What is the best diet for high cholesterol – What’s the best diet for high cholesterol? This question is at the forefront of many minds, especially those seeking to improve their heart health. High cholesterol, a common condition, can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, but dietary changes can significantly impact its management. Understanding the different types of cholesterol, the role of genetics and lifestyle, and the impact of various foods can empower individuals to make informed choices for a healthier future.
The journey to lowering cholesterol begins with recognizing its impact on the body. Cholesterol, a waxy substance found in all cells, plays a vital role in producing hormones and vitamin D. However, when levels become elevated, it can build up in the arteries, forming plaque that restricts blood flow. This buildup, known as atherosclerosis, can lead to serious health complications. While genetics play a role in cholesterol levels, lifestyle choices, particularly diet, have a significant influence.
Understanding High Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in all cells of the body. It is essential for building healthy cells, producing hormones, and absorbing vitamins. However, high levels of cholesterol in the blood can lead to serious health problems.
Types of Cholesterol and Their Impact on Health
Cholesterol is transported in the blood by lipoproteins, which are tiny particles made of fat and protein. There are two main types of cholesterol:
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often called “bad” cholesterol, can build up in the arteries and form plaque. This plaque can harden and narrow the arteries, making it harder for blood to flow through. This condition is called atherosclerosis, and it can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases.
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL), often called “good” cholesterol, helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream and transport it to the liver for processing. High levels of HDL cholesterol can help lower the risk of heart disease.
The Role of Genetics and Lifestyle Factors in Cholesterol Levels
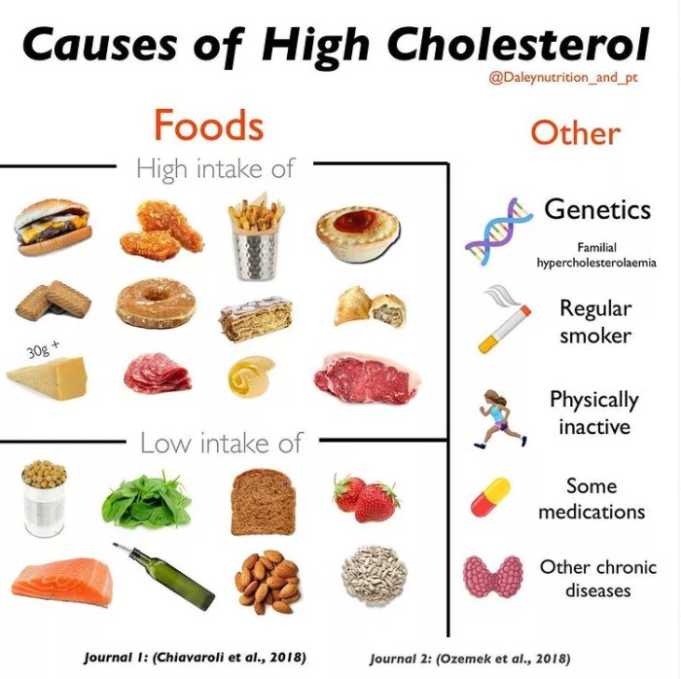
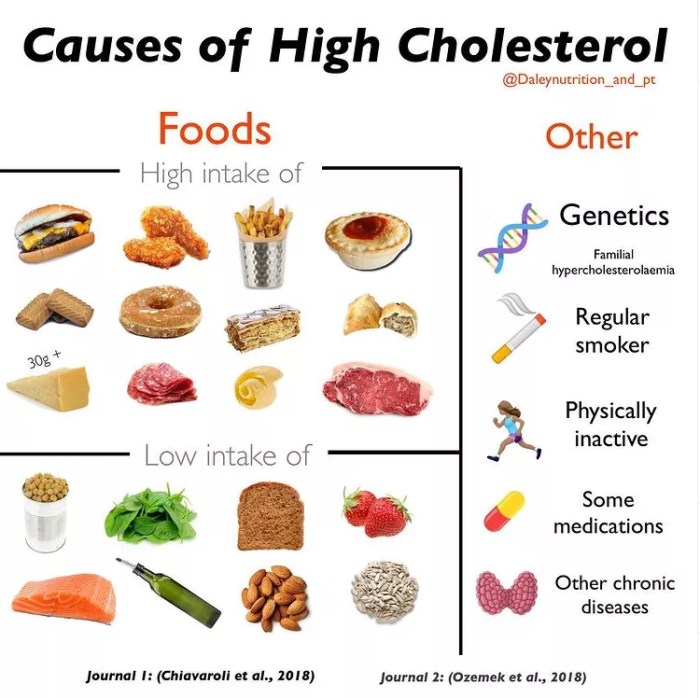
Your genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining your cholesterol levels. Some people are genetically predisposed to having higher cholesterol levels than others. However, lifestyle factors also play a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels.
- Diet: Consuming a diet high in saturated and trans fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise can help raise HDL cholesterol levels and lower LDL cholesterol levels.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese can increase LDL cholesterol levels and lower HDL cholesterol levels.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and can lower HDL cholesterol levels.
Potential Health Risks Associated with High Cholesterol
High cholesterol can lead to a number of serious health problems, including:
- Heart disease: High cholesterol can contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases.
- Stroke: High cholesterol can contribute to the formation of blood clots, which can block blood flow to the brain, causing a stroke.
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD): High cholesterol can narrow the arteries in the legs and feet, reducing blood flow and causing pain, numbness, and fatigue.
Dietary Strategies for Lowering Cholesterol
Making dietary changes is a crucial step in managing high cholesterol. By incorporating specific foods and limiting others, you can effectively lower your cholesterol levels and improve your overall health.
Foods to Include in a High-Cholesterol Diet
A heart-healthy diet emphasizes foods rich in nutrients that can help lower cholesterol. These include:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are packed with fiber, which helps bind to cholesterol in the digestive tract and remove it from the body. Aim for at least five servings daily, including a variety of colors and types. Examples include apples, bananas, berries, broccoli, carrots, spinach, and tomatoes.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains provide fiber, which is beneficial for lowering cholesterol. Choose whole-grain breads, cereals, pasta, and rice over refined grains. Look for products labeled “100% whole grain” on the packaging.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Plant-based proteins, such as beans, lentils, tofu, and nuts, are excellent sources of protein and fiber. They also tend to be lower in saturated fat than animal-based proteins.
- Healthy Fats: Unsaturated fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and raise HDL (good) cholesterol. Good sources include avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel.
Benefits of Incorporating Plant-Based Proteins, Whole Grains, and Fruits & Vegetables, What is the best diet for high cholesterol
Incorporating these foods into your diet offers numerous benefits for managing cholesterol:
- Fiber: Fiber plays a significant role in lowering cholesterol by binding to it in the digestive tract and preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. This helps reduce LDL cholesterol levels.
- Antioxidants: Fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. This can contribute to overall heart health.
- Nutrient Density: These foods are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that support overall health and well-being.
Role of Healthy Fats
Healthy fats are essential for good health, but choosing the right types is crucial for managing cholesterol.
- Monounsaturated Fats: Found in avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds, these fats can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol. They also promote heart health by reducing inflammation.
- Polyunsaturated Fats: These fats include omega-3 fatty acids, which are found in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel. Omega-3s have been shown to lower triglycerides and improve heart health.
Importance of Limiting Saturated and Trans Fats
Saturated and trans fats raise LDL cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. Limiting these fats is essential for managing cholesterol.
- Saturated Fats: Found in animal products like red meat, butter, and full-fat dairy products. Choose leaner cuts of meat and low-fat dairy options to reduce saturated fat intake.
- Trans Fats: Often found in processed foods, fried foods, and baked goods. Avoid products containing “partially hydrogenated oil” as it indicates the presence of trans fats.
Sample Meal Plan
Here is a sample meal plan that demonstrates a balanced diet for managing cholesterol:
| Meal | Food Choices |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts, a slice of whole-grain toast with avocado |
| Lunch | Lentil soup with a side salad, a whole-wheat wrap with hummus and vegetables |
| Dinner | Grilled salmon with roasted vegetables and brown rice, a side of quinoa salad with chickpeas and lemon dressing |
| Snacks | Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, plain yogurt |
Lifestyle Modifications for Cholesterol Management
Making healthy lifestyle changes can significantly impact your cholesterol levels. By incorporating regular physical activity, quitting smoking, managing stress, and adopting a balanced diet, you can effectively lower your cholesterol and improve your overall health.
Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for lowering cholesterol levels. Exercise helps increase the body’s ability to use cholesterol and can improve your overall cardiovascular health. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Recommendations for Incorporating Exercise into a Daily Routine
- Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
- Find activities you enjoy to make exercise more sustainable.
- Incorporate a variety of exercises, including cardio, strength training, and flexibility exercises.
- Set realistic goals and track your progress to stay motivated.
Smoking and Cholesterol
Smoking significantly increases your risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems, including high cholesterol. Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces the body’s ability to transport cholesterol effectively.
Managing Stress
Stress can also contribute to high cholesterol levels. When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones that can raise cholesterol levels.
Tips for Managing Stress
- Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get enough sleep.
- Spend time in nature.
- Engage in hobbies and activities you enjoy.
Benefits of Healthy Lifestyle Choices for Managing Cholesterol
| Lifestyle Choice | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular Physical Activity | Lowers LDL (bad) cholesterol, raises HDL (good) cholesterol, improves cardiovascular health. |
| Quitting Smoking | Reduces risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems, improves blood circulation, lowers LDL cholesterol. |
| Managing Stress | Reduces the release of stress hormones that can raise cholesterol, promotes relaxation and well-being. |
| Balanced Diet | Lowers LDL cholesterol, raises HDL cholesterol, provides essential nutrients for overall health. |
The Role of Medications in Cholesterol Management
While lifestyle modifications are the cornerstone of managing high cholesterol, sometimes medication is necessary to reach optimal levels. Cholesterol-lowering medications, also known as statins, are a powerful tool in reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Types of Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
Cholesterol-lowering medications work in different ways to reduce cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Statins: These are the most common type of cholesterol-lowering medication. They work by blocking an enzyme in the liver that is responsible for producing cholesterol. Examples of statins include atorvastatin (Lipitor), simvastatin (Zocor), and rosuvastatin (Crestor).
- Bile Acid Sequestrants: These medications bind to bile acids in the gut, preventing their reabsorption and promoting the liver to use more cholesterol to produce new bile acids. Examples include cholestyramine (Questran) and colesevelam (Welchol).
- Fibrates: These medications work by increasing the breakdown of cholesterol and reducing the production of triglycerides. Examples include fenofibrate (Tricor) and gemfibrozil (Lopid).
- Niacin (Vitamin B3): Niacin can lower both LDL (“bad”) and triglyceride levels, and raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol. It’s often used in combination with other cholesterol-lowering medications.
- Ezetimibe (Zetia): This medication works by blocking the absorption of cholesterol in the gut.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: These are newer medications that work by blocking a protein called PCSK9, which helps remove LDL cholesterol from the blood. Examples include alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha).
Potential Side Effects and Benefits of Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
- Statins: Statins are generally well-tolerated, but potential side effects include muscle pain, weakness, and liver problems. However, these side effects are uncommon and usually mild. Statins have been shown to significantly reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
- Bile Acid Sequestrants: These medications can cause constipation, bloating, and gas. They can also interfere with the absorption of some nutrients, such as fat-soluble vitamins.
- Fibrates: Fibrates can cause muscle pain, liver problems, and gallstones. They can also interact with other medications.
- Niacin: Niacin can cause flushing (redness and warmth in the face and neck), itching, and stomach upset. High doses can also raise blood sugar levels.
- Ezetimibe: Ezetimibe is generally well-tolerated, but potential side effects include diarrhea, muscle pain, and liver problems.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: These medications are generally well-tolerated, but potential side effects include injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, and muscle pain. PCSK9 inhibitors have been shown to be very effective at lowering LDL cholesterol levels.
Guidelines for When Medication is Recommended
- Your doctor will recommend medication based on your individual risk factors, including your cholesterol levels, age, family history of heart disease, and other health conditions.
- Medication is usually recommended when lifestyle changes alone have not been successful in lowering cholesterol levels.
- For people with very high cholesterol levels or a high risk of heart disease, medication may be recommended even if lifestyle changes have been made.
Managing Medication Effectively
- It is important to take your medication as prescribed by your doctor.
- Do not stop taking your medication without talking to your doctor first.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor.
- It is also important to follow a healthy lifestyle, including eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Expert Recommendations and Resources
It’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals and reliable organizations for personalized guidance and the latest information on managing high cholesterol. They provide evidence-based recommendations and support tailored to your individual needs.
Leading Health Organizations and Their Recommendations
Several reputable organizations offer valuable insights and guidelines for managing high cholesterol. These organizations conduct extensive research and provide evidence-based recommendations.
- The American Heart Association (AHA) emphasizes the importance of a heart-healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. They recommend lowering LDL cholesterol levels and increasing HDL cholesterol levels through dietary changes, exercise, and, if necessary, medication.
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH) offers comprehensive information on high cholesterol, including its causes, risks, and management. They recommend following a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight to manage cholesterol levels.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) promotes healthy lifestyles worldwide and provides guidelines for managing cardiovascular diseases, including high cholesterol. They advocate for a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Reputable Resources for Further Information and Support
Numerous resources offer valuable information and support for individuals managing high cholesterol. These resources can provide in-depth insights, tips for lifestyle changes, and access to support groups.
- The American Heart Association (AHA) website offers a wealth of information on high cholesterol, including its causes, risks, and management strategies. They also provide resources for healthy recipes, exercise tips, and support groups.
- The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) website provides comprehensive information on high cholesterol, including its diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. They also offer tools and resources for managing cholesterol levels.
- The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) website provides guidelines for managing high cholesterol, including dietary recommendations, exercise guidelines, and medication options.
Qualified Healthcare Professionals for Personalized Guidance
Consulting with qualified healthcare professionals is crucial for managing high cholesterol effectively. These professionals can provide personalized guidance, monitor your progress, and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
- Cardiologist: A cardiologist specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions, including high cholesterol. They can provide comprehensive assessments, recommend appropriate lifestyle changes, and prescribe medications if necessary.
- Primary Care Physician: Your primary care physician can monitor your cholesterol levels, provide initial guidance on lifestyle changes, and refer you to a specialist if needed.
- Registered Dietitian: A registered dietitian can provide personalized nutrition counseling, helping you create a heart-healthy eating plan to manage your cholesterol levels.
Concluding Remarks: What Is The Best Diet For High Cholesterol
Managing high cholesterol involves a multifaceted approach encompassing diet, exercise, and, in some cases, medication. By incorporating heart-healthy foods, engaging in regular physical activity, and making mindful lifestyle choices, individuals can take control of their cholesterol levels and reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized plan that addresses individual needs and goals.
Query Resolution
What are the different types of cholesterol?
There are two main types of cholesterol: low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often called “bad” cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), known as “good” cholesterol. LDL cholesterol contributes to plaque buildup in arteries, while HDL cholesterol helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Can I lower my cholesterol without medication?
Yes, many people can successfully lower their cholesterol through diet and lifestyle changes. Adopting a heart-healthy diet, incorporating regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly improve cholesterol levels.
What foods should I avoid if I have high cholesterol?
Foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as red meat, butter, and fried foods, should be limited. Processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of alcohol can also negatively impact cholesterol levels.
A heart-healthy diet for high cholesterol focuses on reducing saturated and trans fats while incorporating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. You can also boost your collagen intake, which is important for skin health and joint support, by incorporating bone-in meats, fish, and eggs into your meals.
If you’re looking for more ways to get your daily dose of collagen, check out this helpful guide on how to get collagen in your diet. Remember, making small changes to your diet can have a big impact on your overall health, including your cholesterol levels.
The best diet for high cholesterol is one that focuses on heart-healthy foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. It’s also important to limit saturated and trans fats, as well as cholesterol-rich foods. While these dietary changes are essential, some people might wonder about the role of what diet pills in managing cholesterol.
However, it’s crucial to remember that diet pills are not a substitute for a healthy diet and lifestyle.
A diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol is key for managing high cholesterol levels. One way to incorporate more vegetables into your diet is with a hearty and flavorful cabbage soup. Learn how to make a delicious and healthy version how to make diet cabbage soup , which can be a great addition to your overall cholesterol-lowering plan.
Remember to consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian for personalized advice on the best diet for your individual needs.