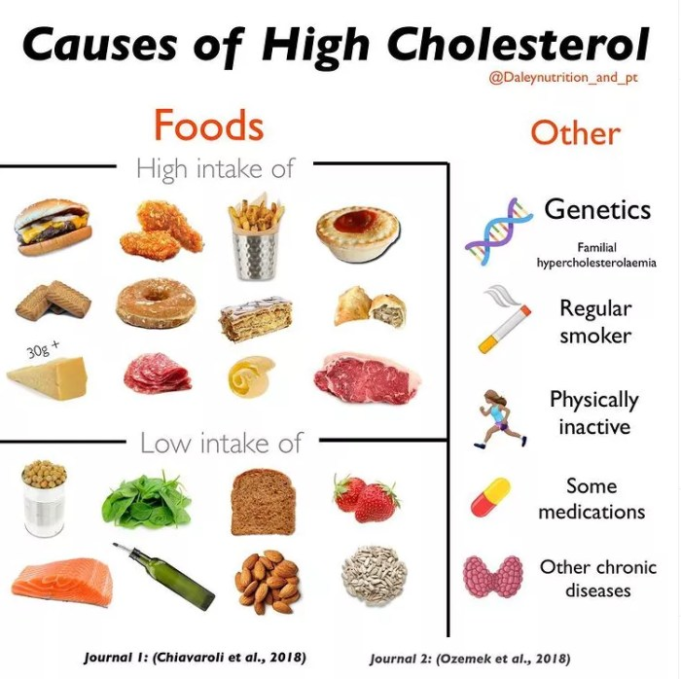
Cholesterol and Heart Health
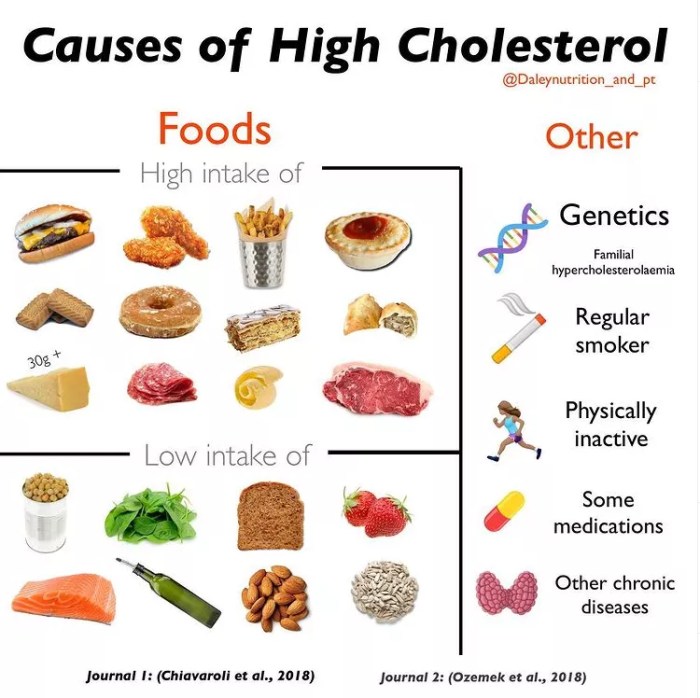
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that is essential for the body’s proper functioning. It plays a vital role in building cell membranes, producing hormones, and aiding in the digestion of fats. However, high cholesterol levels can pose a serious health risk, particularly for cardiovascular health.
Types of Cholesterol and Their Roles, Is keto diet good for high cholesterol
Cholesterol exists in two primary forms: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
- LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol): LDL cholesterol carries cholesterol from the liver to the body’s cells. When there is too much LDL cholesterol, it can build up in the arteries, forming plaque that can narrow and harden the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This buildup can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
- HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol): HDL cholesterol collects excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and carries it back to the liver for processing and removal from the body. Higher levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with a lower risk of heart disease.
Relationship Between High Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Disease
High cholesterol, particularly high LDL cholesterol, is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in the arteries, is a primary contributor to CVD. As plaque accumulates, it can restrict blood flow, leading to various cardiovascular complications, including:
- Heart attack: When a blood clot forms in a narrowed artery and blocks blood flow to the heart, it can cause a heart attack.
- Stroke: A stroke occurs when a blood clot blocks an artery in the brain, disrupting blood flow and damaging brain tissue.
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD): PAD occurs when plaque builds up in the arteries of the legs, feet, arms, and hands, reducing blood flow and causing pain, numbness, or fatigue.
Role of Diet in Managing Cholesterol Levels
Dietary choices play a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels. A healthy diet can help lower LDL cholesterol and increase HDL cholesterol.
- Limit saturated and trans fats: These fats are found in red meat, butter, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods. They raise LDL cholesterol levels.
- Choose lean protein sources: Opt for lean meats like chicken, fish, and beans. These provide protein without adding excess saturated fat.
- Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains: These foods are rich in fiber, which helps lower LDL cholesterol levels.
- Eat heart-healthy fats: Unsaturated fats, such as those found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds, can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol.
Ketogenic Diet and Cholesterol
The ketogenic diet, with its high-fat, low-carbohydrate approach, has garnered significant attention for its potential health benefits. However, its impact on cholesterol levels remains a subject of ongoing research and debate. Understanding the nuances of how a ketogenic diet affects different types of cholesterol is crucial for individuals considering this dietary approach, especially those with high cholesterol.
Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Cholesterol Levels
The ketogenic diet’s impact on cholesterol levels is complex and can vary depending on individual factors, including genetics, starting cholesterol levels, and adherence to the diet.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Cholesterol: HDL cholesterol is often referred to as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing the risk of heart disease. Some studies suggest that a ketogenic diet can increase HDL cholesterol levels.
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Cholesterol: LDL cholesterol is known as “bad” cholesterol because high levels can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease. Research on the impact of the ketogenic diet on LDL cholesterol is mixed. Some studies show a decrease in LDL cholesterol levels, while others show an increase or no significant change.
- Total Cholesterol: Total cholesterol is the sum of all cholesterol types in the blood. The ketogenic diet’s effect on total cholesterol is variable, depending on the individual’s response to the diet and the changes in HDL and LDL cholesterol levels.
- Triglycerides: Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood. The ketogenic diet is generally associated with a reduction in triglyceride levels, which is considered beneficial for heart health.
Potential Benefits of a Ketogenic Diet for High Cholesterol
While the ketogenic diet’s impact on cholesterol is not always predictable, it holds potential benefits for individuals with high cholesterol:
- Weight Loss: Obesity is a significant risk factor for high cholesterol. The ketogenic diet’s focus on fat and protein can promote satiety and lead to weight loss, which can subsequently improve cholesterol levels.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: The ketogenic diet’s low-carbohydrate nature can improve insulin sensitivity, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and potentially contribute to better cholesterol management.
- Increased HDL Cholesterol: As mentioned earlier, some studies suggest that the ketogenic diet can increase HDL cholesterol levels, potentially contributing to a more favorable cholesterol profile.
Potential Risks and Concerns of a Ketogenic Diet for High Cholesterol
Despite its potential benefits, the ketogenic diet also presents some risks and concerns for individuals with high cholesterol:
- Increased LDL Cholesterol: Some individuals may experience an increase in LDL cholesterol levels on a ketogenic diet, which could negate the potential benefits of the diet.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: The restrictive nature of the ketogenic diet can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals, potentially impacting overall health and cholesterol management.
- Kidney Stones: The ketogenic diet’s high-fat content can increase the risk of kidney stones in susceptible individuals.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Some people may experience digestive problems like constipation, diarrhea, or nausea on a ketogenic diet.
- Long-Term Effects: The long-term effects of a ketogenic diet on cholesterol and overall health are still under investigation.
Research and Evidence
The ketogenic diet’s impact on cholesterol levels has been a subject of considerable research, yielding mixed results. Studies have investigated the effects of the keto diet on various aspects of cholesterol, including total cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol, HDL (good) cholesterol, and triglycerides. Understanding the findings and limitations of these studies is crucial for assessing the potential benefits and risks of the keto diet for individuals with high cholesterol.
Findings of Studies
- Some studies have reported a decrease in total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels in individuals following a ketogenic diet. For instance, a study published in the journal “Nutrition and Metabolism” found that a ketogenic diet significantly reduced total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol in overweight and obese individuals.
- Other studies have shown that the ketogenic diet can increase HDL cholesterol levels, which is considered beneficial for heart health. A study published in the journal “Lipids in Health and Disease” found that a ketogenic diet increased HDL cholesterol levels in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
- However, it’s important to note that not all studies have found consistent results. Some studies have reported no significant changes in cholesterol levels, while others have even observed increases in LDL cholesterol.
Limitations of Existing Research
- The duration of most studies investigating the effects of the ketogenic diet on cholesterol has been relatively short, ranging from a few weeks to a few months. Long-term studies are needed to fully understand the long-term impact of the keto diet on cholesterol levels.
- Many studies have included a limited number of participants, making it difficult to generalize the findings to the broader population. Larger-scale studies with diverse populations are needed to confirm the results.
- The ketogenic diet can vary significantly in its composition and adherence, making it challenging to standardize the diet across studies. This variability can influence the results and make it difficult to compare findings across different studies.
Areas Where Further Research is Needed
- More research is needed to investigate the long-term effects of the ketogenic diet on cholesterol levels, particularly in individuals with pre-existing high cholesterol.
- Studies should explore the potential interactions between the ketogenic diet and various medications used to manage cholesterol levels.
- Further research is needed to understand the impact of the ketogenic diet on different subgroups of individuals with high cholesterol, such as those with familial hypercholesterolemia.
Considerations for Individuals with High Cholesterol
While the ketogenic diet can be beneficial for some individuals, it’s crucial to understand its potential impact on cholesterol levels, especially for those with pre-existing high cholesterol.
Monitoring Cholesterol Levels
Regularly monitoring cholesterol levels is essential when following a ketogenic diet. This involves getting regular blood tests to check for any changes in your total cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol, HDL (good) cholesterol, and triglycerides. This allows you to track the effects of the diet on your cholesterol profile and make adjustments if necessary.
Foods High in Different Fats
The ketogenic diet emphasizes fat intake, but it’s important to differentiate between the types of fat consumed.
| Type of Fat | Examples |
|---|---|
| Saturated Fat | Butter, coconut oil, full-fat dairy, fatty meats |
| Monounsaturated Fat | Olive oil, avocados, nuts (almonds, macadamia nuts), seeds (chia seeds, flax seeds) |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | Oils (sunflower, corn, soybean), fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel) |
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in managing cholesterol levels, regardless of dietary choices. Regular physical activity helps lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol. Stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can also contribute to improved cholesterol levels.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
While the ketogenic diet can be beneficial for some, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before embarking on this dietary journey, especially if you have high cholesterol.
This is because the ketogenic diet can significantly impact your cholesterol levels, potentially leading to both positive and negative changes. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures you understand the potential risks and benefits, receive personalized guidance, and make informed decisions about your health.
Benefits of Working with a Healthcare Professional
Working with a registered dietitian or other qualified healthcare professional can offer numerous advantages:
- Personalized Diet Plan: A healthcare professional can create a personalized ketogenic diet plan tailored to your individual needs, health goals, and medical history, including your cholesterol levels.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Regular monitoring of your cholesterol levels and other health indicators is essential. A healthcare professional can track your progress, make necessary adjustments to your diet plan, and ensure you’re on the right track.
- Addressing Potential Risks: A healthcare professional can identify and address potential risks associated with the ketogenic diet, such as nutrient deficiencies, kidney stones, or electrolyte imbalances.
- Safe and Effective Implementation: With the guidance of a healthcare professional, you can implement the ketogenic diet safely and effectively, reducing the risk of complications.
Finding a Qualified Healthcare Professional
Finding a qualified healthcare professional to guide you on your ketogenic journey is essential.
- Registered Dietitian: A registered dietitian (RD) is a qualified nutrition professional who can provide personalized dietary advice and help you manage your cholesterol levels.
- Physician: Your primary care physician can assess your overall health, review your medical history, and provide guidance on whether the ketogenic diet is suitable for you.
- Cardiologist: If you have high cholesterol or other cardiovascular concerns, consulting a cardiologist is highly recommended.
Closing Notes
The keto diet’s effects on cholesterol are complex and multifaceted. While some studies suggest potential benefits for individuals with high cholesterol, others raise concerns about the potential risks associated with increased saturated fat intake. Ultimately, the decision to adopt a ketogenic diet, especially for individuals with high cholesterol, should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. A personalized approach that considers individual health history, risk factors, and lifestyle choices is essential for achieving optimal health outcomes. By working closely with a qualified healthcare provider, individuals can navigate the intricacies of the keto diet and make informed choices that align with their health goals.
FAQ Compilation: Is Keto Diet Good For High Cholesterol
What are the potential benefits of a keto diet for high cholesterol?
Some studies suggest that the keto diet may help lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Can a keto diet increase my risk of heart disease?
The keto diet can be high in saturated fat, which may increase the risk of heart disease if not managed carefully. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional to determine if a keto diet is right for you.
How do I monitor my cholesterol levels while on a keto diet?
Regular blood tests are essential to monitor your cholesterol levels while on a keto diet. Your healthcare provider can advise on the frequency of these tests.
While the keto diet can be beneficial for some with high cholesterol, it’s crucial to remember that everyone’s body reacts differently. If you’re considering this diet, it’s important to focus on getting enough protein, which can help manage cholesterol levels.
Learn more about how to add protein to diet and discuss your individual needs with a healthcare professional. This will help you make the best decisions for your health, whether or not you choose the keto diet.
The keto diet can be beneficial for lowering cholesterol levels, but it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary changes. While the diet may help with cholesterol, it’s important to consider other factors like the potential impact on overall health and weight management.
For instance, some people may wonder if is diet soda bad for weight loss , as it’s often consumed in conjunction with keto. Ultimately, the keto diet’s effectiveness for cholesterol management depends on individual factors and should be approached with a balanced perspective.
Whether the keto diet is good for high cholesterol is a complex question. It depends on the individual and how their body responds to the diet. Ultimately, the best way to approach any diet, including keto, is to consult with a healthcare professional and find the best way to diet for your specific needs.
This will help ensure you are making the best choices for your overall health and well-being.