What’s DASH diet sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is a scientifically-backed eating plan designed to lower blood pressure and improve overall health. Developed in the 1990s by the National Institutes of Health, the DASH diet emphasizes fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, while limiting saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium. It’s a flexible approach that can be customized to individual needs and preferences, making it a sustainable and effective way to improve your well-being.
The DASH diet has gained widespread recognition for its effectiveness in managing hypertension, a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Studies have shown that following the DASH diet can significantly reduce blood pressure, even in individuals who are not taking medication. This dietary approach also helps improve cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes, and promote weight management.
What is the DASH Diet?: What’s Dash Diet
The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is a well-regarded dietary pattern designed to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease. It emphasizes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting saturated and unhealthy fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
The Purpose of the DASH Diet
The primary goal of the DASH diet is to help individuals manage and lower their blood pressure. It does this by promoting a balanced intake of nutrients that support cardiovascular health. The DASH diet is a comprehensive approach to healthy eating that can benefit individuals with high blood pressure and those seeking to prevent heart disease.
A Brief History of the DASH Diet, What’s dash diet
The DASH diet was developed in the 1990s by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as part of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) research project. This project aimed to investigate the effectiveness of dietary interventions in reducing high blood pressure. The DASH diet emerged as a successful strategy and has since been widely recommended by health professionals worldwide.
Key Principles of the DASH Diet
The DASH diet emphasizes a balanced intake of nutrients and promotes healthy eating habits. Key principles include:
* Focus on fruits and vegetables: The DASH diet encourages consuming plenty of fruits and vegetables, which are naturally low in sodium and rich in potassium, magnesium, and fiber.
* Include whole grains: Whole grains are an excellent source of fiber, which helps regulate blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
* Limit saturated and unhealthy fats: The DASH diet recommends limiting saturated and unhealthy fats, such as those found in red meat, butter, and fried foods.
* Reduce sodium intake: Sodium is a major contributor to high blood pressure. The DASH diet emphasizes reducing sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams per day, with an ideal target of 1,500 milligrams.
* Increase potassium intake: Potassium helps counter the effects of sodium and lower blood pressure. The DASH diet encourages consuming foods rich in potassium, such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and spinach.
* Consume calcium and magnesium: Calcium and magnesium are essential minerals for cardiovascular health and blood pressure regulation. The DASH diet promotes consuming foods rich in these minerals, such as dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and nuts.
Impact of the DASH Diet on Blood Pressure
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of the DASH diet in lowering blood pressure. A large-scale study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that individuals following the DASH diet experienced a significant reduction in blood pressure, even without medication. The DASH diet’s impact on blood pressure is attributed to its emphasis on nutrient-rich foods and its limitation of sodium intake.
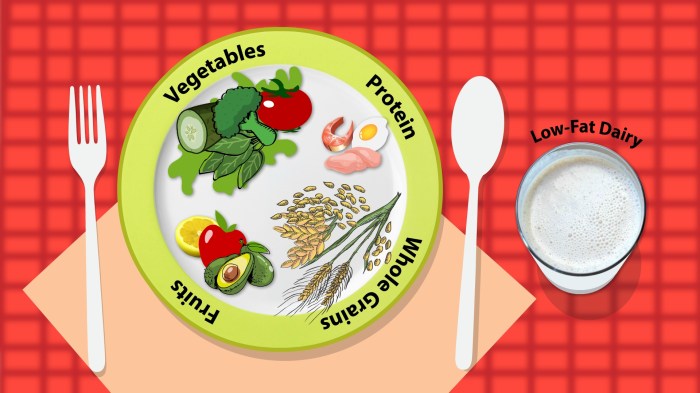
Food Groups and Portions
The DASH diet emphasizes consuming a variety of foods from different food groups in specific portions. This approach ensures a balanced intake of essential nutrients, while also helping to manage blood pressure and overall health.
Recommended Daily Servings
The following table provides a breakdown of the recommended daily servings for each food group on the DASH diet:
| Food Group | Servings per Day |
|---|---|
| Fruits | 4-5 |
| Vegetables | 4-5 |
| Grains | 6-8 |
| Lean Meat, Poultry, Fish | 2-3 |
| Low-Fat Dairy | 2-3 |
| Nuts, Seeds, Legumes | 4-5 |
| Fats and Oils | 2-3 |
Sample DASH Diet Meal Plan
A sample DASH diet meal plan for a day might look like this:
Breakfast: 1 cup oatmeal with 1/2 cup berries, 1/2 cup skim milk, and 1/4 cup chopped nuts.
Lunch: 1 cup lentil soup with 1 whole-wheat sandwich on whole-grain bread, 1/2 cup mixed greens salad with vinaigrette dressing, and 1 small apple.
Dinner: 4 oz grilled salmon, 1 cup steamed broccoli, 1/2 cup brown rice, and 1/2 cup mixed green salad with vinaigrette dressing.
Snacks: 1/4 cup trail mix, 1/2 cup low-fat yogurt, or 1 small banana.
Foods to Include in Each Food Group
It is important to include a variety of foods within each food group to maximize nutritional benefits. Here are some examples:
Fruits: Apples, bananas, oranges, berries, melons, grapes, pears, peaches, plums, dried fruits.
Vegetables: Broccoli, carrots, spinach, kale, bell peppers, onions, tomatoes, cucumbers, lettuce, mushrooms, asparagus, zucchini, green beans, sweet potatoes.
Grains: Whole-grain bread, brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, whole-grain pasta.
Lean Meat, Poultry, Fish: Chicken breast, turkey breast, lean beef, fish, beans, lentils, tofu.
Low-Fat Dairy: Milk, yogurt, cheese, cottage cheese.
Nuts, Seeds, Legumes: Almonds, walnuts, cashews, peanuts, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, lentils, chickpeas.
Fats and Oils: Olive oil, canola oil, avocado oil, nuts, seeds.
Benefits of the DASH Diet
The DASH diet, designed to lower blood pressure, offers numerous health benefits beyond its primary focus. This dietary approach emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, while limiting saturated and unhealthy fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
Improved Blood Pressure
The DASH diet’s effectiveness in reducing blood pressure is well-documented. Studies have shown that following the DASH diet can lower systolic blood pressure by 8 to 14 points and diastolic blood pressure by 3 to 6 points. This reduction in blood pressure significantly lowers the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
Enhanced Heart Health
The DASH diet’s emphasis on heart-healthy foods contributes to overall cardiovascular health. The diet’s rich source of potassium, magnesium, and fiber helps regulate blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and improve blood flow.
Weight Management
The DASH diet’s focus on nutrient-dense foods promotes satiety, making it easier to maintain a healthy weight. The emphasis on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, while limiting calorie intake.
Improved Cholesterol Levels
The DASH diet’s emphasis on healthy fats and limited intake of saturated fats and cholesterol helps improve cholesterol levels. The diet’s high fiber content also contributes to lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol and raising HDL (good) cholesterol.
Reduced Risk of Stroke
By lowering blood pressure and improving cholesterol levels, the DASH diet effectively reduces the risk of stroke. Studies have shown that following the DASH diet can reduce the risk of stroke by up to 20%.
Research Findings
Numerous studies have confirmed the effectiveness of the DASH diet in promoting overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. For example, the DASH-Sodium trial, a large-scale study, demonstrated the significant impact of the DASH diet on blood pressure reduction. The study found that the DASH diet, combined with a low-sodium intake, lowered blood pressure more effectively than a standard low-sodium diet.
“The DASH diet is a powerful tool for improving overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. By incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein, while limiting saturated and unhealthy fats, cholesterol, and sodium, the DASH diet promotes heart health, blood pressure control, and weight management.”
Implementing the DASH Diet
Making the DASH diet a part of your everyday life requires a shift in your eating habits. It’s not about drastic changes but rather about making gradual, sustainable adjustments that lead to a healthier lifestyle.
Practical Tips and Strategies
Here are some practical tips and strategies to help you incorporate the DASH diet into your daily life:
- Start Gradually: Don’t try to change everything at once. Begin by focusing on making small, manageable changes to your diet, such as replacing sugary drinks with water or adding more fruits and vegetables to your meals.
- Plan Your Meals and Snacks: Planning ahead can help you stay on track with the DASH diet. This involves making a grocery list based on the DASH eating plan, preparing meals in advance, and packing healthy snacks to avoid impulsive unhealthy choices.
- Cook More Meals at Home: Cooking at home gives you more control over the ingredients and portion sizes. Experiment with new recipes and find healthy alternatives to your favorite dishes.
- Read Food Labels: Pay attention to the sodium content of processed foods. Choose options with lower sodium levels.
- Eat Out Smartly: When dining out, request dishes with less salt and fat. Opt for grilled or baked options over fried ones.
- Incorporate Physical Activity: Regular physical activity complements the DASH diet by promoting weight management and overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Challenges and Solutions
While the DASH diet offers numerous benefits, adhering to it can present challenges. Here are some common challenges and potential solutions:
- Sodium Reduction: Reducing sodium intake can be difficult, especially if you’re used to eating processed foods.
- Gradually Reduce Sodium: Start by slowly reducing your sodium intake over time.
- Read Food Labels: Pay attention to the sodium content of processed foods.
- Cook More Meals at Home: You have more control over the ingredients and sodium levels.
- Choose Fresh Foods: Fresh produce, lean meats, and whole grains are naturally low in sodium.
- Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain high levels of sodium.
- Finding Time to Cook: A busy schedule can make it challenging to cook healthy meals regularly.
- Prepare Meals in Advance: Cook large batches of meals on weekends and freeze portions for quick and easy meals during the week.
- Use a Slow Cooker: Slow cookers are great for preparing healthy meals with minimal effort.
- Plan Meals Around Your Schedule: Set aside specific times for meal preparation and grocery shopping.
- Maintaining Motivation: Staying motivated to follow the DASH diet can be challenging over the long term.
- Set Realistic Goals: Don’t try to change everything at once. Start with small, achievable goals.
- Find Support: Share your goals with friends or family, or join a support group.
- Reward Yourself: Celebrate your successes and acknowledge your efforts.
- Focus on the Benefits: Remind yourself of the health benefits of the DASH diet.
Healthy Substitutions
Here are some healthy substitutions for common unhealthy foods:
- Instead of fried foods, opt for grilled, baked, or roasted options.
- Instead of sugary drinks, choose water, unsweetened tea, or sparkling water.
- Instead of processed snacks, reach for fruits, vegetables, nuts, or seeds.
- Instead of high-fat dairy products, choose low-fat or fat-free options.
- Instead of red meat, choose lean protein sources like poultry, fish, beans, or lentils.
DASH Diet Recipes
Following the DASH diet doesn’t mean sacrificing flavor or variety. There are numerous delicious and healthy recipes that align with the diet’s principles.
Breakfast Recipes
The DASH diet emphasizes a balanced breakfast rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Here are a few breakfast recipe ideas:
- Oatmeal with Berries and Nuts: Start your day with a hearty bowl of oatmeal topped with fresh berries, a handful of almonds or walnuts, and a sprinkle of cinnamon. This combination provides fiber, protein, and healthy fats, keeping you full and energized.
- Whole-Wheat Toast with Avocado and Egg: Combine a slice of whole-wheat toast with mashed avocado, a poached or scrambled egg, and a sprinkle of salt and pepper. This breakfast option offers a good source of healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Yogurt Parfait with Granola and Fruit: Layer plain yogurt with granola, chopped fruit (such as berries, banana, or peaches), and a drizzle of honey or maple syrup. This parfait is a convenient and delicious breakfast option.
Lunch Recipes
Lunchtime is a great opportunity to incorporate more vegetables and lean protein into your diet.
- Quinoa Salad with Grilled Chicken or Tofu: Combine cooked quinoa with chopped vegetables (such as bell peppers, cucumbers, tomatoes, and onions), grilled chicken or tofu, and a light vinaigrette dressing. This salad is packed with protein, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals.
- Lentil Soup: Lentil soup is a hearty and nutritious lunch option. It is packed with protein, fiber, and essential nutrients. You can make it with various vegetables like carrots, celery, onions, and spinach.
- Tuna Salad Sandwich on Whole-Wheat Bread: A classic tuna salad sandwich can be made healthier by using whole-wheat bread, low-fat mayonnaise, and plenty of vegetables like celery, onion, and lettuce.
Dinner Recipes
Dinner is the perfect time to enjoy a flavorful and satisfying meal that adheres to the DASH diet principles.
- Baked Salmon with Roasted Vegetables: Bake salmon with a drizzle of olive oil, lemon juice, and herbs. Serve it with roasted vegetables like broccoli, asparagus, or bell peppers. This dinner option provides a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and fiber.
- Chicken Stir-Fry with Brown Rice: Stir-fry chicken with your favorite vegetables (such as broccoli, carrots, and bell peppers) and serve it over brown rice. This dish is quick, easy, and packed with flavor and nutrients.
- Vegetarian Chili: Vegetarian chili is a hearty and flavorful dinner option that is packed with fiber, protein, and essential nutrients. It can be made with various beans, vegetables, and spices.
Snack Recipes
Snacking can be a healthy and delicious way to keep your energy levels up throughout the day.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are excellent snacks, providing essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Some healthy options include apples, bananas, oranges, carrots, celery, and bell peppers.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds are a great source of healthy fats, protein, and fiber. Some healthy options include almonds, walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds.
- Yogurt with Berries: Yogurt with berries is a delicious and refreshing snack. Choose plain yogurt and add your favorite berries for a boost of flavor and nutrients.
Final Review
Embarking on the DASH diet journey is an investment in your health and longevity. By incorporating its principles into your daily life, you can reap numerous benefits, including lower blood pressure, improved heart health, and a reduced risk of chronic diseases. Remember, consistency is key to success, and with a little planning and effort, you can enjoy delicious and nutritious meals that align with the DASH diet guidelines. Embrace this transformative eating plan and embark on a path towards a healthier and happier you.
Helpful Answers
Is the DASH diet difficult to follow?
The DASH diet is flexible and can be adapted to your preferences. It’s not about eliminating entire food groups but rather focusing on healthy choices and portion control.
Can I lose weight on the DASH diet?
The DASH diet is not specifically designed for weight loss, but it can help you manage your weight by promoting healthy eating habits and reducing calorie intake.
How long does it take to see results from the DASH diet?
You may start noticing improvements in your blood pressure within a few weeks of following the DASH diet. However, it’s important to note that individual results may vary.
The DASH diet, or Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, is a great example of a healthy eating plan. It focuses on consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while limiting saturated and unhealthy fats. To learn more about what constitutes a good diet overall, check out this resource: what is good diet.
Like a good diet, the DASH diet emphasizes portion control and balanced meals, making it a sustainable way to manage blood pressure and improve overall health.
The DASH diet, short for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, focuses on reducing sodium and increasing potassium, magnesium, and calcium intake. It’s a healthy way to manage blood pressure, but if you’re looking for a more intense approach, you might be interested in learning about how does fasting diet work.
Fasting diets, which involve periods of restricted eating, can be effective for weight loss and have been linked to other health benefits. While the DASH diet focuses on long-term dietary changes, fasting diets offer a different approach to improving health and well-being.
The DASH diet, or Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, is a popular eating plan that focuses on reducing sodium and increasing potassium, magnesium, and calcium. It emphasizes fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. These types of foods are generally considered to be good diet foods, and you can learn more about them by visiting what is good diet food.
The DASH diet has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease.
























