What is good diet for fatty liver – What is a good diet for fatty liver? This question is becoming increasingly relevant as fatty liver disease, a condition characterized by an excessive buildup of fat in the liver, is on the rise. While there is no cure for fatty liver disease, a healthy diet can play a crucial role in managing symptoms, preventing complications, and even reversing the condition in some cases.
The good news is that making simple dietary changes can have a significant impact on liver health. By understanding the relationship between diet and fatty liver disease, individuals can take control of their health and work towards a healthier future.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease

Fatty liver disease is a condition in which there is an excessive buildup of fat in the liver. This can lead to inflammation and damage to the liver, potentially progressing to serious complications.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
There are two main types of fatty liver disease:
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): This is the most common type of fatty liver disease. It is not caused by excessive alcohol consumption. NAFLD is often associated with obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD): This type of fatty liver disease is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. It is less common than NAFLD, but it can be more serious.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of NAFLD are not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of factors, including:
- Obesity: Excess body fat is a major risk factor for NAFLD. The more fat a person has, the more likely they are to develop fatty liver disease.
- Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body does not use insulin properly. This can lead to a buildup of sugar in the blood, which can contribute to the development of fatty liver disease.
- High cholesterol: High levels of cholesterol in the blood can also increase the risk of fatty liver disease.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are at increased risk of developing fatty liver disease.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to developing fatty liver disease.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, can increase the risk of fatty liver disease.
Potential Complications
Fatty liver disease can lead to a number of complications, including:
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): This is a more serious form of NAFLD in which the liver becomes inflamed and damaged. NASH can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer.
- Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver becomes scarred and damaged. This can lead to liver failure and death.
- Liver cancer: People with fatty liver disease are at increased risk of developing liver cancer.
- Heart disease: Fatty liver disease is associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
The Importance of Diet for Fatty Liver
Your diet plays a crucial role in managing and potentially reversing fatty liver disease. Understanding how your food choices impact your liver health is vital for improving your overall well-being.
The Connection Between Diet and Inflammation in the Liver
Excess fat accumulation in the liver, known as fatty liver disease, often triggers inflammation. This inflammation can lead to further liver damage, potentially progressing to more severe forms like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Your diet plays a direct role in this inflammatory process.
A diet high in saturated and trans fats, refined carbohydrates, and sugary drinks contributes to inflammation. These foods can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body doesn’t use insulin effectively. Insulin resistance can trigger inflammation in the liver.
Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help reduce inflammation. These foods provide antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that protect the liver from damage.
The Role of Diet in Managing Liver Function
A healthy diet is essential for maintaining optimal liver function. The liver is responsible for numerous vital tasks, including:
* Filtering blood: Removing toxins and waste products from the bloodstream.
* Producing bile: A substance that helps digest fats.
* Storing energy: Converting glucose into glycogen for later use.
* Synthesizing proteins: Building and repairing tissues.
A diet that supports these functions can help prevent further damage to the liver and improve its ability to perform its vital roles.
Dietary Recommendations for Fatty Liver: What Is Good Diet For Fatty Liver
A healthy diet is crucial for managing fatty liver disease. By making smart food choices, you can help reduce inflammation, improve liver function, and potentially reverse the condition.
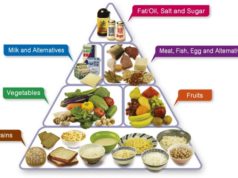
Foods to Include in a Healthy Diet for Fatty Liver
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is essential for individuals with fatty liver disease. Here’s a list of foods that can contribute to a healthy liver:
- Fruits: Apples, bananas, berries, citrus fruits, grapes, melons, pears
- Vegetables: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, carrots, cauliflower, celery, cucumbers, green beans, leafy greens, onions, peppers, spinach, sweet potatoes, tomatoes
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, whole-wheat bread
- Lean Protein: Chicken, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, eggs
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds
Foods to Avoid or Limit in a Diet for Fatty Liver
Certain foods can worsen fatty liver disease. It’s important to limit or avoid these:
- Sugary Drinks: Soda, juice, sweetened tea, energy drinks
- Processed Foods: Fast food, packaged snacks, frozen dinners
- Red Meat: Beef, pork, lamb
- Saturated and Trans Fats: Butter, margarine, fried foods, processed meats
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can damage the liver
Sample Meal Plan for Individuals with Fatty Liver Disease
Here’s a sample meal plan that incorporates the recommended foods and avoids the ones to limit:
Breakfast
* Oatmeal with berries and nuts
* Whole-wheat toast with avocado and a poached egg
* Smoothie made with fruit, yogurt, and spinach
Lunch
* Salad with grilled chicken or fish, mixed greens, vegetables, and a light vinaigrette dressing
* Lentil soup with a whole-wheat roll
* Leftovers from dinner
Dinner
* Baked salmon with roasted vegetables
* Chicken stir-fry with brown rice
* Vegetarian chili with a side salad
Snacks
* Fruits
* Vegetables with hummus
* Nuts and seeds
* Yogurt
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations based on your specific needs and medical history.
Nutritional Considerations
Making the right dietary choices is crucial for managing fatty liver disease. A well-balanced diet can help reduce inflammation, improve liver function, and promote overall health. Let’s delve into the key nutritional aspects to consider.
Adequate Protein Intake
Protein is essential for liver repair and regeneration. When you have fatty liver, your liver needs extra protein to function properly. It helps build and maintain healthy liver cells, which are vital for processing nutrients and removing toxins from your body.
The Role of Healthy Fats
While “fatty” might seem counterintuitive in the context of fatty liver, the right types of fats are actually beneficial. Unsaturated fats, found in foods like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish, help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity, both of which are important for managing fatty liver.
Managing Carbohydrate Intake
Excess carbohydrates can contribute to the buildup of fat in the liver. It’s important to choose complex carbohydrates, like those found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, over refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, sugary drinks, and processed foods. Complex carbohydrates are digested more slowly and help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of fat accumulation in the liver.
Recommended Daily Servings
A balanced diet for fatty liver includes a variety of foods from different food groups. Here’s a table that Artikels recommended daily servings:
| Food Group | Recommended Servings |
|---|---|
| Fruits | 2-3 servings |
| Vegetables | 4-5 servings |
| Whole Grains | 6-8 servings |
| Lean Protein | 2-3 servings |
| Healthy Fats | 2-3 servings |
Remember, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice tailored to your specific needs and medical history.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing fatty liver disease and improving overall health. Alongside dietary changes, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly contribute to reducing liver fat and preventing complications.
Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing liver fat. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Examples of moderate-intensity activities include brisk walking, swimming, cycling, and dancing. Vigorous-intensity activities include running, jumping rope, and playing sports.
Engage in activities that you enjoy to make exercise a sustainable part of your routine.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing fatty liver disease. If you are overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can significantly improve liver health.
Aim for a gradual weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week. This can be achieved by making sustainable changes to your diet and incorporating regular physical activity into your routine.
Consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to create a personalized weight management plan.
Managing Stress, What is good diet for fatty liver
Chronic stress can contribute to fatty liver disease by increasing inflammation and insulin resistance.
Effective stress management techniques include:
- Regular exercise
- Deep breathing exercises
- Meditation or yoga
- Spending time in nature
- Seeking support from friends and family
Identifying and addressing stress triggers is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Alcohol Reduction
Excessive alcohol consumption is a major risk factor for fatty liver disease and can lead to more serious liver conditions like alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
If you drink alcohol, limiting your intake to moderate levels is essential for liver health. For women, this means no more than one drink per day, and for men, no more than two drinks per day.
Abstaining from alcohol altogether is the safest option for individuals with fatty liver disease.
Supplements and Medications
While a healthy diet and lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of managing fatty liver disease, some supplements and medications may play a supporting role.
Supplements
Certain supplements may offer potential benefits for fatty liver disease, but it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Supplements are not a substitute for a healthy diet and lifestyle changes.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is an antioxidant that may help protect liver cells from damage caused by free radicals. Studies have shown that vitamin E supplementation might improve liver function and reduce inflammation in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). However, more research is needed to confirm these findings and determine the optimal dosage.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel, have anti-inflammatory properties that may benefit liver health. Studies suggest that omega-3 supplementation might reduce liver fat accumulation and improve liver function in people with NAFLD. However, the evidence is mixed, and further research is required to establish definitive conclusions.
Medications
While there is no specific medication to cure fatty liver disease, certain medications can help manage symptoms and complications.
Medications for Associated Conditions
Some medications may be prescribed to address underlying conditions that contribute to fatty liver disease, such as:
* Insulin Sensitizers: These medications, like metformin, improve insulin sensitivity, which can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce fat accumulation in the liver.
* Statins: These medications lower cholesterol levels, which may be beneficial for people with NAFLD who also have high cholesterol.
* Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or other anti-inflammatory medications may be used to reduce liver inflammation.
Medications for Complications
If fatty liver disease progresses to more severe stages, such as cirrhosis or liver failure, medications may be prescribed to manage complications, including:
* Diuretics: These medications help remove excess fluid from the body, which can relieve swelling and fluid retention associated with liver failure.
* Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be used to treat infections that can occur in people with liver failure.
* Liver Transplant: In cases of end-stage liver failure, a liver transplant may be the only treatment option.
It’s important to note that the use of supplements and medications for fatty liver disease should always be discussed with a healthcare professional. Self-treating can be dangerous and may worsen existing conditions.
Final Thoughts
By embracing a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, and limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats, individuals can take a proactive approach to managing fatty liver disease. While dietary changes are essential, remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and to address any underlying health concerns.
User Queries
Can I reverse fatty liver disease with diet alone?
While diet plays a significant role in managing fatty liver disease, it may not always be enough to completely reverse the condition. Lifestyle changes, including weight loss, regular exercise, and alcohol moderation, are also crucial. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
What are some common symptoms of fatty liver disease?
Many people with fatty liver disease experience no symptoms. However, some may experience fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and swelling in the legs and ankles. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a doctor.
Are there specific foods I should avoid completely?
While limiting certain foods is recommended, it’s generally better to focus on incorporating healthy choices into your diet rather than eliminating specific foods entirely. For example, instead of completely eliminating sugary drinks, aim to reduce their consumption gradually.
How often should I eat to manage fatty liver disease?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. However, aiming for regular, balanced meals throughout the day can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing fatty liver disease. Talk to a registered dietitian for personalized advice.
A healthy diet for fatty liver focuses on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. It’s important to limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats. While these dietary changes are crucial, it’s also worth considering the potential impact of artificial sweeteners.
Some studies suggest a link between artificial sweeteners and an increased risk of diabetes, as explored in this article on can diet soda cause diabetes. So, while focusing on a healthy diet for fatty liver, it’s wise to be mindful of your overall sugar intake, including artificial sweeteners.
A good diet for fatty liver focuses on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. While avoiding sugary drinks is key, you might wonder about the difference between diet options like Diet Coke and Coke Zero Sugar. Learn more about the difference between these popular drinks here.
Ultimately, sticking to water and unsweetened beverages is best for managing fatty liver disease.
A good diet for fatty liver focuses on reducing inflammation and promoting liver health. This often means limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats. Interestingly, many of these dietary recommendations align with the recommended diet for diabetics , which also emphasizes whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables.
By adopting these principles, you can support both liver health and blood sugar management.